Python web server related knowledge points
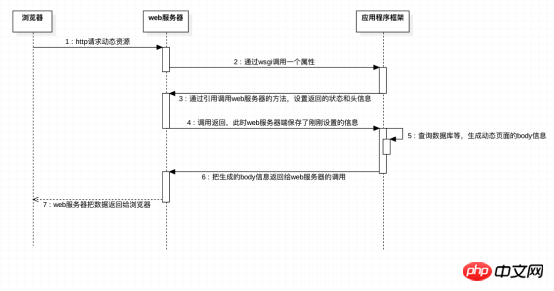
1. The process of browser requesting dynamic pages
def application(environ, start_response):
start_response('200 OK', [('Content-Type', 'text/html')])return 'Hello World!'- environ: a dict object containing all HTTP request information;
- start_response: a function that sends an HTTP response.
import time,multiprocessing,socket,os,reclass MyHttpServer(object):def __init__(self):
serveSocket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
self.serveSocket = serveSocket
self.HTMLPATH = './html'def bind(self,port=8000):
self.serveSocket.bind(('',port))def start(self):
self.serveSocket.listen()while True:
clientSocket, clientAddr = self.serveSocket.accept()
print(clientSocket)
multiprocessing.Process(target=self.serveHandler, args=(clientSocket, clientAddr)).start()
clientSocket.close()def serveHandler(self,clientSocket,clientAddr):try:
recvData = clientSocket.recv(1024).decode('gbk')
fileName = re.split(r' +', recvData.splitlines()[0])[1]
filePath = self.HTMLPATHif fileName.endswith('.py'):try:
pyname=fileName[1:-3]# 导入
pyModule = __import__(pyname)
env={}
responseBody = pyModule.application(env,self.startResponse)
responseLine = self.responseLine
responseHeader = self.responseHeaderexcept ImportError:
responseLine = 'HTTP/1.1 404 NOT FOUND'
responseHeader = 'Server: ererbai' + os.linesep
responseHeader += 'Date: %s' % time.ctime()
responseBody = '<h1>很抱歉,服务器中找不到你想要的内容<h1>'else:if '/'== fileName:
filePath += '/index.html'else:
filePath += fileNametry:
file = None
file =open(filePath,'r',encoding='gbk')
responseBody = file.read()
responseLine = 'HTTP/1.1 200 OK'
responseHeader = 'Server: ererbai' + os.linesep
responseHeader += 'Date:%s' % time.ctime()except FileNotFoundError:
responseLine = 'HTTP/1.1 404 NOT FOUND'
responseHeader = 'Server: ererbai' + os.linesep
responseHeader += 'Date:%s' % time.ctime()
responseBody = '很抱歉,服务器中找不到你想要的内容'finally:if (file!=None) and (not file.closed):
file.close()except Exception as ex:
responseLine = 'HTTP/1.1 500 ERROR'
responseHeader = 'Server: ererbai' + os.linesep
responseHeader += 'Date: %s' % time.ctime()
responseBody = '服务器正在维护中,请稍后再试。%s'%exfinally:
senData = responseLine + os.linesep + responseHeader + os.linesep + os.linesep + responseBody
print(senData)
senData = senData.encode('gbk')
clientSocket.send(senData)if (clientSocket!=None) and ( not clientSocket._closed):
clientSocket.close()def startResponse(self,status,responseHeaders):
self.responseLine = status
self.responseHeader = ''for k,v in responseHeaders:
kv = k + ':' + v + os.linesep
self.responseHeader += kvif __name__ == '__main__':
server = MyHttpServer()
server.bind(8000)
server.start()- index.html
<html><head><title>首页-毕业季</title><meta http-equiv=Content-Type content="text/html;charset=gbk"></head><body>我们仍需共生命的慷慨与繁华相爱,即使岁月以刻薄和荒芜相欺。</body></html>
- biye.html
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="gbk"><title>毕业季</title></head><body><br>当年以为六月不过也很平常<br>当自己真正经历了毕业<br>才知道偶尔看到六月毕业季等字里所流露的种种想要重温却不敢提及的回忆<br>毕业了<br>那个夏天,我的毕业季,我的青春年少<br>六月<br>有人笑着说解脱,有人哭着说不舍<br>那年,<br>你对我说的你好<br>在不知不觉中<br>变成了<br>再见。</body></html>

biyeji.png
import timedef application(env,startResponse):
status = 'HTTP/1.1 200 OK'
responseHeaders = [('Server','bfe/1.0.8.18'),('Date','%s'%time.ctime()),('Content-Type','text/plain')]
startResponse(status,responseHeaders)
responseBody = str(time.ctime())return responseBodyCopy after login
Access results:import timedef application(env,startResponse):
status = 'HTTP/1.1 200 OK'
responseHeaders = [('Server','bfe/1.0.8.18'),('Date','%s'%time.ctime()),('Content-Type','text/plain')]
startResponse(status,responseHeaders)
responseBody = str(time.ctime())return responseBody
Home page

biye.html
 ##mytime.py
##mytime.py'''
自定义的符合wsgi的框架
'''import timeclass Application(object):def __init__(self, urls):'''框架初始化的时候需要获取路由列表'''
self.urls = urlsdef __call__(self, env, startResponse):'''
判断是静态资源还是动态资源。
设置状态码和响应头和响应体
:param env:
:param startResponse:
:return:
'''# 从请求头中获取文件名
fileName = env.get('PATH_INFO')# 判断静态还是动态if fileName.startwith('/static'):
fileName = fileName[7:]if '/' == fileName:
filePath += '/index.html'else:
filePath += fileNametry:
file = None
file = open(filePath, 'r', encoding='gbk')
responseBody = file.read()
status = 'HTTP/1.1 200 OK'
responseHeaders = [('Server', 'ererbai')]except FileNotFoundError:
status = 'HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found'
responseHeaders = [('Server', 'ererbai')]
responseBody = '<h1>找不到<h1>'finally:
startResponse(status, responseHeaders)if (file != None) and (not file.closed):
file.close()else:
isHas = False # 表示请求的名字是否在urls中,True:存在,False:不存在for url, func in self.urls:if url == fileName:
responseBody = func(env, startResponse)
isHas = Truebreakif isHas == False:
status = 'HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found'
responseHeaders = [('Server', 'ererbai')]
responseBody = '<h1>找不到<h1>'
startResponse(status, responseHeaders)return responseBodydef mytime(env, startResponse):
status = 'HTTP/1.1 200 OK'
responseHeaders = [('Server', 'time')]
startResponse(status, responseHeaders)
