 Java
Java
 javaTutorial
javaTutorial
 Restore the binary tree through the sequence after pre-order traversal and in-order traversal
Restore the binary tree through the sequence after pre-order traversal and in-order traversal
Restore the binary tree through the sequence after pre-order traversal and in-order traversal
When we have a
Pre-order traversal sequence: 1,3,7,9,5,11
In-order traversal sequence: 9,7,3,1,5, 11
We can easily write the corresponding binary tree with a pen. But how to implement it using code?
Let’s briefly talk about the basic ideas.
First of all, the order of pre-order traversal is based on the order of root-left child-right child, then the first thing we can confirm is the pre-order traversal sequence The first number is the root node, and then the in-order traversal is traversed in the order of left child-root-right child. We have confirmed the root node through pre-order traversal, then we only need to find the location of the root node in in-order traversal, and then we can easily distinguish those nodes that belong to the left subtree and those that belong to the right subtree. . As shown in the figure below:
We determine the number 1 as the root node, and then determine it according to the traversal order of the in-order traversal. In the in-order traversal sequence, all the left subtree nodes of the number 1 are left subtree nodes, and all the right subtrees are right subtrees. Through the number of left subtree nodes, it can be concluded that the three consecutive numbers from the root node in the preorder traversal sequence belong to the left subtree, and the remaining ones are the right subtree. In this way, the above steps are repeated in the sequence of the left and right subtrees, until finally no child nodes are found.

The implementation code is as follows:
1 package com.tree.traverse; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.List; 5 6 /** 7 * @author Caijh 8 * 9 * 2017年6月2日 下午7:21:10 10 */ 11 12 public class BuildTreePreOrderInOrder { 13 14 /** 15 * 1
16 * / \ 17 * 3 5
18 * / \ 19 * 7 11 20 * /
21 * 9
22 */ 23 public static int treeNode = 0;//记录先序遍历节点的个数 24 private List<Node> nodeList = new ArrayList<>();//层次遍历节点的队列 25 public static void main(String[] args) { 26 BuildTreePreOrderInOrder build = new BuildTreePreOrderInOrder(); 27 int[] preOrder = { 1, 3, 7, 9, 5, 11}; 28 int[] inOrder = { 9, 7, 3, 1, 5, 11}; 29 30 treeNode = preOrder.length;//初始化二叉树的节点数 31 Node root = build.buildTreePreOrderInOrder(preOrder, 0, preOrder.length - 1, inOrder, 0, preOrder.length - 1); 32 System.out.print("先序遍历:"); 33 build.preOrder(root); 34 System.out.print("\n中序遍历:"); 35 build.inOrder(root); 36 System.out.print("\n原二叉树:\n"); 37 build.prototypeTree(root); 38 } 39 40 /** 41 * 分治法 42 * 通过先序遍历结果和中序遍历结果还原二叉树 43 * @param preOrder 先序遍历结果序列 44 * @param preOrderBegin 先序遍历起始位置下标 45 * @param preOrderEnd 先序遍历末尾位置下标 46 * @param inOrder 中序遍历结果序列 47 * @param inOrderBegin 中序遍历起始位置下标 48 * @param inOrderEnd 中序遍历末尾位置下标 49 * @return 50 */ 51 public Node buildTreePreOrderInOrder(int[] preOrder, int preOrderBegin, int preOrderEnd, int[] inOrder, int inOrderBegin, int inOrderEnd) { 52 if (preOrderBegin > preOrderEnd || inOrderBegin > inOrderEnd) { 53 return null; 54 } 55 int rootData = preOrder[preOrderBegin];//先序遍历的第一个字符为当前序列根节点 56 Node head = new Node(rootData); 57 int divider = findIndexInArray(inOrder, rootData, inOrderBegin, inOrderEnd);//找打中序遍历结果集中根节点的位置 58 int offSet = divider - inOrderBegin - 1;//计算左子树共有几个节点,节点数减一,为数组偏移量 59 Node left = buildTreePreOrderInOrder(preOrder, preOrderBegin + 1, preOrderBegin + 1 + offSet, inOrder, inOrderBegin,inOrderBegin + offSet); 60 Node right = buildTreePreOrderInOrder(preOrder, preOrderBegin + offSet + 2, preOrderEnd, inOrder, divider + 1, inOrderEnd); 61 head.left = left; 62 head.right = right; 63 return head; 64 } 65 /** 66 * 通过先序遍历找到的rootData根节点,在中序遍历结果中区分出:中左子树和右子树 