
Position is a very important property in CSS. Through the position property, we can offset the element relative to its normal position, parent element or browser window. Position is also an attribute that beginners can easily get confused about. This article will start with the most basic knowledge and talk about some theories and applications about the position attribute.
The postion attribute is called positioning. It has 4 different types of positioning. These types will affect the way elements are generated. Below we explain the position attribute in detail.
(1)static
static is the default value of the position attribute. By default, block-level elements and inline elements are displayed according to their respective characteristics
(2) relative
relative is translated into Chinese as relative positioning. After setting this attribute, the element will be offset according to top, left, bottom, and right. The key point is that its original space is still retained. Let’s look at the following example:
HTML code
<div class="relative"> </div> <div></div>
CSS code
div { background: #0094ff; width: 250px; height: 100px; }
.relative { background: #ff6a00; position: relative; width: 200px; height: 100px; top: 20px; left: 50px; }Rendering

After the element is set to absolute, it will be separated from the document flow and will not occupy the original space. Subsequent elements will replace it, and regardless of whether the element is an inline element or a block-level element, it will be generated A block-level box, that is, for example, after the inline element span is set to absolute, the height and width attributes can be set. Look at the following example:
HTML code
<span class="absolute"> </span> <div></div>
div { background: #0094ff; width: 250px; height: 100px; }
.absolute { background: #ff6a00; position: absolute; width: 200px; height: 100px; top: 20px; left: 50px; } ##absolute effect
##absolute effect
As shown in the figure, if the span tag is set to
absolute positioning, the height and width attributes can be set without occupying the original space. The subsequent p element will replace it. (4) fixed
The performance of fixed is similar to absolute, but compared with absolute's offset relative to an uncertain parent element, fixed is offset relative to the browser window
Containing block
2. The containing block of the non-root element, if the position of the element is relative or static, its containing block is the nearest block-level box, table cell or inline block The content boundary
Let’s take an example to illustrate,
HTML code
<div>
我是父级元素的内容
<div class="relative">
相对定位元素
</div>
</div>div { background: #0094ff; width: 250px; height: 100px; }
.relative { background: #ff6a00; position: relative; width: 200px; height: 100px; top: 20px; left: 50px; }Rendering
 contains Block
contains Block
This is the containing block of the relatively positioned element, which is the content boundary of the nearest block-level box, table cell or inline block. The relatively positioned element is offset relative to its containing block. We can simply understand To offset relative to its original position.
3. The containing block of a non-root element. If the position of the element is absolute, the containing block is the nearest ancestor element whose position is not static.
Simply put, its containing block will search upwards from the parent element until it finds the first element whose position is not static.
Offset attribute
Absolute positioning
Basic absolute positioning
HTML code
<div class="absolute">
相对于初始What is the use of CSS position property?定位
</div>
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<div class="relative">
<div class="absolute">
相对于最近relative祖先元素定位
</div>
</div>div { background: #0094ff; width: 250px; height: 100px; }
.relative { background: #ff6a00; position: relative; width: 200px; height: 100px; top: 20px; left: 50px; }
.absolute { background: #988c8c; position: absolute; width: 200px; height: 100px; top: 20px; left: 50px; }Rendering
 Basic absolute positioning
Basic absolute positioning
The second absolutely positioned element sets a relative parent element, which is offset according to the parent element.
元素设置成绝对定位后会脱离文档流,并且失去占用的空间,而且如果偏移的位置接近,会造成重叠问题。看看下面的例子:
HTML代码
<div class="relative">
<div class="absolute">
相对于最近relative祖先元素定位1
</div>
<div class="absolute light">
相对于最近relative祖先元素定位2
</div>
</div>CSS代码
div { background: #0094ff; width: 250px; height: 100px; }
.relative { background: #ff6a00; position: relative; width: 500px; height: 300px; top: 20px; left: 50px; }
.absolute { background: #988c8c; position: absolute; width: 200px; height: 100px; top: 20px; left: 50px; }
.light { background: #f3d6d6; top: 70px; left: 80px; }效果图

