Java--Generics
Type parameters
Use when defining a generic class or declaring a variable of a generic class Angle brackets to specify formal type parameters. The relationship between formal type parameters and actual type parameters is similar to the relationship between formal method parameters and actual method parameters, except that type parameters represent types rather than values.
Named type parameters
The recommended naming convention is to use uppercase, single-letter names for type parameters. This differs from the C++ convention (see Appendix A: Comparison with C++ templates), and reflects the assumption that most generic classes will have a small number of type parameters. For common generic patterns, the recommended name is:
K - key, such as a mapped key.
V —— Value, such as the contents of List and Set, or the value in Map.
E ——Exception class.
T —— Generic.
方法签名由方法名称和一个参数列表(方法的参数的顺序和类型)组成。
##1. Why use generics
1. There is no limit to the elements that can be put in. Putting in two different objects may cause exceptions.
2. Throw the object into the collection. The collection loses the state information of the object. The collection only knows that it holds Object, so after taking out the collection elements, it usually Force conversion is also required
2. What are generics
Java's parameterized types are called generics, which allow the program to specify the type of collection elements when creating a collection
3. Generic diamond Syntax

4. Create a custom class with a generic declaration. When defining a constructor for the class, the constructor name should still be the original class name. Do not add a generic declaration.
5. Derive a subclass from a generic class. When inheriting, you must pass in the actual parameters for the parent class
public class A extends Apple
##All methods in it that override the parent class become the corresponding type
You can also pass in no actual parameters
##public class A extends Apple{}Treat as Object type
6. There is no generic class
No matter what the actual type parameters of generics are, they always have the same class at runtime. No matter which type of actual parameter is passed into the generic type parameter, ( lies in the purpose of the concept of generics in Java, which causes it to only act in the code compilation phase. During the compilation process, After the generic result is correctly verified, the generic related information will be erased. That is to say, the successfully compiled class file does not contain any generic information and will not enter the runtime phase##. #.) For Java, they are still treated as the same class and occupy a memory space in the memory. Therefore, types are not allowed to be used in the declaration and initialization of static methods, static initialization blocks or static variables. Formal parameters
