
Cookie, sometimes also used in its plural form Cookies, refers to the data that some websites store on the user’s local terminal in order to identify the user’s identity and perform session tracking( usually encrypted).
The server can use the arbitrariness of the information contained in Cookies to filter and regularly maintain this information to determine the status of HTTP transmission.
The most typical application of Cookies is to determine whether a registered user has logged in to the website. The user may be prompted whether to retain user information the next time he enters this website to simplify the login procedure. These are Functions of Cookies.
Another important application occasion is "shopping cart" processing. Users may choose different products on different pages of the same website within a period of time, and this information will be written to Cookies so that the information can be retrieved when making the final payment.
1 #获取普通Cookie2 request.COOKIES['key']3 4 #获取签名Cookie5 request.get_signed_cookie(key, default=RAISE_ERROR, salt='', max_age=None)6 参数:7 default: 默认值8 salt: 加密盐9 max_age: 后台控制过期时间
#先获取views函数的返回对象rep = HttpResponse(...) 或 rep = render(request, ...) #设置普通Cookie,键值对rep.set_cookie(key,value,...)#设置签名Cookierep.set_signed_cookie(key,value,salt='加密盐',...) 参数: key, 键 value='', 值 max_age=None, 超时时间 expires=None, 超时时间(IE requires expires, so set it if hasn't been already.)path='/', Cookie生效的路径,/ 表示根路径,特殊的:跟路径的cookie可以被任何url的页面访问 domain=None, Cookie生效的域名 secure=False, https传输 httponly=False 只能http协议传输,无法被JavaScript获取(不是绝对,底层抓包可以获取到也可以被覆盖)
Since cookies are stored on the client's computer, JavaScript and jquery can also operate cookies.
<script src='/static/js/jquery.cookie.js'></script>
$.cookie("list_pager_num", 30,{ path: '/' });
 ##
## 1 from django.shortcuts import render, HttpResponse, redirect 2 3 4 #Cookie登陆验证装饰器 5 def auth(func): 6 def wrapper(request): 7 tk = request.COOKIES.get('login_keys') # 根据键获取cookies 8 if not tk: # 若cookie不存在,跳转至登陆页面 9 return redirect('/login.html/')10 else:11 return func(request) # 否则,执行当前url12 return wrapper13 14 15 16 #登陆验证,登陆成功则返回客户端Cookie17 def login(request):18 if request.method == 'GET':19 return render(request, 'login.html')20 else:21 user_name = request.POST.get('user') # 获取用户名22 user_pwd = request.POST.get('pwd') # 获取用户密码23 if user_name == 'jack' and user_pwd == '123': # 若用户名和密码匹配24 obj_cookie = HttpResponse('登陆成功!')25 obj_cookie.set_cookie('login_keys', '123456', max_age=3600) # 设置Cookie,有效期1小时26 return obj_cookie27 else:28 return HttpResponse('密码错误')29 30 31 @auth
32 def index(request):33 return HttpResponse('welcome to index')Different from Cookie, Session is session data saved on the server side.
In computers, especially in network applications, it is called "session control".The Session object stores the properties and configuration information required for a specific user session. In this way, when the user jumps between the application's Web pages, the variables stored in the Session object will not be lost, but will persist throughout the user session. When a user requests a Web page from an application, the Web server automatically creates a Session object if the user does not already have a session. When a session expires or is abandoned, the server terminates the session. One of the most common uses of the Session object is to store user preferences. For example, if the user indicates that they do not like to view graphics, this information can be stored in the Session object.
Django supports Session by default, and it provides 5 types of Session internally for developers to use:


