 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Linux Operation and Maintenance
Linux Operation and Maintenance
 What are the ways to start bash shell?
What are the ways to start bash shell?
What are the ways to start bash shell?
Three ways to start bash shell
1. As the default login shell when logging in
2. As an interactive shell as a non-login shell
3. As a run Non-interactive shell of script
1. Login shell
When logging in to the Linux system, the bash shell will be started as the login shell, and the login shell will start from 4 different startup files Read the command here, the following is the order in which the bash shell processes these files:
1./etc/profile
2.$HOME/.bash_profile
3.$HOME /.bash_login
4.$HOME/.profile
The /etc/profile file is the main startup file of the system’s default bash shell. Each user on the system will execute this when logging in. startup files, and the other three startup files are user-specific. For example, each user can configure his or her own jdk, tomcat, etc.
1), /etc/profile
The profile file has a complex feature. There is a for statement, which will access each file in the /etc/profile.d directory one by one. It is Linux The system provides a centralized place to store application-specific startup files to be executed when the user logs in. These are basically related to the specific applications of the system. Most applications will create two startup files, one for the bash shell and one for the c shell.

2), the startup file in the $HOME directory
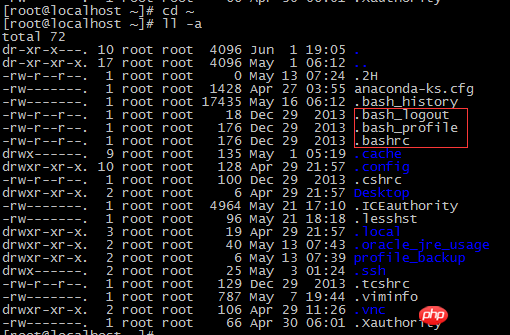
Most Linux distributions only use one of these three startup files; each Individual users can edit these files and add their own environment variables to each bash shell session they start.
.bash_profile file: This file will first check whether there is a startup file called .bashrc in the HOME directory. If there is, the startup file will first execute the commands in the .bashrc file, and then A directory is added to the PATH environment variable.
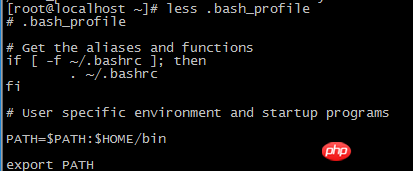
2. Interactive shell
If the bash shell is not started when logging in to the system, for example Enter the bash command at the command line prompt to start. The shell started is called an interactive shell. In this case, the /etc/profile file will not be started, but the bashrc will be checked in the user's HOME directory to see whether it exists. This file has two functions:
1. View the shared bashrc file in the /etc directory
2. Provide users with a place to customize their own command aliases and private script functions.
The common /etc/bashrc startup file will be executed by every user on the system who starts an interactive shell session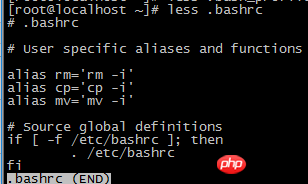
Three , Non-interactive shell
This is the shell that the system uses when executing shell scripts. In this case there is no need to worry that it does not have a command line prompt, but you still have to run a specific startup command every time you run the script on the system. To handle this situation, the bash shell provides the BASE_ENV environment variable. When the shell starts a When the shell process is non-interactive, it will check this environment variable to see the startup file to be executed. If specified, the shell will execute the commands in the file.
The above is the detailed content of What are the ways to start bash shell?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1390
1390
 52
52
 How to solve application startup error 0xc000012d problem
Jan 02, 2024 pm 12:53 PM
How to solve application startup error 0xc000012d problem
Jan 02, 2024 pm 12:53 PM
When a friend's computer is missing certain files, the application cannot start normally with error code 0xc000012d. In fact, it can be solved by re-downloading the files and installing them. The application cannot start normally 0xc000012d: 1. First, the user needs to download ".netframework". 2. Then find the download address and download it to your computer. 3. Then double-click on the desktop to start running. 4. After the installation is completed, return to the wrong program location and open the program again.
