 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Linux Operation and Maintenance
Linux Operation and Maintenance
 Detailed explanation of scenario linux examples
Detailed explanation of scenario linux examples
Detailed explanation of scenario linux examples
Scenario linux--How to exit telnet gracefully in a script
Scenario
The telnet command is the user interface of the TELNET protocol. It supports two modes: Command mode and Session Mode. Although telnet supports many commands, in most cases, we just use it to check whether the target host has opened a certain port (default is 23).
There are two execution results:- The port is not open
$ telnet 101.199.97.65 62715
Trying 101.199.97.65... telnet: connect to address 101.199.97.65: Connection refused
- The port is open
$ telnet 101.199.97.65 62715
Trying 101.199.97.65... Connected to 101.199.97.65. Escape character is '^]'.
According to the prompt
Escape character is '^]'.It can be seen that the exit character is '^]' (CTRL+]). Entering other characters at this time will not cause it to exit, nor will CTRL+C. After entering CTRL+], it will be automatically executed and enter the command mode:
^]
telnet>
quit at this time to truly exit.
telnet> quit
Connection closed.
-e:
$ telnet -e p 101.199.97.65 62715 Telnet escape character is 'p'. Trying 101.199.97.65... Connected to 101.199.97.65. Escape character is 'p'. p telnet> quit Connection closed.
- Exit immediately after outputting the results
$ echo "" | telnet 101.199.97.65 62715
Copy after loginCopy after login
Trying 101.199.97.65... Connected to 101.199.97.65. Escape character is '^]'. Connection closed by foreign host.
$ echo "" | telnet 101.199.97.65 62715
Trying 101.199.97.65... telnet: connect to address 101.199.97.65: Connection refused
- Delayed exit after outputting results
sleep 2 causes telnet to output results and stay for 2 seconds before exiting command mode.
$ sleep 2 | telnet 101.199.97.65 62715
Copy after login
Trying 101.199.97.65... Connected to 101.199.97.65. Escape character is '^]'. Connection closed by foreign host.
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of scenario linux examples. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1382
1382
 52
52
 Why are wallpapers gone after wallpaperengine exits?
Mar 12, 2024 pm 05:40 PM
Why are wallpapers gone after wallpaperengine exits?
Mar 12, 2024 pm 05:40 PM
Users can get various wallpapers by using wallpaperengine. Many users don't know why the wallpapers are gone after wallpaperengine exits. Dynamic wallpapers can only run on the desktop when the software you installed the wallpaper is turned on. Why are the wallpapers gone after wallpaperengine exits? 1. Dynamic wallpapers can only run on the desktop when the software you installed the wallpaper is turned on. 2. WallpaperEngine overwrites the original wallpaper, and of course it will be gone when you exit. 3. The wallpaper is still there after it is turned off, unless the file format is an image type, which can be obtained through some means, but it is not dynamic. 4. There is no video or dynamic image as a wall in Windows.
 Microsoft account exit tutorial: How to exit Win11 account
Dec 25, 2023 pm 08:04 PM
Microsoft account exit tutorial: How to exit Win11 account
Dec 25, 2023 pm 08:04 PM
In previous win11 updates, we could skip logging in with a Microsoft account, but the latest win11 home version forces users to log in with a Microsoft account to install. However, logging in with a Microsoft account will cause a lot of trouble. Many friends want to log out after the installation is completed. Let me teach you how to exit. How to log out of Microsoft account in win11 1. First click on the start menu below and find "Settings" in it, as shown in the picture. 2. Find the "Users" or "accounts" option in the settings interface. 3. Find "Log in with a local account instead" in the user interface, which is a line of blue text. 4. Then just enter the password of our local account to log in to the local account and log out of the Microsoft account.
 How to withdraw from Meituan Mutual Aid_Meituan's steps to withdraw from mutual aid
Mar 28, 2024 pm 03:01 PM
How to withdraw from Meituan Mutual Aid_Meituan's steps to withdraw from mutual aid
Mar 28, 2024 pm 03:01 PM
1. After logging in to your Meituan account, you first need to click on the [My] function. 2. After entering the [My] page, click the [Enter Wallet] function on the page. 3. The [Meituan Wallet] page will pop up, then scroll down to the bottom and click the [Meituan Mutual Aid] function in the [More Services] column. 4. At this time, you will enter the [Meituan Mutual Aid] page, and then click the [View Details] function on the page. 5. After entering the [Mutual Aid Details] page, scroll down to the bottom again, and then click the [Waiver of Protection] function. 6. A dialog box will pop up. Then click the [Deterministic Exit] function in the dialog box to successfully exit Meituan Mutual Aid.