responseBody = str(time.ctime())return responseBodydef mynews(env, startResponse):
status = 'HTTP/1.1 200 OK'
responseHeaders = [('Server', 'news')]
startResponse(status, responseHeaders)
responseBody = str('xx新闻')return responseBody'''路由列表'''
urls = [
('/mytime', mytime),
('/mynews', mynews)
]
application = Application(urls)The above is the detailed content of Python web server related knowledge points. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Is there a mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:45 PM
Is there a mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:45 PM
There is no APP that can convert all XML files into PDFs because the XML structure is flexible and diverse. The core of XML to PDF is to convert the data structure into a page layout, which requires parsing XML and generating PDF. Common methods include parsing XML using Python libraries such as ElementTree and generating PDFs using ReportLab library. For complex XML, it may be necessary to use XSLT transformation structures. When optimizing performance, consider using multithreaded or multiprocesses and select the appropriate library.
 How to convert XML files to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to convert XML files to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
It is impossible to complete XML to PDF conversion directly on your phone with a single application. It is necessary to use cloud services, which can be achieved through two steps: 1. Convert XML to PDF in the cloud, 2. Access or download the converted PDF file on the mobile phone.
 Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
An application that converts XML directly to PDF cannot be found because they are two fundamentally different formats. XML is used to store data, while PDF is used to display documents. To complete the transformation, you can use programming languages and libraries such as Python and ReportLab to parse XML data and generate PDF documents.
 How to beautify the XML format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:57 PM
How to beautify the XML format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:57 PM
XML beautification is essentially improving its readability, including reasonable indentation, line breaks and tag organization. The principle is to traverse the XML tree, add indentation according to the level, and handle empty tags and tags containing text. Python's xml.etree.ElementTree library provides a convenient pretty_xml() function that can implement the above beautification process.
 Is the conversion speed fast when converting XML to PDF on mobile phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
Is the conversion speed fast when converting XML to PDF on mobile phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
The speed of mobile XML to PDF depends on the following factors: the complexity of XML structure. Mobile hardware configuration conversion method (library, algorithm) code quality optimization methods (select efficient libraries, optimize algorithms, cache data, and utilize multi-threading). Overall, there is no absolute answer and it needs to be optimized according to the specific situation.
 How to control the size of XML converted to images?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
How to control the size of XML converted to images?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
To generate images through XML, you need to use graph libraries (such as Pillow and JFreeChart) as bridges to generate images based on metadata (size, color) in XML. The key to controlling the size of the image is to adjust the values of the <width> and <height> tags in XML. However, in practical applications, the complexity of XML structure, the fineness of graph drawing, the speed of image generation and memory consumption, and the selection of image formats all have an impact on the generated image size. Therefore, it is necessary to have a deep understanding of XML structure, proficient in the graphics library, and consider factors such as optimization algorithms and image format selection.
 How to open xml format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
How to open xml format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
Use most text editors to open XML files; if you need a more intuitive tree display, you can use an XML editor, such as Oxygen XML Editor or XMLSpy; if you process XML data in a program, you need to use a programming language (such as Python) and XML libraries (such as xml.etree.ElementTree) to parse.
 Is there a free XML to PDF tool for mobile phones?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
Is there a free XML to PDF tool for mobile phones?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
There is no simple and direct free XML to PDF tool on mobile. The required data visualization process involves complex data understanding and rendering, and most of the so-called "free" tools on the market have poor experience. It is recommended to use computer-side tools or use cloud services, or develop apps yourself to obtain more reliable conversion effects.