67 * @param inOrder 中序遍历的结果数组 68 * @param rootData 根节点位置 69 * @param begin 中序遍历结果数组起始位置下标 70 * @param end 中序遍历结果数组末尾位置下标 71 * @return return中序遍历结果数组中根节点的位置 72 */ 73 public int findIndexInArray(int[] inOrder, int rootData, int begin, int end) { 74 for (int i = begin; i <= end; i++) { 75 if (inOrder[i] == rootData) 76 return i; 77 } 78 return -1; 79 } 80 /** 81 * 二叉树先序遍历结果 82 * @param n 83 */ 84 public void preOrder(Node n) { 85 if (n != null) { 86 System.out.print(n.val + ","); 87 preOrder(n.left); 88 preOrder(n.right); 89 } 90 } 91 /** 92 * 二叉树中序遍历结果 93 * @param n 94 */ 95 public void inOrder(Node n) { 96 if (n != null) { 97 inOrder(n.left); 98 System.out.print(n.val + ","); 99 inOrder(n.right);100 }101 }102 /**103 * 还原后的二叉树104 * 二叉数层次遍历105 * 基本思想:106 * 1.因为推导出来的二叉树是保存在Node类对象的子对象里面的,(类似于c语言的结构体)如果通过递归实现层次遍历的话,不容易实现107 * 2.这里采用List队列逐层保存Node对象节点的方式实现对二叉树的层次遍历输出108 * 3.如果父节点的位置为i,那么子节点的位置为,2i 和 2i+1;依据这个规律逐层遍历,通过保存的父节点,找到子节点。并保存,不断向下遍历保存。109 * @param tree110 */111 public void prototypeTree(Node tree){112 //用list存储层次遍历的节点113 if(tree !=null){114 if(tree!=null)115 nodeList.add(tree);116 nodeList.add(tree.left);117 nodeList.add(tree.right);118 int count=3;119 //从第三层开始120 for(int i=3;count<treeNode;i++){121 //第i层第一个子节点的父节点的位置下标122 int index = (int) Math.pow(2, i-1-1)-1;123 /**124 * 二叉树的每一层节点数遍历125 * 因为第i层的最大节点数为2的i-1次方个,126 */127 for(int j=1;j<=Math.pow(2, i-1);){128 //计算有效的节点的个数,和遍历序列的总数做比较,作为判断循环结束的标志129 if(nodeList.get(index).left!=null)130 count++;131 if(nodeList.get(index).right!=null)132 count++;133 nodeList.add(nodeList.get(index).left);134 nodeList.add(nodeList.get(index).right);135 index++;136 if(count>=treeNode)//当所有有效节点都遍历到了就结束遍历137 break;138 j+=2;//每次存储两个子节点,所以每次加2139 }140 }141 int flag=0,floor=1;142 for(Node node:nodeList){143 if(node!=null)144 System.out.print(node.val+" ");145 else146 System.out.print("# ");//#号表示空节点147 flag++;148 /**149 * 逐层遍历输出二叉树150 *
151 */152 if(flag>=Math.pow(2, floor-1)){153 flag=0;154 floor++;155 System.out.println();156 }157 }158 }159 }160 /**161 * 内部类162 * 1.每个Node类对象为一个节点,163 * 2.每个节点包含根节点,左子节点和右子节点164 */165 class Node {166 Node left;167 Node right;168 int val;169 public Node(int val) {170 this.val = val;171 }172 }173 }
Running result:
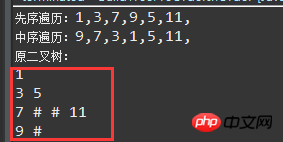
Finally, the basic idea of outputting the binary tree layer by layer:
* 1. Because the derived binary tree is stored in the sub-object of the Node class object, (similar to the structure of the c language) if through recursion It is not easy to implement hierarchical traversal
* 2. Here, the List queue is used to save Node object nodes layer by layer to realize the hierarchical traversal output of the binary tree
* 3. If the position of the parent node is i, then the child node The positions are 2i and 2i+1; according to this rule, traverse layer by layer and find the child nodes through the saved parent nodes. And save, keep traversing downwards to save.

The above is the detailed content of Restore the binary tree through the sequence after pre-order traversal and in-order traversal. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Java how to loop through a folder and get all file names
Mar 29, 2024 pm 01:24 PM
Java how to loop through a folder and get all file names
Mar 29, 2024 pm 01:24 PM
Java is a popular programming language with powerful file handling capabilities. In Java, traversing a folder and getting all file names is a common operation, which can help us quickly locate and process files in a specific directory. This article will introduce how to implement a method of traversing a folder and getting all file names in Java, and provide specific code examples. 1. Use the recursive method to traverse the folder. We can use the recursive method to traverse the folder. The recursive method is a way of calling itself, which can effectively traverse the folder.