 How to solve the computer prompt 'reboot and select proper boot device'
Jan 15, 2024 pm 02:00 PM
How to solve the computer prompt 'reboot and select proper boot device'
Jan 15, 2024 pm 02:00 PM
Reinstalling the system may not be a foolproof solution, but after reinstalling, I found that when the computer is turned on, it will display white text on a black background, and then give a prompt: rebootandselectproperbootdevice, what is going on? Such a prompt is usually caused by a boot error. In order to help everyone, the editor has brought you a solution. Computer use is becoming more and more popular, and computer failures are becoming more and more common. No, recently some users encountered a black screen when turning on the computer, and prompted Reboot and Select Proper Boot device, and the computer system could not start normally. What's going on? How to solve it? The user is confused. Next, the editor will follow
 Effective solutions and techniques for Ubuntu startup black screen problem
Dec 29, 2023 am 10:30 AM
Effective solutions and techniques for Ubuntu startup black screen problem
Dec 29, 2023 am 10:30 AM
Practical tips and methods to solve the black screen on Ubuntu startup Introduction: Ubuntu is a popular Linux operating system, but sometimes you may encounter a black screen problem during the startup process. This problem can be caused by a variety of reasons, such as graphics card driver issues, software conflicts, or system errors. This article will introduce some practical tips and methods to help solve the black screen problem at Ubuntu startup to ensure the stable operation of the system. 1. Update and reinstall the graphics card driver to enter recovery mode: press the Shift key during startup to enter
 What should I do if wps cannot start the source application of this object?
Mar 13, 2024 pm 09:13 PM
What should I do if wps cannot start the source application of this object?
Mar 13, 2024 pm 09:13 PM
WPS is a very widely used office software, including documents, forms and PPT, and supports multi-terminal synchronization. If the prompt "The source application for this object cannot be launched" appears when editing wps, how to solve it? This problem may occur because you are trying to open a link or file, but its source application no longer exists or has been deleted. Here are some fixes: 1. Reinstall WPS software: Try reinstalling WPSOffice to fix the problem and make sure you are using the latest version. 2. Manually change the default program: Try to change the default program to WPS. You can right-click the file you want to open, select "Open with", and then
 How to quickly delete the line at the end of a file in Linux
Mar 01, 2024 pm 09:36 PM
How to quickly delete the line at the end of a file in Linux
Mar 01, 2024 pm 09:36 PM
When processing files under Linux systems, it is sometimes necessary to delete lines at the end of the file. This operation is very common in practical applications and can be achieved through some simple commands. This article will introduce the steps to quickly delete the line at the end of the file in Linux system, and provide specific code examples. Step 1: Check the last line of the file. Before performing the deletion operation, you first need to confirm which line is the last line of the file. You can use the tail command to view the last line of the file. The specific command is as follows: tail-n1filena
 Steps to restart your iPhone
Aug 29, 2023 am 10:53 AM
Steps to restart your iPhone
Aug 29, 2023 am 10:53 AM
Although it seems like a basic task, quite a few people often find themselves wondering how to restart their iPhone. This article will give you a comprehensive guide with everything you need to know about the process of restarting your iPhone effectively. There may be countless reasons why you want to restart your iPhone. Often, you might deal with unexpected issues on your device, in which case a simple reboot might be the magic bullet to fix the problem. Technical glitches, poor performance, and unresponsive applications are just a few examples of problems that a restart can correct. One of the initial troubleshooting steps I take when faced with a challenge regarding my iPhone is to perform a quick restart of the device. This seemingly simple action can solve a variety of small problems quickly and easily
 How to set the boot priority of Apple dual system
Feb 19, 2024 pm 06:49 PM
How to set the boot priority of Apple dual system
Feb 19, 2024 pm 06:49 PM
As technology continues to develop, the need to use different operating systems is becoming more and more common. For Apple users, sometimes you may need to install and use two different operating systems on one device, such as macOS and Windows. In this case, it is particularly important to set the startup sequence of the dual system. This article will introduce how to set up Apple devices to start the dual system first when turning on the device. First, we need to make sure that both operating systems have been successfully installed on the Apple device. You can use BootCamp this Apple
 Which one to choose when starting wallpaperengine?
Mar 19, 2024 am 08:49 AM
Which one to choose when starting wallpaperengine?
Mar 19, 2024 am 08:49 AM
When wallpaperengine starts, there are 4 different options. Many users don't know which one to choose when starting wallpaperengine. Generally, when wallpaperengine starts, choose the first one: start 32-bit. Which one to choose when starting wallpaperengine? Answer: Start 32-bit. 1. Generally, when wallpaperengine starts, select the first one: start 32-bit. 2. When wallpaperengine starts, there are 4 different options: start 32-bit; start 64-bit. 3. Start 32-bit: This is a generally recommended option and suitable for most users. 4. Start 64-bit: If the system supports 64-bit, you can choose this option



