
1.javascript output
The command issued by the JavaScript statement to the browser. The purpose of a statement is to tell the browser what to do.
<script>
document.write("hello world!");
</script>Insert, output.
document.getElementById("pid").innerHTML="jikexueyuan.com";2. Semicolon
The separation between statements is a semicolon (;)
Note: The semicolon is optional, sometimes See those that are not separated by semicolons.
3. JavaScript code:
Execute in order of writing
4. Identifier:
JavaScript identifiers must begin with a letter, underscore, or dollar sign
JavaScript keywords
5. JavaScript is case-sensitive
JavaScript is also case-sensitive Case is very sensitive.
6. Spaces
JavaScript will ignore extra spaces
7. Code line breaks
Line breaks between words are not allowed
8. Reserved words
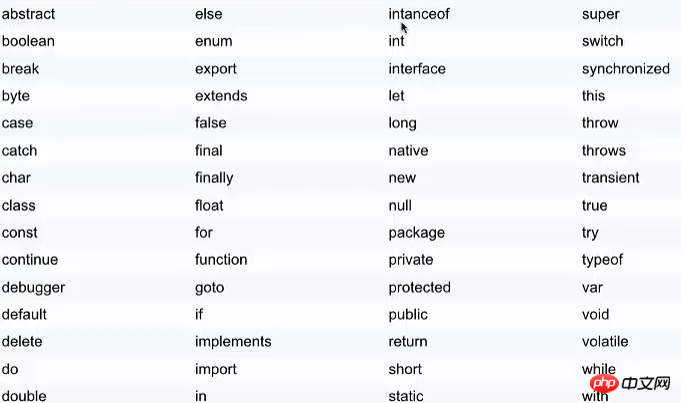
##Comments
Single-line comments //Multi-line comments /**/JavaScript variables
Variables are "containers" used to store informationvar x=10; var y=10.1; var z="hello";
<script>
var i=10;
var j=10;
var m=i+j;
document.write(m);
</script>JavaScript Data Type
1. String (String) 2. Number (Number) 3. Boolean ) 4. Array The first way to define an array:var arr=["hello","jike","xueyuan","women"]; document.write(arr[0]);
var arr=new Array("hello","jike","nihao");
document.write(arr[2]);var arr=new Array(); arr[0]=10; arr[1]=20; arr[2]=30; document.write(arr[2]);
var n=null;
var r;
var i=10;
var i=null;
document.write("i"); //nullJavaScript Operator
1. Arithmetic Operator
+ - * % / ++ --<p>i=10,j=10,i+j=?</p>
<p id="mySum"></p>
<button onclick="jisuan()">结果<button>
<script>
function jisuan(){
var i=10;
var j=10;
var m=i+j;
document.getElementById("mySum").innerHTML=m;
}
</script>2. Assignment operator
= += -= *= /= %=3. String operation (string splicing)
Any type added to a string will be converted into a string typefunction musum(){
var i=5;
var j="5";
var m=i+j;
document.getElementById("sumid").innerHTML=m;
}
// 554. Comparison operation Symbols
== === != !== > <#5. Logical operators
## && || !
6. Conditional operatorsx<10 Compare size
Ternary operation Judgment condition? Output when the condition is met. : Output when the condition is not met
JavaScript conditional statementif...else..
<script>
var i=19;
if(i>=10){
document.write("我就喜欢i>=10");
}else{
document.write("为什么i<10");
}
</script>
<script>
var i=10;
if(i>10){
document.write("我就喜欢i>=10");
}else if(i<10){
document.write("为什么i<10?");
}else{
document.write("i到底是多少,原来是10");
}
</script>
swicth(执行条件){
代码段
}<script>
var i=5;
switch(i){
case 1:
document.write("i=1");
break; //跳出当前
case 2:
document.write("i=2");
break;
default:
document.write("条件不满足case");
break;
}
</script>
Ternary operation
JavaScript loop statementfor loop , for/in<script>
var i=[1,2,3,4,5,6];
for(j=0;j<6;j++){
document.write(i[j]+"、");
}
</script><script>
var j=[1,2,3,4,5,6];
var j=0;
for(;j<6;){
document.write(i[j]+"、");
j++;
}
</script><script>
var i=[1,2,3,4,5,6];
var j;
for(j in i){ //j是i中的元素
document.write(i[j]+"<br/>");
}
</script>
<script>
var i=1;
while(i<10){
document.write("i="+i+"<br/>");
i++;
}
</script><script>
var i=1;
do{
document.write("i="+i+"<br/>");
}while(i<10){
}
</script>
JavaScript jump statement
break
Jump out Current cycle
<script>
for(var i=0;i<10;i++){
if(i==5){
break;
}
document.write("i="+i+"<br/>");
}
</script>continue
End this cycle and continue the next cycle
<script>
for(var i=0;i<10;i++){
if(i==5){
continue;
}
document.write("i="+i+"<br/>");
}
</script>The above is the detailed content of The basic syntax of JavaScript you need to know. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