What is the use of CSS position property?
我们可以看到,第二个绝对定位元素盖住了第一个元素,那怎么让第一个元素盖住第二个元素呢,这就要用到z-index属性,这个属性表示元素的叠加顺序,默认情况下,z-index为0,数值越高的元素层级越高,就可以盖住低于其层级的元素,我们设置第一个原色的z-index为10,结果如下
What is the use of CSS position property?
如果两个元素的层级相同,则越后面的元素会覆盖前面的元素,默认情况下,第二个元素就会盖住第一个元素。
fixed定位很简单,类似与absoulte,但是它的What is the use of CSS position property?就是浏览器窗口,相对来说简单很多。常见的应用比如固定导航,回到顶部。在这里不再赘述,大家可以查找相关资料。
relative定位的元素进行偏移后,不会脱离文档流,还有占据原本的空间。除此之外,我们还要注意一个细节:如果元素设置了margin为负值之后发生重叠的情况下,相对定位的元素会覆盖普通元素。我们看看下面的例子:
HTML代码
<div class="no-relative">
未相对定位的元素
</div>
<div class="minus-margin">
负margin元素
</div>CSS代码
div { background: #0094ff; width: 250px; height: 100px; }
.no-relative { background: #ff6a00; width: 200px; height: 100px; }
.relative { background: #ff6a00; width: 200px; height: 100px; position: relative; }
.minus-margin { margin-top: -30px; }效果图

What is the use of CSS position property?
默认情况下,两个元素都是正常的元素,设置了负的margin属性后,后面的元素会覆盖前面的元素,我们修改第一个元素的class为relative,可以看到效果如下: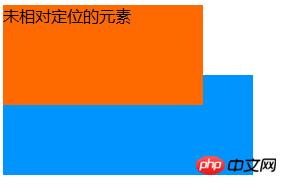
What is the use of CSS position property?
添加了相对定位后,第一个元素就会覆盖其他正常的元素了。
relative属性最经常的一个应用应该是作为absolute元素的What is the use of CSS position property?了,为了限制absolute元素的偏移位置,常常设置其父元素为relative来作为其What is the use of CSS position property?。
position的应用非常频繁,下面我来说说常见的一些场景:
在电商网站中,我们常常可以看到产品的左上角或右上角有一些比如“新品”,“促销”,“热卖”等标签,比如下图:
What is the use of CSS position property?
这个是怎么实现的呢,我们来模拟一下:
HTML代码:
<div class="product">
我是产品
<span class="hot">
热卖
</span>
</div>CSS代码:
.product { width: 150px; height: 150px; background: #0094ff; position: relative; }
.hot { position: absolute; right: 10px; top: 10px; width: 40px; height: 20px; background: #ff6a00; text-align: center; }效果如下:

What is the use of CSS position property?
如图所示,右上角有一个标签。原理很简单,就是设置父元素相对定位,标签元素绝对定位,然后相对于父元素偏移到右上角。
自动完成框是一个非常常见的应用,其生成的下拉菜单也是用到了position属性。我们先看看下面的效果:
What is the use of CSS position property?
这是一个很简单常见的下来自动完成框,我们来看看它的HTML和CSS代码:
HTML代码
<input class="search-box" type="text" placeholder="请输入关键字" value="position" />
<ul style="left:58px;">
<li>position属性</li>
<li>position应用</li>
<li>position是什么</li>
<li>position翻译</li>
</ul>CSS代码
.search-box { border: 1px solid #ccc; width: 200px; padding: 5px; height: 24px; margin-left: 50px; }
ul, li { list-style-type: none; }
ul { border: 1px solid #ccc; width: 210px; position: absolute; }
li { padding: 5px; }这个原理也很简单,通过设置下拉菜单为绝对定位,然后设置其left属性与输入框对齐。
当然position的应用还有很多,比如布局,比如fixed可以用来做固定导航菜单,网页右下角的固定菜单等,有兴趣的同学可以自行查找相关资料进行学习。
The position attribute is an attribute that can easily confuse beginners, especially the applications of absolute and relative. To make good use of them, you must first understand the basic characteristics of absolute and relative. After understanding their characteristics, they will be easy to apply. After understanding the basic principles, write a few examples to experience their characteristics in practice, and slowly You will become familiar with it.
The above is the detailed content of What is the use of CSS position property?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




