The difference between jquery $(document).ready() and window.onload
The function of $(
document).ready() in Jquery is similar to the window.onload method in traditional JavaScript, but it is different from the window.onload method There is still a difference.
1. Execution time
Window.onload must wait until all the elements included in the page are loaded before it can be executed.
$(document).ready() is executed after the DOM structure is drawn, without waiting until it is loaded.
2. The difference in writing is different. (document) .Ready () can be written at the same time, and all can be executed
3. Simplified writing
## Window.Onload. (document).ready(function(){}) can be abbreviated as $(function(){});
In my previous development, I generally used javascript, and I always used jquery mode. That is to say, most of the time, the first line is:
The code is as follows:
$(document).ready(function(){
}) ;
At this time, you don’t have to wait for all js and images to be loaded before you can execute some methods. However, sometimes, you must wait for all
elements to be loaded. , only when some methods can be executed, for example, some pictures or other aspects have not been loaded. At this time, clicking some buttons will cause unexpected situations. At this time, you need to use Go to:
The code is as follows:
$(window).load(function() {
$("#btn-upload").click(function(){ //For example Say:uploadPhotos();
});});
The following is the reproduced content,use $(window).load(function() {...}) instead of body.onload() for several reasons
First of all, they are all images in all elements of the page (including
html tags
and
references
, Flash and other media) are executed after loading, this is what they have in common.
Reason 1 for not using body.Onload():
If we want to load multiple functions at the same time, we must Writing like this looks extremely ugly. If we use $(window).load() we can load multiple ones like this FunctionThe code is as follows:
$(window).load(function() {
alert("hello, I am jQuery!");});
$(window).load(function() {alert("hello, I am also jQuery");
});Written like this it will be executed from top to bottom These two functions look much more beautiful.
Reason 2 for not using body.Onload():
Using body.Onload() cannot completely separate js and html. This It is a very serious problem.
In addition, using $(window).load(function(){...}) and body.onload() has the same problem, because as mentioned at the beginning, they You need to wait until all the content of the page
is loaded before executing. However, if the network speed is relatively slow, it often takes a long time to load a page (ranging from a few seconds to more than ten seconds, or even longer). ...), so we often
encounter the situation that the page has not been completely loaded but the user is already operating the page, so the effect displayed by the page is different from what we expected.
So here I recommend using $(document).ready(function(){}), or abbreviated as $(function(){}), because it will be loaded after the dom element of the page is loaded. Execute,
without waiting for pictures or other media to be downloaded.
But sometimes we do need to wait until everything on the page is loaded before executing the function we want to execute, so it is Whether to use $(window).load(function(){...}) or
Whether to use $(function(){}) often requires different choices based on specific needs.
Finally, attach a piece of jQuery code that is executed before all DOM elements are loaded.
The code is as follows:
Haha, sometimes we also have this need!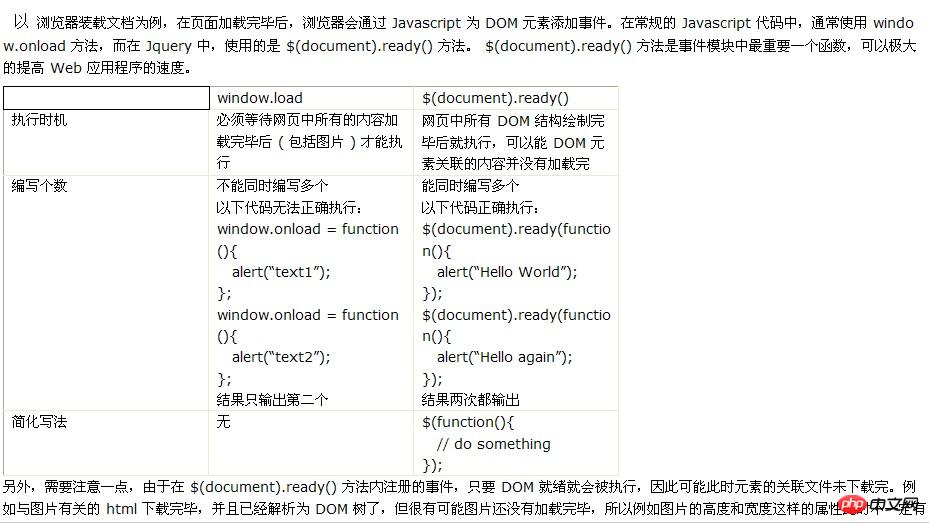 Take the browser loading a document as an example. After the page is loaded, the browser will add event to the DOM element through Javascript. In regular Javascript code, the window.onload method is usually used, while in Jquery, the $(document).ready() method is used. The $(document).ready() method is the most important function in the event module, which can greatly improve the speed of web applications.