 What is the use of Douyin fan club? How to leave someone else's fan club?
Apr 01, 2024 am 09:51 AM
What is the use of Douyin fan club? How to leave someone else's fan club?
Apr 01, 2024 am 09:51 AM
With the rapid development of mobile Internet, social media has become an indispensable part of people's lives. As one of the most popular social platforms, Douyin has won the love of a large number of users for its short video content and lively and interesting creativity. On Douyin, many users will join various fan groups, so what is the use of Douyin fan groups? 1. What is the use of Douyin fan club? The Douyin fan group provides users with a community that gathers interested enthusiasts. In this community, users can find like-minded people to discuss and share topics of interest. Whether you are a groupie, a music lover or a food expert, as long as you have the same interests and hobbies, you can find your own small circle in the Douyin fan group. The Douyin fan group also provides users with a
 Can't exit win11 preview program
Jun 29, 2023 pm 12:04 PM
Can't exit win11 preview program
Jun 29, 2023 pm 12:04 PM
Can't exit win11 preview program? When we use the win11 system, the win11 preview program will be launched on the computer for us to use. However, some friends do not want to use this preview program. I hope this preview program can be launched. If you don’t know how to exit, the editor below We have compiled a tutorial guide for exiting the Win11 preview experience program. If you are interested, let’s take a look below! Tutorial guide for exiting the Win11 Insider Program 1. First press the shortcut key "win+i" to enter Windows Settings and click "Update and Security". 2. Then click "Windows Insider Program" in the left taskbar, as shown in the figure. 3. At this point you can see the experience on the right
 How to log out of WeChat account on Douyin
Mar 22, 2024 pm 03:30 PM
How to log out of WeChat account on Douyin
Mar 22, 2024 pm 03:30 PM
Interoperability between major social platforms and applications has become the norm. As one of the most popular social software in China, WeChat’s authorization function is widely used in various APPs, including Douyin. However, as time goes by, some users may wish to cancel Douyin’s authorization to WeChat for privacy protection or other reasons. So many users may still not understand how to cancel WeChat’s authorization for Douyin. Below, the editor of this website will introduce you in detail the steps to cancel Douyin’s WeChat authorization. Users who want to know can come and follow Let’s continue this article to learn more! How to cancel WeChat authorization for Douyin. First, we open the WeChat app and then on the WeChat main page, click Settings and select the privacy function. Find Authorization Management in the privacy function and then find Douyin and select Delete.
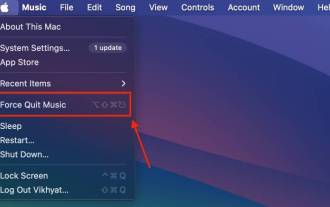 Six Ways to Force Quit on Mac
Nov 07, 2023 am 11:13 AM
Six Ways to Force Quit on Mac
Nov 07, 2023 am 11:13 AM
1. Use the Apple Menu to Force Quit an Application on a Mac Using the Apple Menu to Force Quit an application on a Mac provides an easy way to deal with unresponsive or frozen applications without having to remember extra keyboard shortcuts. Here's how to force quit an app in macOS Sonoma: Click the Apple logo in the upper left corner of your Mac screen. Here, find and click on the “Force Quit” option in the drop-down menu that appears. Once completed, a pop-up window will appear with all the applications currently running on your Mac. Select the app you want to quit, then click the "Force Quit" button in the lower right corner of the window. 2. Use Keyboard Shortcuts to Force Quit Apps on Mac When you encounter the problem
 How to leave Douyin fan club
Mar 26, 2024 pm 12:31 PM
How to leave Douyin fan club
Mar 26, 2024 pm 12:31 PM
After users follow their favorite anchors on Douyin, they can join the anchor's fan group by paying a dime to get a light sign. So how can we withdraw from the fan group? Today, the editor will bring you a graphic tutorial on how to exit the Douyin fan group. If you are interested, come and take a look. Douyin usage tutorial: How to exit the fan club in Douyin. Method 1: 1. Let’s open Douyin first, click the three-bar icon in the upper right corner of the My interface, and then click Wallet. 2. Then we click on More Functions in the wallet interface. 3. Finally, we find the Douyin service in all functions, click on the fan group, and confirm to exit the fan group. Method 2: 1. When the anchor is live broadcasting, we need to click on the fan club mark in the upper left corner, and then click on the intimacy level in the lower right corner. 2. Click on the three to the right of My Level Rights