 PHP glob() function usage example: traverse all files in a specified folder
Jun 27, 2023 am 09:16 AM
PHP glob() function usage example: traverse all files in a specified folder
Jun 27, 2023 am 09:16 AM
Example of using PHPglob() function: Traverse all files in a specified folder In PHP development, it is often necessary to traverse all files in a specified folder to implement batch operation or reading of files. PHP's glob() function is used to achieve this requirement. The glob() function can obtain the path information of all files that meet the conditions in the specified folder by specifying a wildcard matching pattern. In this article, we will demonstrate how to use the glob() function to iterate through all files in a specified folder
 In-depth comparison of Java Iterator and Iterable: pros and cons analysis
Feb 19, 2024 pm 04:20 PM
In-depth comparison of Java Iterator and Iterable: pros and cons analysis
Feb 19, 2024 pm 04:20 PM
Conceptual differences: Iterator: Iterator is an interface that represents an iterator that obtains values from a collection. It provides methods such as MoveNext(), Current() and Reset(), allowing you to traverse the elements in the collection and operate on the current element. Iterable: Iterable is also an interface, representing an iterable object. It provides the Iterator() method, which returns an Iterator object to facilitate traversing the elements in the collection. Usage: Iterator: To use Iterator, you need to first obtain an Iterator object, and then call the MoveNext() method to move to the next
 How to use the os module to traverse files in a directory in Python 3.x
Jul 29, 2023 pm 02:57 PM
How to use the os module to traverse files in a directory in Python 3.x
Jul 29, 2023 pm 02:57 PM
How to use the os module to traverse files in a directory in Python3.x In Python, we can use the os module to operate files and directories. The os module is an important module in the Python standard library, providing many operating system-related functions. In this article, we will explain how to use the os module to iterate through all files in a directory. First, we need to import the os module: importos Next, we can use the os.walk() function to walk the directory.
 Recursively insert and traverse linked list in C++
Sep 10, 2023 am 09:21 AM
Recursively insert and traverse linked list in C++
Sep 10, 2023 am 09:21 AM
We get the integer values used to form the linked list. The task is to first insert and then traverse the singly linked list using recursive method. Add node recursively at the end if head is NULL → add node to head otherwise add to head (head → next) recursively traverse nodes if head is NULL → exit otherwise print (head → next) Example input −1-2-7-9 -10 output outputstrong>− linked list: 1→2→7→9→10→NULL input−12-21-17-94-18 output− linked list: 12→21→17→94→18→NULL used in the following program The method is as follows In this method, we will use the function to add nodes and traverse the singly linked list and pass
 Java Iterator and Iterable: The key to collection traversal, demystified
Feb 20, 2024 am 10:27 AM
Java Iterator and Iterable: The key to collection traversal, demystified
Feb 20, 2024 am 10:27 AM
Introduction to IteratorIterator is an interface in Java for traversing collections. It provides a set of methods that allow you to access elements in a collection in a sequential manner. You can use Iterator to iterate over collection types such as List, Set, and Map. Demo code: Listlist=newArrayList();list.add("one");list.add("two");list.add("three");Iteratoriterator=list.iterator();while(iter
 Java Iterator and Iterable: Unlocking the Mysteries of Java Collection Traversal
Feb 19, 2024 pm 11:50 PM
Java Iterator and Iterable: Unlocking the Mysteries of Java Collection Traversal
Feb 19, 2024 pm 11:50 PM
Iterator interface The Iterator interface is an interface defined in the Java collection framework. It provides a series of methods for traversing collection elements. The Iterator interface defines the following main methods: hasNext(): Returns a Boolean value indicating whether the next element exists. next(): Returns the next element. If there is no next element, a NoSuchElementException is thrown. remove(): Delete the currently pointed element. The following is sample code for traversing a collection using the Iterator interface: Listlist=newArrayList();list
 Python's range() function: generate a sequence of numbers
Nov 18, 2023 am 11:51 AM
Python's range() function: generate a sequence of numbers
Nov 18, 2023 am 11:51 AM
Python's range() function: Generate a sequence of numbers, specific code examples are required. Python is a powerful programming language with many built-in functions that are very helpful for writing programs. One of them is the range() function, which is used to generate a sequence of numbers. This article will introduce the usage of the range() function in detail and illustrate it through specific code examples. The basic syntax of the range() function is as follows: range(start,stop,step) where, s