Explanation: Static variables are shared by all instances of a generic class. For a class declared as MyClass MyClass MyClass class1.myStaticVar = "hello"; class2.myStaticVar = 5; Due to the type erasure of the generic system Except (type erasure). myStaticVar is restored to the Object type, and then when class1.myStaticVar= "hello"; is called, the compiler performs forced type conversion, that is, myStaticVar = (String)"hello"; and then when the class2.myStaticVar statement is called, the compiler continues to perform forced type conversion. , myStaticVar = (Integer)Integer.valueOf(5); At this time, myStaticVar is of type String. Of course, this statement will throw a ClassCastException at runtime, so there is a type safety issue. Therefore, the generic system does not allow static variables of a class to use type parameters as variable types.
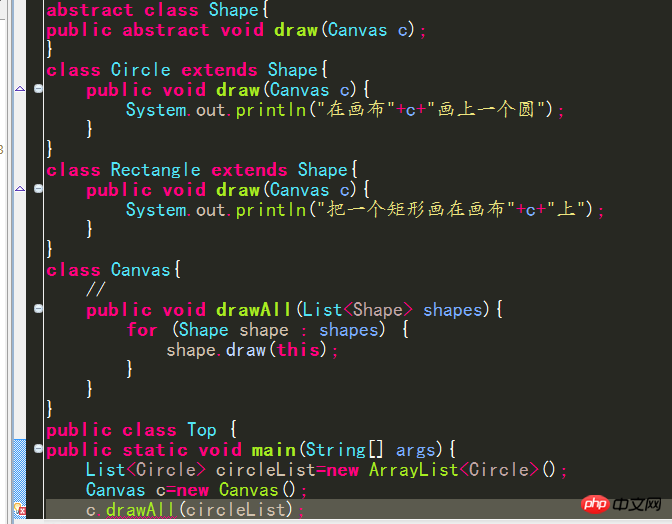
# Generic classes will not actually be generated in the system, so the generic class cannot be used after the instanceod operator because it does not exist at all! 7. Type wildcard Note that, If Foo is a subtype of Bar and G is a class or interface with a generic declaration, G ##Assuming that List 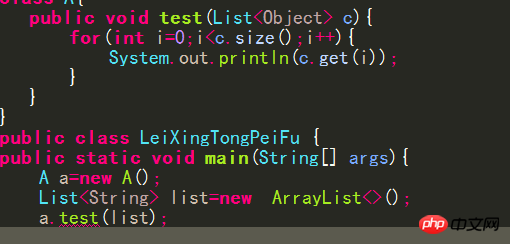 In order to represent the parent class of various generic collections, you can use type wildcards. The type wildcard is a Question mark, it can match any type:
In order to represent the parent class of various generic collections, you can use type wildcards. The type wildcard is a Question mark, it can match any type:
No matter what the real type of the list is, it contains Object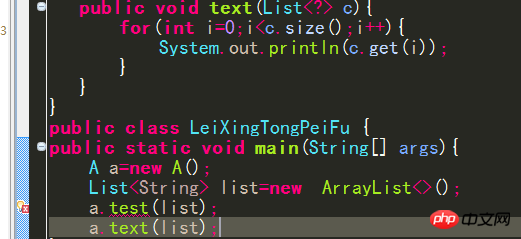

We do not know the type of elements in the c collection and cannot add objects to it
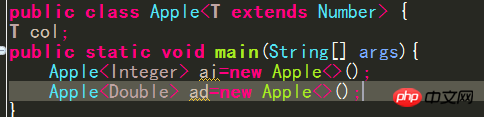
7.1 Set the upper limit of wildcards
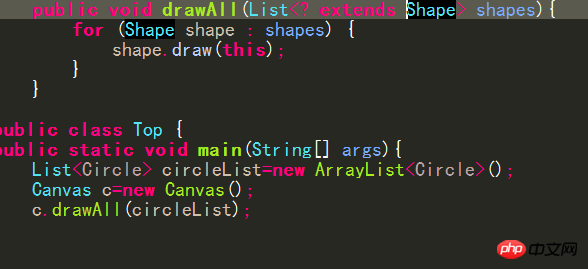
7.2 Setting upper limits on type parameters
8. Generic method
define class, The interface does not use type parameters. When defining the method, I want to define
independent generic static method at the same time without considering multi-threading. point, it will only be initialized and called once, there will be no overlapping initialization and incorrect calls, and there will be no situation like reading dirty data in the database, so there will be no code errors in forced type conversion.
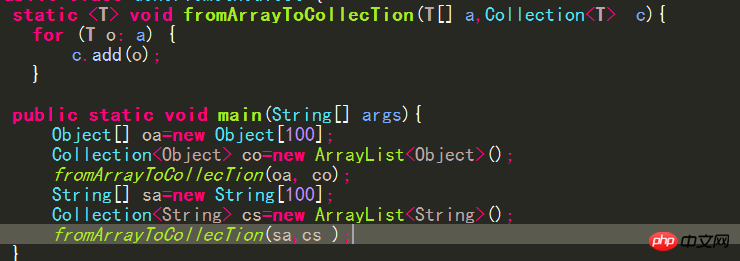
Generic method
(in type parameter one section) You have seen that you can make a class generic by adding a list of formal type parameters to its definition. Methods can also be genericized, regardless of whether the class in which they are defined is generic or not.
