 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 Detailed explanation of the difference between stop() and :is(:animated) in jquery
Detailed explanation of the difference between stop() and :is(:animated) in jquery
Detailed explanation of the difference between stop() and :is(:animated) in jquery
stop(true,true):
means to stop the ongoing animation of the matching element and jump to the end state, clearing the unfinished animationqueue . Often used to "solve the problem of inconsistent animation effects and cursor movements caused by moving the cursor in and out too quickly"!
jQuery stop() method
jQuery stop() method is used to stop animations or effects before they are completed.
The stop() method works with all jQuery effects Functions, including slides, fades, and custom animations.
Syntax
$(selector).stop(stopAll,goToEnd);The optional stopAll parameter specifies whether the animation queue should be cleared. The default is false, which only stops active animations, allowing any queued animations to execute backwards.
The optional goToEnd parameter specifies whether to complete the current animation immediately. The default is false.
So, by default, stop() will clear the current animation specified on the selected element.
The following example demonstrates the stop() method without parameters:
1 2 3 |
|
:is(":animated") :animated is the jQ selector that selects all animated elements
Determine whether the element is in an animated state. It is often used when "continuously clicking the previous/next button and only responding to the user's first click action".
1 2 3 4 5 |
|
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of the difference between stop() and :is(:animated) in jquery. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
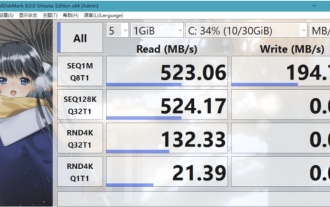 What software is crystaldiskmark? -How to use crystaldiskmark?
Mar 18, 2024 pm 02:58 PM
What software is crystaldiskmark? -How to use crystaldiskmark?
Mar 18, 2024 pm 02:58 PM
CrystalDiskMark is a small HDD benchmark tool for hard drives that quickly measures sequential and random read/write speeds. Next, let the editor introduce CrystalDiskMark to you and how to use crystaldiskmark~ 1. Introduction to CrystalDiskMark CrystalDiskMark is a widely used disk performance testing tool used to evaluate the read and write speed and performance of mechanical hard drives and solid-state drives (SSD). Random I/O performance. It is a free Windows application and provides a user-friendly interface and various test modes to evaluate different aspects of hard drive performance and is widely used in hardware reviews
 How to download foobar2000? -How to use foobar2000
Mar 18, 2024 am 10:58 AM
How to download foobar2000? -How to use foobar2000
Mar 18, 2024 am 10:58 AM
foobar2000 is a software that can listen to music resources at any time. It brings you all kinds of music with lossless sound quality. The enhanced version of the music player allows you to get a more comprehensive and comfortable music experience. Its design concept is to play the advanced audio on the computer The device is transplanted to mobile phones to provide a more convenient and efficient music playback experience. The interface design is simple, clear and easy to use. It adopts a minimalist design style without too many decorations and cumbersome operations to get started quickly. It also supports a variety of skins and Theme, personalize settings according to your own preferences, and create an exclusive music player that supports the playback of multiple audio formats. It also supports the audio gain function to adjust the volume according to your own hearing conditions to avoid hearing damage caused by excessive volume. Next, let me help you
 How to use NetEase Mailbox Master
Mar 27, 2024 pm 05:32 PM
How to use NetEase Mailbox Master
Mar 27, 2024 pm 05:32 PM
NetEase Mailbox, as an email address widely used by Chinese netizens, has always won the trust of users with its stable and efficient services. NetEase Mailbox Master is an email software specially created for mobile phone users. It greatly simplifies the process of sending and receiving emails and makes our email processing more convenient. So how to use NetEase Mailbox Master, and what specific functions it has. Below, the editor of this site will give you a detailed introduction, hoping to help you! First, you can search and download the NetEase Mailbox Master app in the mobile app store. Search for "NetEase Mailbox Master" in App Store or Baidu Mobile Assistant, and then follow the prompts to install it. After the download and installation is completed, we open the NetEase email account and log in. The login interface is as shown below
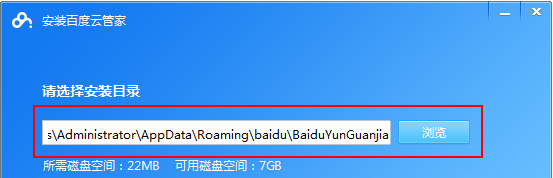 How to use Baidu Netdisk app
Mar 27, 2024 pm 06:46 PM
How to use Baidu Netdisk app
Mar 27, 2024 pm 06:46 PM
Cloud storage has become an indispensable part of our daily life and work nowadays. As one of the leading cloud storage services in China, Baidu Netdisk has won the favor of a large number of users with its powerful storage functions, efficient transmission speed and convenient operation experience. And whether you want to back up important files, share information, watch videos online, or listen to music, Baidu Cloud Disk can meet your needs. However, many users may not understand the specific use method of Baidu Netdisk app, so this tutorial will introduce in detail how to use Baidu Netdisk app. Users who are still confused can follow this article to learn more. ! How to use Baidu Cloud Network Disk: 1. Installation First, when downloading and installing Baidu Cloud software, please select the custom installation option.