Take the browser loading a document as an example. After the page is loaded, the browser will add event to the DOM element through Javascript. In regular Javascript code, the window.onload method is usually used, while in Jquery, the $(document).ready() method is used. The $(document).ready() method is the most important function in the event module, which can greatly improve the speed of web applications.
window.load $(document).ready()
Execution timing You must wait for all content in the webpage to be loaded (including pictures) before executing it. Execute after all DOM structures in the webpage are drawn. You can The content associated with the DOM element has not been loaded.
The number of writes cannot be written multiple times at the same time.
The following code cannot be executed correctly:
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
|
The result is only the second one. Multiple writing can be done at the same time.
The following code is executed correctly:
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
|
The result is output twice
Simplified writing method None
1 2 3 |
|
In addition, you need to pay attention to one thing, because it is registered in the $(document).ready() method The event will be executed as soon as the DOM is ready, so the associated file of the element may not be downloaded at this time. For example, the html related to the image has been downloaded and parsed into a DOM tree, but it is very likely that the image has not been loaded yet, so attributes such as the height and width of the image may not be valid at this time. To solve this problem, you can use another page loading method in Jquery --- the load() method. The Load() method binds a handler function to the element's onload event. If the handler function is bound to the window object, it will be triggered after all content (including windows, frames, objects, images, etc.) is loaded. If the handler function is bound to an element, it will be triggered after the content of the element is loaded.
Jquery code is as follows:
$(window).load(function (){
// Write code
}); Equivalent to the following code in JavaScript
Window.onload = function (){
// Write code
}
------------------------------
When I recently changed a page embedded in a frame, I used jquery for effect, and the page itself was also bound to the onload event. After the modification, the test runs normally and smoothly under Firefox, but it takes more than ten seconds for the jquery effect to appear under IE, and the day lily is cold.
At first I thought it was conflicting with my own onload loading method. A common saying on the Internet is that $(document).ready() is executed after the page DOM parsing is completed, and the onload event is executed after all resources are prepared. In other words, $(document).ready() is executed after the DOM parsing of the page is completed. Executed before onload, especially when the page pictures are larger and more, the time difference may be larger. But on my page, the picture has been displayed for more than ten seconds, but the jquery effect has not yet appeared.
Try deleting the onload loading method, but the result is still the same. It seems that there is no need to use $(document).ready() to write the original onload event binding. So what is the reason why Firefox works but IE does? Then debugging, I found that the originally bound onload method under IE was executed before the content of $(document).ready(), while Firefox executed the content of $(document).ready() first, and then executed the original onload method. . This doesn’t seem to be completely consistent with what’s said online. Haha, it’s interesting. It seems to be getting closer to the truth.
Look through the source code of jquery to see how $(document).ready() is implemented
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
|
The result is very clear. IE only works when the page is not embedded in a frame. Like Firefox, etc., the content of $(document).ready() is executed first, and then the original onload method is executed. For the page embedded in the frame, it is only bound to the load event for execution, so naturally it is the turn after the original onload binding method is executed. And this page happens to have a resource that is inaccessible in the test environment, and the delay of more than ten seconds is exactly the time difference it amplifies.