# Generic classes enforce type constraints across multiple method signatures. In List
#Similarly, you declare a generic method generally because you want to declare a type constraint between multiple parameters of the method. For example, the ifThenElse() method in the following code will return either the second or third argument, depending on the Boolean value of its first argument:
public
return b ? first : second;
}
Note that you can call ifThenElse() without explicitly telling the compiler what you want for T value. The compiler doesn't have to be told explicitly what values T will have; it just knows that the values must all be the same. The compiler allows you to call the following code because the compiler can use type inference to deduce that the String substituted for T satisfies all type constraints:
##String s = ifThenElse(b, "a", "b");
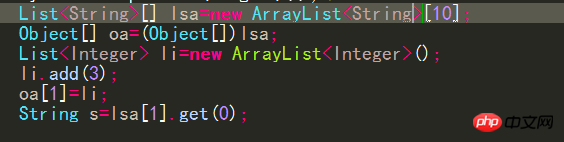
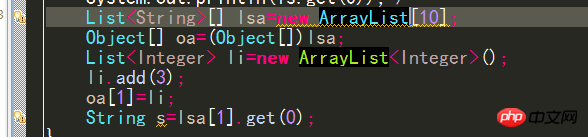
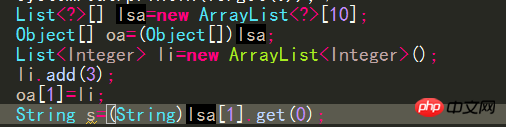
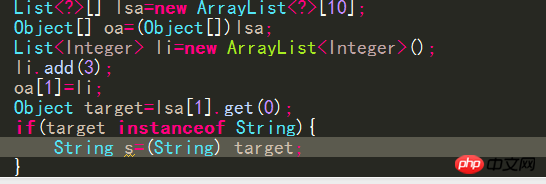
##Similarly, you can call:Integer i = ifThenElse(b, new Integer(1), new Integer(2)); However, compile The following code is not allowed by the compiler because no type would satisfy the required type constraints: ##String s = ifThenElse(b, "pi", new Float( 3.14)); Why did you choose to use a generic method instead of adding type T to the class definition? There are (at least) two cases where this should be done: #When a generic method is static, class type parameters cannot be used in this case. When a type constraint on T is truly local to a method, it means that there is no use of the same type T in another method signature of the same class constraint. The signature of a closed type can be simplified by making the type parameters of a generic method local to the method. Generic methods in the previous screen In the example, the type parameter V is an unconstrained or unrestricted type. Sometimes it is necessary to specify additional constraints on type parameters when the type parameters have not been fully specified. Consider the example Matrix class, which uses a type parameter V, which is bounded by the Number class: public class Matrix The compiler allows you to create Matrix 9. The difference between generic methods and type wildcards If a method If the type of formal parameter (a) or the type of the return value depends on the type of another formal parameter (b), then the type declaration of formal parameter (b) should not use wildcards, and only the type parameter can be considered to be declared in the method signature. , that is, a generic method. What I understand is that the type wildcard does not need to add or modify the elements in the collection, and it is attached to others rather than others attached to him. Use Type wildcards can be used to define the type of formal parameters in method signatures or to define the types of variables. Type parameters in generic methods must be explicitly declared in the corresponding method. 10. Wiping and conversion When assigning an object with generic information to another When adding a variable without generic information, all type information between angle brackets is thrown away. ##When assigning li to List, the compiler will Erase the former's generic information, that is, lose the type information of the elements in the list collection. Java also allows the list object to be directly assigned to a List "unchecked conversion" is issued (the logical parent class directly assigned to the subclass), but the list variable actually refers to the list 11. Generics and arrays Java generics have a very important design principle---if a piece of code does not raise an "unconverted exception" warning when compiling, the program will not cause a ClassCastException exception. For this reason, The type of all array elements cannot contain type variables or type parameters, unless it is an unlimited type wildcard, but the element type can be declared to contain an array of type variables or type parameters Assuming it can pass, no warning will be caused, but an exception will be thrown Change Into the following format: The first line will have an "unchecked conversion" warning, and the last line will also throw an exception Create unlimited wildcards Generic array #Compilation will not issue any warnings, but an exception will be thrown at runtime because the program needs to force the first collection element of the first array element of lsa Convert to String type, so the program should use the instanceof operator to ensure its data type Similarly, creating an array object whose element type is a type variable will also cause compilation Error { return new T[cool.size()] } The type variable does not exist at runtime and the compiler cannot determine what the actual type is
Restricted types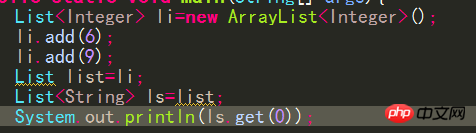

The above is the detailed content of Java--Generics. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1385
1385
 52
52
 Do generic functions solve the problem of variadic parameter types in Golang?
