Introduction to String, StringBuffer and StringBulider
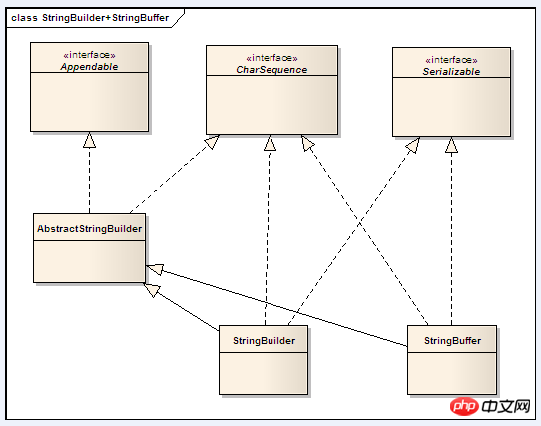
All three implement the CharSequence interface, so CharSequence can be considered as a string protocol interface
1. The String class is an immutable class, that is, once a String object is created, the content contained in this object The character sequence in is immutable until the object is destroyed;
When we often define String str=new String("defined me");
str="changed I";
The output has changed. It seems that Str has changed. In fact, the point of str has been changed. The original object in the heap memory has become garbage
2.StringBuffer class
StringBuffer represents a string with a variable character sequence. After a StringBuffer is created, the string can be changed through the insert(), append(), reverse(), serChaAt(), and setLength() methods. Finally, After generation, it can be converted into a String object through the toString() method
3. StringBuilder is new in JDK1.5 and also represents a string object. It is similar to StringBuffer. The constructors and methods of the two classes are also Basically the same, StringBuffer was thread-safe at that time, and StringBulider did not implement thread safety, so the performance was slightly higher. Therefore, if you create a string object with variable characters, you should give priority to the StringBuilder class
Comparison
1. The three have the following relationship in terms of execution speed:
StringBuilder>StringBuffer> String;
2.: First, the length is expandable; second, StringBuffer is thread-safe, and StringBuilder is thread-unsafe. So how are their lengths dynamically expanded and how is the thread safety of StringBuffer implemented?
All three implement the CharSequence interface, so CharSequence can be considered as a string protocol interface
All methods in StringBuffer except the construction method Limited by synchronized
The two extendable lengths are verified by ensureCapacity(int minimumCapacity) to verify whether the current length is less than the parameter minimumCapacity. If true, space is allocated. The step size for allocating new space is twice (current length + 1).

The above is the detailed content of Introduction to String, StringBuffer and StringBulider. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1376
1376
 52
52
 Convert basic data types to strings using Java's String.valueOf() function
Jul 24, 2023 pm 07:55 PM
Convert basic data types to strings using Java's String.valueOf() function
Jul 24, 2023 pm 07:55 PM
Convert basic data types to strings using Java's String.valueOf() function In Java development, when we need to convert basic data types to strings, a common method is to use the valueOf() function of the String class. This function can accept parameters of basic data types and return the corresponding string representation. In this article, we will explore how to use the String.valueOf() function for basic data type conversions and provide some code examples to
 How to convert char array to string
Jun 09, 2023 am 10:04 AM
How to convert char array to string
Jun 09, 2023 am 10:04 AM
Method of converting char array to string: It can be achieved by assignment. Use {char a[]=" abc d\0efg ";string s=a;} syntax to let the char array directly assign a value to string, and execute the code to complete the conversion.
 Use Java's String.replace() function to replace characters (strings) in a string
Jul 25, 2023 pm 05:16 PM
Use Java's String.replace() function to replace characters (strings) in a string
Jul 25, 2023 pm 05:16 PM
Replace characters (strings) in a string using Java's String.replace() function In Java, strings are immutable objects, which means that once a string object is created, its value cannot be modified. However, you may encounter situations where you need to replace certain characters or strings in a string. At this time, we can use the replace() method in Java's String class to implement string replacement. The replace() method of String class has two types:
 2w words detailed explanation String, yyds
Aug 24, 2023 pm 03:56 PM
2w words detailed explanation String, yyds
Aug 24, 2023 pm 03:56 PM
Hello everyone, today I will share with you the basic knowledge of Java: String. Needless to say the importance of the String class, it can be said to be the most used class in our back-end development, so it is necessary to talk about it.
 Use java's String.length() function to get the length of a string
Jul 25, 2023 am 09:09 AM
Use java's String.length() function to get the length of a string
Jul 25, 2023 am 09:09 AM
Use Java's String.length() function to get the length of a string. In Java programming, string is a very common data type. We often need to get the length of a string, that is, the number of characters in the string. In Java, we can use the length() function of the String class to get the length of a string. Here is a simple example code: publicclassStringLengthExample{publ
 Golang function byte, rune and string type conversion skills
May 17, 2023 am 08:21 AM
Golang function byte, rune and string type conversion skills
May 17, 2023 am 08:21 AM
In Golang programming, byte, rune and string types are very basic and common data types. They play an important role in processing data operations such as strings and file streams. When performing these data operations, we usually need to convert them to each other, which requires mastering some conversion skills. This article will introduce the byte, rune and string type conversion techniques of Golang functions, aiming to help readers better understand these data types and be able to apply them skillfully in programming practice.
 How to use java's String class
Apr 19, 2023 pm 01:19 PM
How to use java's String class
Apr 19, 2023 pm 01:19 PM
1. Understanding String1. String in JDK First, let’s take a look at the source code of the String class in the JDK. It implements many interfaces. You can see that the String class is modified by final. This means that the String class cannot be inherited and there is no subclass of String. class, so that all people using JDK use the same String class. If String is allowed to be inherited, everyone can extend String. Everyone uses different versions of String, and two different people Using the same method shows different results, which makes it impossible to develop the code. Inheritance and method overriding not only bring flexibility, but also cause many subclasses to behave differently.
 How to use the split method in Java String
May 02, 2023 am 09:37 AM
How to use the split method in Java String
May 02, 2023 am 09:37 AM
The split method in String uses the split() method of String to split the String according to the incoming characters or strings and return the split array. 1. General usage When using general characters, such as @ or, as separators: Stringaddress="Shanghai@Shanghai City@Minhang District@Wuzhong Road";String[]splitAddr=address.split("@");System .out.println(splitAddr[0]+splitAddr[1]+splitAddr[2]+splitAddr[3




