Detailed explanation of simple FTP implementation
作业要示:
开发简单的FTP:
1. 用户登陆
2. 上传/下载文件
3. 不同用户家目录不同
4. 查看当前目录下文件
5. 充分使用面向对象知识
REDMAE
1 用户登陆 2 3 1、查看用户目录文件 4 2、上传文件, 5 3、下载方件 6 4、退出 7 8 程序结构: 9 socket_server_client/#程序目录10 |- - -clients/#client程序主目录11 | |- - -__init__.py12 | |- - -bin/#启用目录13 | | |- - - __init__.py14 | | |- - -socket_client.py#客户端启动15 | |16 | |- - -cfg/#配置文件目录17 | | |- - - __init__.py18 | | |- - -config.py#配置文件19 | |20 | |- - -core/#主要程序目录21 | | |- - - __init__.py22 | | |- - -client_func.py#主要函数23 | |24 | |- - -home/#客户端下载文件目录25 |26 |- - -servers/#server程序主目录27 | |- - -__init__.py28 | |- - -bin/#启用目录29 | | |- - - __init__.py30 | | |- - -registration.py#用户注册31 | | |- - -socket_server.py#服务端启动32 33 | |34 | |- - -cfg/#配置文件目录35 | | |- - - __init__.py36 | | |- - -config.py#配置文件37 | |38 | |- - -core/#主要程序目录39 | | |- - - __init__.py40 | | |- - -server_classc.py#主要函数41 | |42 | |- - -db/#用户上传文件主目录43 | |- - -user_file/#用户上传目录44 | |- - -user_names#注册用户文件45 |
服务端
servers/
bin/
registration.py
1 #!usr/bin/env python 2 #-*-coding:utf-8-*- 3 # Author calmyan 4 import socket,os,json,sys,pickle 5 6 BASE_DIR=os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)))#获取相对路径转为绝对路径赋于变量 7 sys.path.append(BASE_DIR)#增加环境变量 8 from cfg import config 9 print('用户注册'.center(60,'='))10 while True:11 user_=input('请输入您要注册的用户名:').strip()12 user_dir=os.path.join(config.USER_DIR,user_)#拼接用户目录路径13 if os.path.isdir(user_dir):# 判断一个目录是否存在14 print('用户已经存在请重输!')15 continue16 else:17 pwd_=input('请输入密码:').strip()18 pwd_two=input('请确认密码:').strip()19 if pwd_==pwd_two:20 try:21 os.mkdir(user_dir)#创建目录22 except Exception as e:23 print(e)24 continue25 finally:26 file_dir=user_dir+'\\user'#用户目录下的用户名文件27 if not os.path.isfile(config.USER_FILE):28 with open(config.USER_FILE,'w',encoding='utf-8') as f:29 f.write('{}')30 with open(config.USER_FILE,'r+',encoding='utf-8') as f:31 data=eval(f.readline())32 data[user_]=pwd_33 f.seek(0)34 f.write(str(data))35 print('用户[%s]注册成功!'%user_)36 exit()socket_server.py
1 #!usr/bin/env python 2 #-*-coding:utf-8-*- 3 # Author calmyan 4 import socket,os,json 5 import sys 6 BASE_DIR=os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)))#获取相对路径转为绝对路径赋于变量 7 sys.path.append(BASE_DIR)#增加环境变量 8 9 from core.server_class import listen_func10 s=socket.socket()#定义11 s.bind(('localhost',9000))#绑定要监听的 端口12 s.listen(5)#对列513 print('正在监听中')14 listen_func(s)cfg/
config.py
1 #!usr/bin/env python 2 #-*-coding:utf-8-*- 3 # Author calmyan 4 import os ,sys 5 BASE_DIR=os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)))#获取相对路径转为绝对路径赋于变量 6 sys.path.append(BASE_DIR)#增加环境变量 7 8 9 USER_DIR=BASE_DIR+'\db\\user_file\\'#定义用户目录文件路径变量10 11 USER_FILE=BASE_DIR+'\db\\user_names'#定义用户文件路径变量
core/
server_class.py
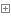
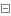
1 #!usr/bin/env python 2 #-*-coding:utf-8-*- 3 # Author calmyan 4 import socket,os,json,sys,pickle 5 6 BASE_DIR=os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)))#获取相对路径转为绝对路径赋于变量 7 sys.path.append(BASE_DIR)#增加环境变量 8 9 from cfg import config 10 11 12 #用户名检测函数 13 def open_file_list(name,pas):#传入当前类 14 with open(config.USER_FILE,'r',encoding='utf-8') as f: 15 data=eval(f.readline()) 16 if name in data and pas==data[name]: 17 return True 18 else: 19 return False 20 21 22 #连接类 23 class socket_server(object): 24 '''连接类''' 25 file_path=config.USER_DIR#用户路经变量 26 def __init__(self,data,conn):#传入用户名,密码 27 self.DATA=data 28 self.conn=conn 29 30 31 def show_process(self,lens): 32 received_size=0#定义大小 33 current_percent=0#当前大小百分比 34 while received_size<lens: 35 if int((received_size/lens)*100)>current_percent: 36 print('#',end='',flush=True) 37 current_percent=int((received_size/lens)*100) 38 new_size=yield 39 received_size+=new_size 40 41 def