Apr 16, 2024 pm 06:12 PM
Do generic functions solve the problem of variadic parameter types in Golang?
Apr 16, 2024 pm 06:12 PM
Generic functions in Go solve the problem of variadic types: generic functions allow type parameters to be specified at runtime. This makes it possible to write functions that can handle parameters of different types. For example, the Max function is a generic function that accepts two comparable parameters and returns the larger value. By using generic functions, we can write more flexible and general code that can handle different types of parameters.
 Specific application scenarios of generics in golang
May 04, 2024 am 11:45 AM
Specific application scenarios of generics in golang
May 04, 2024 am 11:45 AM
Application scenarios of generics in Go: Collection operations: Create collection operations suitable for any type, such as filtering. Data Structures: Write general-purpose data structures such as queues, stacks, and maps to store and manipulate various types of data. Algorithms: Write general-purpose algorithms such as sorting, search, and reduction that can handle different types of data.
 What are the upper and lower bounds of Java function generics? how to use?
Apr 26, 2024 am 11:45 AM
What are the upper and lower bounds of Java function generics? how to use?
Apr 26, 2024 am 11:45 AM
Java function generics allow setting upper and lower bounds. Extends specifies that the data type accepted or returned by a function must be a subtype of the specified type, e.g. The lower bound (super) specifies that the data type accepted or returned by a function must be a supertype of the specified type, e.g. The use of generics improves code reusability and security.
 Explore the advantages and uses of generics in Golang
Apr 03, 2024 pm 02:03 PM
Explore the advantages and uses of generics in Golang
Apr 03, 2024 pm 02:03 PM
Answer: Golang generics are a powerful tool for improving code reusability, flexibility, type safety, and scalability. Detailed description: Advantages: Code reusability: Common algorithms and data structures Flexibility: Runtime creation of instances of specific types Type safety: Compile time type checking Extensibility: Easy to extend and customize Purpose: Common functions: sorting, comparison Common data structures such as lists, maps, stacks, etc. Type aliases: simplify type declarations Constrained generics: ensure type safety
 What is the impact of Golang generics on function signatures and parameters?
Apr 17, 2024 am 08:39 AM
What is the impact of Golang generics on function signatures and parameters?
Apr 17, 2024 am 08:39 AM
The impact of generics on Go function signatures and parameters includes: Type parameters: Function signatures can contain type parameters, specifying the types that the function can use. Type constraints: Type parameters can have constraints that specify conditions that they must satisfy. Parameter type inference: The compiler can infer the type of unspecified type parameters. Specifying types: Parameter types can be explicitly specified to call generic functions. This increases code reusability and flexibility, allowing you to write functions and types that can be used with multiple types.
 Application of Java generics in Android development
Apr 12, 2024 pm 01:54 PM
Application of Java generics in Android development
Apr 12, 2024 pm 01:54 PM
The application of generics in Android development enhances code reusability, security and flexibility. The syntax consists of declaring a type variable T that can be used to manipulate type-parameterized data. Generics in action include custom data adapters, allowing the adapter to adapt to any type of custom data object. Android also provides generic list classes (such as ArrayList) and generic methods that allow the manipulation of parameters of different types. The benefits of using generics include code reusability, security, and flexibility, but care needs to be taken to specify the correct bounds and use them in moderation to ensure code readability.
 What are the limitations of generic functions in Golang?
Apr 16, 2024 pm 05:12 PM
What are the limitations of generic functions in Golang?
Apr 16, 2024 pm 05:12 PM
Limitations of Go generic functions: only type parameters are supported, value parameters are not supported. Function recursion is not supported. Type parameters cannot be specified explicitly, they are inferred by the compiler.
 How do Java enum types work with generics?
May 04, 2024 am 08:36 AM
How do Java enum types work with generics?
May 04, 2024 am 08:36 AM
The combination of enumeration types and generics in Java: When declaring an enumeration with generics, you need to add angle brackets, and T is the type parameter. When creating a generic class, you also need to add angle brackets, T is a type parameter that can store any type. This combination improves code flexibility, type safety, and simplifies code.