The above is the detailed content of The difference between jquery $(document).ready() and window.onload. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1376
1376
 52
52
 The difference between multithreading and asynchronous c#
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:57 PM
The difference between multithreading and asynchronous c#
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:57 PM
The difference between multithreading and asynchronous is that multithreading executes multiple threads at the same time, while asynchronously performs operations without blocking the current thread. Multithreading is used for compute-intensive tasks, while asynchronously is used for user interaction. The advantage of multi-threading is to improve computing performance, while the advantage of asynchronous is to not block UI threads. Choosing multithreading or asynchronous depends on the nature of the task: Computation-intensive tasks use multithreading, tasks that interact with external resources and need to keep UI responsiveness use asynchronous.
 What is the function of C language sum?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
What is the function of C language sum?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
There is no built-in sum function in C language, so it needs to be written by yourself. Sum can be achieved by traversing the array and accumulating elements: Loop version: Sum is calculated using for loop and array length. Pointer version: Use pointers to point to array elements, and efficient summing is achieved through self-increment pointers. Dynamically allocate array version: Dynamically allocate arrays and manage memory yourself, ensuring that allocated memory is freed to prevent memory leaks.
 The difference between char and wchar_t in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
The difference between char and wchar_t in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
In C language, the main difference between char and wchar_t is character encoding: char uses ASCII or extends ASCII, wchar_t uses Unicode; char takes up 1-2 bytes, wchar_t takes up 2-4 bytes; char is suitable for English text, wchar_t is suitable for multilingual text; char is widely supported, wchar_t depends on whether the compiler and operating system support Unicode; char is limited in character range, wchar_t has a larger character range, and special functions are used for arithmetic operations.
 Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
An application that converts XML directly to PDF cannot be found because they are two fundamentally different formats. XML is used to store data, while PDF is used to display documents. To complete the transformation, you can use programming languages and libraries such as Python and ReportLab to parse XML data and generate PDF documents.
 What are the basic requirements for c language functions
Apr 03, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
What are the basic requirements for c language functions
Apr 03, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
C language functions are the basis for code modularization and program building. They consist of declarations (function headers) and definitions (function bodies). C language uses values to pass parameters by default, but external variables can also be modified using address pass. Functions can have or have no return value, and the return value type must be consistent with the declaration. Function naming should be clear and easy to understand, using camel or underscore nomenclature. Follow the single responsibility principle and keep the function simplicity to improve maintainability and readability.
 What is the difference between `var` and `type` keyword definition structure in Go language?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
What is the difference between `var` and `type` keyword definition structure in Go language?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
Two ways to define structures in Go language: the difference between var and type keywords. When defining structures, Go language often sees two different ways of writing: First...
 How to use XPath to search from a specified DOM node in JavaScript?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 11:15 PM
How to use XPath to search from a specified DOM node in JavaScript?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 11:15 PM
Detailed explanation of XPath search method under DOM nodes In JavaScript, we often need to find specific nodes from the DOM tree based on XPath expressions. If you need to...
 The difference between Ether and Bitcoin What is the difference between Ether and Bitcoin
Mar 19, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
The difference between Ether and Bitcoin What is the difference between Ether and Bitcoin
Mar 19, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
The difference between Ethereum and Bitcoin is significant. Technically, Bitcoin uses PoW, and Ether has shifted from PoW to PoS. Trading speed is slow for Bitcoin and Ethereum is fast. In application scenarios, Bitcoin focuses on payment storage, while Ether supports smart contracts and DApps. In terms of issuance, the total amount of Bitcoin is 21 million, and there is no fixed total amount of Ether coins. Each security challenge is available. In terms of market value, Bitcoin ranks first, and the price fluctuations of both are large, but due to different characteristics, the price trend of Ethereum is unique.