ret_l(self): 42 ret=socket_server.login(self.DATA["name"],self.DATA['pwd'],self.conn)#用户名检测 43 return ret 44 def open_f(self,ret):#打开目录 45 file_dir=os.path.join(socket_server.file_path,ret['data']['user'])#用户目录 46 file_name=os.listdir(file_dir)#目录文件列表 47 f=file_dir+self.DATA['filename']##上传的文件名 48 return file_dir,file_name,f#返回 49 50 def ls_file(self,data):#查看文件 51 self.conn.send(json.dumps(data[1]).encode()) 52 53 def send_file(self,data): 54 55 if self.DATA['filename'] in data[1]: 56 f=data[0]+'/'+self.DATA['filename'] 57 file_obj=open(f,"rb")#打开文件 58 name=file_obj.name.split('/')[-1]#文件名 59 sez=os.path.getsize(f)#获取文件大小 60 print(sez) 61 data_header={ 62 "action":"put", 63 "filename":name, 64 "size":sez 65 } 66 self.conn.send(json.dumps(data_header).encode())#用json 序列化后,发送相关 信息 67 for line in file_obj: 68 self.conn.send(line)#发送数据 69 70 elif self.DATA['filename'].isdigit(): 71 num=int(self.DATA['filename'])#转为数字 72 try: 73 f=data[0]+'/'+data[1][num]# 74 file_obj=open(f,"rb")#打开文件 75 name=file_obj.name.split('/')[-1]#文件名 76 sez=os.path.getsize(f)#获取文件大小 77 print(sez) 78 data_header={ 79 "action":"put", 80 "filename":name, 81 "size":sez 82 } 83 self.conn.send(json.dumps(data_header).encode())#用json 序列化后,发送相关 信息 84 for line in file_obj: 85 self.conn.send(line)#发送数据 86 self.conn.send(json.dumps(f).encode())#发送文件 87 except Exception as e: 88 data={'filename':False} 89 self.conn.send(json.dumps(data).encode()) 90 else: 91 data={'filename':False} 92 self.conn.send(json.dumps(data).encode()) 93 def put_file(self,data):#上传文件 94 file_obj=open(data[2],'wb')#打开新建 这个文件 95 rece_size=0#定义 文件大小值 96 #prten=socket_server.show_process(self.DATA["size"]) 97 #prten.__next__() 98 while rece_size<self.DATA["size"]:#小于接收的文件大小时, 99 recv_data=self.conn.recv(4096)100 file_obj.write(recv_data)#写入文件101 rece_size+=len(recv_data)#增加文件大小计算102 103 else:104 print("文件[%s]接收完毕!"%self.DATA["filename"])105 file_obj.flush()106 file_obj.close()#关闭文件107 108 109 @staticmethod110 def login(name,pas,conn):#用户检测 函数111 try:112 if open_file_list(name,pas):113 tag=True114 error=''115 datas={'user':name}116 data={'mag':'用户认证通过','tag':True}117 print(json.dumps(data).encode())118 conn.send(json.dumps(data).encode())119 else:120 raise Exception('\033[41;1m用户名或密码错误\033[0m' %name)121 except Exception as e:122 tag=False123 error=str(e)124 datas=''125 data={'mag':'用户或密码错误','tag':False}126 print('发送数据%s'%data)127 conn.send(json.dumps(data).encode())128 return {'tag':tag,'error':error,'data':datas}129 130 #监听函数131 def listen_func(s):132 while True:133 conn,client_addr=s.accept()#端口监听中....返回两个值 ,联接编号对象 , ip134 print('获取到新连接:',client_addr)135 while True:136 data=conn.recv(4096)#接收数据 指令137 print('接收的数据:',data)138 data= json.loads(data.decode())#反序列139 if len(data)==0:140 break141 if data['action']=='user':#如果是用户名,进行认证\142 serv=socket_server(data,conn)143 ret=serv.ret_l()144 if ret['tag']:145 pass146 else:147 continue148 149 print(data)150 if data['action']=="put":#如果接收的字典中是put,就是进行接收151 serv=socket_server(data,conn)152 serv.put_file(serv.open_f(ret))#调对象方法153 elif data['action']=='get':#下载154 serv=socket_server(data,conn)#实例化155 serv.send_file(serv.open_f(ret))#调 用方法156 elif data['action']=='ls':#查看157 serv=socket_server(data,conn)158 serv.ls_file(serv.open_f(ret))159 continue
客户端
clients/
bin/
socket_client.py
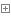
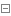