 BTCC tutorial: How to bind and use MetaMask wallet on BTCC exchange?
Apr 26, 2024 am 09:40 AM
BTCC tutorial: How to bind and use MetaMask wallet on BTCC exchange?
Apr 26, 2024 am 09:40 AM
MetaMask (also called Little Fox Wallet in Chinese) is a free and well-received encryption wallet software. Currently, BTCC supports binding to the MetaMask wallet. After binding, you can use the MetaMask wallet to quickly log in, store value, buy coins, etc., and you can also get 20 USDT trial bonus for the first time binding. In the BTCCMetaMask wallet tutorial, we will introduce in detail how to register and use MetaMask, and how to bind and use the Little Fox wallet in BTCC. What is MetaMask wallet? With over 30 million users, MetaMask Little Fox Wallet is one of the most popular cryptocurrency wallets today. It is free to use and can be installed on the network as an extension
 Teach you how to use the new advanced features of iOS 17.4 'Stolen Device Protection'
Mar 10, 2024 pm 04:34 PM
Teach you how to use the new advanced features of iOS 17.4 'Stolen Device Protection'
Mar 10, 2024 pm 04:34 PM
Apple rolled out the iOS 17.4 update on Tuesday, bringing a slew of new features and fixes to iPhones. The update includes new emojis, and EU users will also be able to download them from other app stores. In addition, the update also strengthens the control of iPhone security and introduces more "Stolen Device Protection" setting options to provide users with more choices and protection. "iOS17.3 introduces the "Stolen Device Protection" function for the first time, adding extra security to users' sensitive information. When the user is away from home and other familiar places, this function requires the user to enter biometric information for the first time, and after one hour You must enter information again to access and change certain data, such as changing your Apple ID password or turning off stolen device protection.
 How to use Xiaomi Auto app
Apr 01, 2024 pm 09:19 PM
How to use Xiaomi Auto app
Apr 01, 2024 pm 09:19 PM
Xiaomi car software provides remote car control functions, allowing users to remotely control the vehicle through mobile phones or computers, such as opening and closing the vehicle's doors and windows, starting the engine, controlling the vehicle's air conditioner and audio, etc. The following is the use and content of this software, let's learn about it together . Comprehensive list of Xiaomi Auto app functions and usage methods 1. The Xiaomi Auto app was launched on the Apple AppStore on March 25, and can now be downloaded from the app store on Android phones; Car purchase: Learn about the core highlights and technical parameters of Xiaomi Auto, and make an appointment for a test drive. Configure and order your Xiaomi car, and support online processing of car pickup to-do items. 3. Community: Understand Xiaomi Auto brand information, exchange car experience, and share wonderful car life; 4. Car control: The mobile phone is the remote control, remote control, real-time security, easy
 What is chirp down? -How to use chirp down
Mar 18, 2024 am 11:46 AM
What is chirp down? -How to use chirp down
Mar 18, 2024 am 11:46 AM
Chirp Down can also be called JJDown. This is a video download tool specially created for Bilibili. However, many friends do not understand this software. Today, let the editor explain to you what Chirp Down is? How to use chirp down. 1. The origin of Chirpdown Chirpdown originated in 2014. It is a very old video downloading software. The interface adopts Win10 tile style, which is simple, beautiful and easy to operate. Chirna is the poster girl of Chirpdown, and the artist is あさひクロイ. Jijidown has always been committed to providing users with the best download experience, constantly updating and optimizing the software, solving various problems and bugs, and adding new functions and features. The function of Chirp Down Chirp Down is