1 #!usr/bin/env python 2 #-*-coding:utf-8-*- 3 # Author calmyan 4 5 import socket,os,json,sys 6 BASE_DIR=os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)))#获取相对路径转为绝对路径赋于变量 7 sys.path.append(BASE_DIR)#增加环境变量 8 from core.client_func import user_pwd 9 #from core.client_func import show_process 10 from cfg import config 11 12 #进度条 13 def show_process(lens): 14 received_size=0#定义大小 15 current_percent=0#当前大小百分比 16 while received_size<lens: 17 if int((received_size/lens)*100)>current_percent: 18 print('#',end='',flush=True) 19 current_percent=int((received_size/lens)*100) 20 new_size=yield 21 received_size+=new_size 22 23 24 client=socket.socket() 25 client.connect(('localhost',9000)) 26 while True: 27 data_d=user_pwd(client) 28 if data_d['tag']:#运行#用户名登陆成功 29 while True: 30 print('''=====指令提示==== 31 查看目录文件: ls 32 下载文件: get 文件名 或 文件编号 如: get test.txt 或 get 1 33 上传方件: put 路径/文件名 如 put e:/test.txt 34 退出:exit 35 ''') 36 cho=input('指令 >>:').strip() 37 if len(cho)==0:continue 38 if cho=='exit':exit()#退出指令 39 cmd_list=cho.split() 40 if cmd_list[0]=='put':#如果等于下载指令 41 if len(cmd_list)==1: 42 print('没有输入相关文件名') 43 continue 44 filename=cmd_list[1] 45 if os.path.isfile(filename):#如果文件存在 46 file_obj=open(filename,"rb")#打开文件 47 name=file_obj.name.split('/')[-1]#文件名 48 #name=filename.split("\\")[-1]#文件名 49 sez=os.path.getsize(filename)#获取文件大小 50 data_header={ 51 "action":"put", 52 "filename":name, 53 "size":sez 54 } 55 client.send(json.dumps(data_header).encode())#用json 序列化后,发送相关 信息 56 57 print("文件[%s]发送中...."%data_header["filename"]) 58 for line in file_obj: 59 client.send(line) 60 else: 61 print("文件[%s]发送完毕!"%data_header["filename"]) 62 else: 63 print('该文件不存在') 64 continue 65 elif cmd_list[0]=='get':#如查等 于上传指令 66 if len(cmd_list)==1: 67 print('没有输入相关文件名') 68 continue 69 filename=cmd_list[1] 70 print(filename) 71 data_header={ 72 "action":"get", 73 "filename":filename, 74 "size":'' 75 } 76 client.send(json.dumps(data_header).encode())#用json 序列化后,发送相关 信息 77 datas=client.recv(4096)#接收数据 指令 78 data_l= json.loads(datas.decode())#反序列 79 if not data_l['filename']: 80 print('文件不存在') 81 continue 82 file_dir=config.USER_DIR+data_l["filename"] 83 file_obj=open(file_dir,'wb')#打开新建 这个文件 84 rece_size=0#定义 文件大小值 85 prten=show_process(data_l["size"]) 86 prten.__next__() 87 while rece_size<data_l["size"]:#小于接收的文件大小时, 88 recv_data=client.recv(4096) 89 file_obj.write(recv_data)#写入文件 90 rece_size+=len(recv_data)#增加文件大小计算 91 try: 92 prten.send(len(recv_data)) 93 except StopIteration as e: 94 print('100%') 95 96 else: 97 print("文件[%s]接收完毕!"%data_l["filename"]) 98 file_obj.flush() 99 file_obj.close()#关闭文件100 elif cmd_list[0]=='ls':#查看目录文件101 data_header={102 "action":"ls",103 "filename":'',104 "size":''105 }106 client.send(json.dumps(data_header).encode())#用json 序列化后,发送相关 信息107 datas=client.recv(4096)#接收数据 指令108 data_l= json.loads(datas.decode())#反序列109 for k,v in enumerate(data_l):110 print('编号: %s 文件名:%s'%(k,v))111 112 else:113 print(data_d['mag'])
cfg/
config.py
1 #!usr/bin/env python 2 #-*-coding:utf-8-*- 3 # Author calmyan 4 5 import os ,sys 6 BASE_DIR=os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)))#获取相对路径转为绝对路径赋于变量 7 sys.path.append(BASE_DIR)#增加环境变量 8 9 10 USER_DIR=BASE_DIR+'\home\\'#定义用户目录文件路径变量
core/
client_func.py
1 #!usr/bin/env python 2 #-*-coding:utf-8-*- 3 # Author calmyan 4 import socket,os,json,sys 5 #用户名登陆函数 6 def user_pwd(client): 7 user_=input('请输入用户名:').strip() 8 pwd_=input('请输入密码:').strip() 9 data_header={10 "action":"user",11 "name":user_,12 "pwd":pwd_13 }14 client.send(json.dumps(data_header).encode())#用json 序列化后,发送相关 信息15 data=client.recv(4096)#接收数据 指令16 data_s=json.loads(data.decode('utf-8'))#反序列17 return data_s18 19 20 #进度条21 def show_process(lens):22 received_size=0#定义大小23 current_percent=0#当前大小百分比24 while received_size<lens:25 if int((received_size/lens)*100)>current_percent:26 print('#',end='',flush=True)27 current_percent=int((received_size/lens)*100)28 new_size=yield29 received_size+=new_size
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of simple FTP implementation. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 Python: Exploring Its Primary Applications
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:41 AM
Python: Exploring Its Primary Applications
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:41 AM
Python is widely used in the fields of web development, data science, machine learning, automation and scripting. 1) In web development, Django and Flask frameworks simplify the development process. 2) In the fields of data science and machine learning, NumPy, Pandas, Scikit-learn and TensorFlow libraries provide strong support. 3) In terms of automation and scripting, Python is suitable for tasks such as automated testing and system management.
 The 2-Hour Python Plan: A Realistic Approach
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The 2-Hour Python Plan: A Realistic Approach
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:04 AM
You can learn basic programming concepts and skills of Python within 2 hours. 1. Learn variables and data types, 2. Master control flow (conditional statements and loops), 3. Understand the definition and use of functions, 4. Quickly get started with Python programming through simple examples and code snippets.
 Navicat's method to view MongoDB database password
Apr 08, 2025 pm 09:39 PM
Navicat's method to view MongoDB database password
Apr 08, 2025 pm 09:39 PM
It is impossible to view MongoDB password directly through Navicat because it is stored as hash values. How to retrieve lost passwords: 1. Reset passwords; 2. Check configuration files (may contain hash values); 3. Check codes (may hardcode passwords).
 How to use AWS Glue crawler with Amazon Athena
Apr 09, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
How to use AWS Glue crawler with Amazon Athena
Apr 09, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
As a data professional, you need to process large amounts of data from various sources. This can pose challenges to data management and analysis. Fortunately, two AWS services can help: AWS Glue and Amazon Athena.
 How to start the server with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:12 PM
How to start the server with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:12 PM
The steps to start a Redis server include: Install Redis according to the operating system. Start the Redis service via redis-server (Linux/macOS) or redis-server.exe (Windows). Use the redis-cli ping (Linux/macOS) or redis-cli.exe ping (Windows) command to check the service status. Use a Redis client, such as redis-cli, Python, or Node.js, to access the server.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to view server version of Redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 01:27 PM
How to view server version of Redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 01:27 PM
Question: How to view the Redis server version? Use the command line tool redis-cli --version to view the version of the connected server. Use the INFO server command to view the server's internal version and need to parse and return information. In a cluster environment, check the version consistency of each node and can be automatically checked using scripts. Use scripts to automate viewing versions, such as connecting with Python scripts and printing version information.
 How secure is Navicat's password?
Apr 08, 2025 pm 09:24 PM
How secure is Navicat's password?
Apr 08, 2025 pm 09:24 PM
Navicat's password security relies on the combination of symmetric encryption, password strength and security measures. Specific measures include: using SSL connections (provided that the database server supports and correctly configures the certificate), regularly updating Navicat, using more secure methods (such as SSH tunnels), restricting access rights, and most importantly, never record passwords.