1 Django默认支持Session,并且默认是将Session数据存储在数据库中,即:django_session 表中。 2 3 a. 配置 settings.py 4 5 SESSION_ENGINE = 'django.contrib.sessions.backends.db' # 引擎(默认) 6 7 SESSION_COOKIE_NAME = "sessionid" # Session的cookie保存在浏览器上时的key,即:sessionid=随机字符串(默认) 8 SESSION_COOKIE_PATH = "/" # Session的cookie保存的路径(默认) 9 SESSION_COOKIE_DOMAIN = None # Session的cookie保存的域名(默认)10 SESSION_COOKIE_SECURE = False # 是否Https传输cookie(默认)11 SESSION_COOKIE_HTTPONLY = True # 是否Session的cookie只支持http传输(默认)12 SESSION_COOKIE_AGE = 1209600 # Session的cookie失效日期(2周)(默认)13 SESSION_EXPIRE_AT_BROWSER_CLOSE = False # 是否关闭浏览器使得Session过期(默认)14 SESSION_SAVE_EVERY_REQUEST = False # 是否每次请求都保存Session,默认修改之后才保存(默认)15 16 17 18 b. 使用19 20 def index(request):21 # 获取、设置、删除Session中数据22 request.session['k1']23 request.session.get('k1',None)24 request.session['k1'] = 12325 request.session.setdefault('k1',123) # 存在则不设置26 del request.session['k1']27 28 # 所有 键、值、键值对29 request.session.keys()30 request.session.values()31 request.session.items()32 request.session.iterkeys()33 request.session.itervalues()34 request.session.iteritems()35 36 37 # 用户session的随机字符串38 request.session.session_key39 40 # 将所有Session失效日期小于当前日期的数据删除41 request.session.clear_expired()42 43 # 检查 用户session的随机字符串 在数据库中是否44 request.session.exists("session_key")45 46 # 删除当前用户的所有Session数据47 request.session.delete("session_key")48 49 request.session.set_expiry(value)50 * 如果value是个整数,session会在些秒数后失效。51 * 如果value是个datatime或timedelta,session就会在这个时间后失效。52 * 如果value是0,用户关闭浏览器session就会失效。53 * 如果value是None,session会依赖全局session失效策略。 ##
##1 a. 配置 settings.py 2 3 SESSION_ENGINE = 'django.contrib.sessions.backends.cache' # 引擎 4 SESSION_CACHE_ALIAS = 'default' # 使用的缓存别名(默认内存缓存,也可以是memcache),此处别名依赖缓存的设置 5 6 7 SESSION_COOKIE_NAME = "sessionid" # Session的cookie保存在浏览器上时的key,即:sessionid=随机字符串 8 SESSION_COOKIE_PATH = "/" # Session的cookie保存的路径 9 SESSION_COOKIE_DOMAIN = None # Session的cookie保存的域名10 SESSION_COOKIE_SECURE = False # 是否Https传输cookie11 SESSION_COOKIE_HTTPONLY = True # 是否Session的cookie只支持http传输12 SESSION_COOKIE_AGE = 1209600 # Session的cookie失效日期(2周)13 SESSION_EXPIRE_AT_BROWSER_CLOSE = False # 是否关闭浏览器使得Session过期14 SESSION_SAVE_EVERY_REQUEST = False # 是否每次请求都保存Session,默认修改之后才保存15 16 17 18 b. 使用19 20 同上

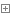
1 a. 配置 settings.py 2 3 SESSION_ENGINE = 'django.contrib.sessions.backends.file' # 引擎 4 SESSION_FILE_PATH = None # 缓存文件路径,如果为None,则使用tempfile模块获取一个临时地址tempfile.gettempdir() # 如:/var/folders/d3/j9tj0gz93dg06bmwxmhh6_xm0000gn/T 5 6 7 SESSION_COOKIE_NAME = "sessionid" # Session的cookie保存在浏览器上时的key,即:sessionid=随机字符串 8 SESSION_COOKIE_PATH = "/" # Session的cookie保存的路径 9 SESSION_COOKIE_DOMAIN = None # Session的cookie保存的域名10 SESSION_COOKIE_SECURE = False # 是否Https传输cookie11 SESSION_COOKIE_HTTPONLY = True # 是否Session的cookie只支持http传输12 SESSION_COOKIE_AGE = 1209600 # Session的cookie失效日期(2周)13 SESSION_EXPIRE_AT_BROWSER_CLOSE = False # 是否关闭浏览器使得Session过期14 SESSION_SAVE_EVERY_REQUEST = False # 是否每次请求都保存Session,默认修改之后才保存15 16 b. 使用17 18 同上


1 数据库用于做持久化,缓存用于提高效率2 3 a. 配置 settings.py4 5 SESSION_ENGINE = 'django.contrib.sessions.backends.cached_db' # 引擎6 7 b. 使用8 9 同上
 缓存提高效率,数据库保持持久
缓存提高效率,数据库保持持久
a. 配置 settings.py SESSION_ENGINE = 'django.contrib.sessions.backends.signed_cookies' # 引擎 b. 使用 同上


1 from django.shortcuts import render, HttpResponse, redirect 2 3 4 #Session登陆验证装饰器 5 def auth(func): 6 def wrapper(request): 7 tk = request.session.get('user') # 根据键获取session 8 if not tk: # 若session不存在,跳转至登陆页面 9 return redirect('/login.html/')10 else:11 return func(request) # 否则,执行当前url12 return wrapper13 14 15 16 #登陆验证17 def login(request):18 if request.method == 'GET':19 return render(request, 'login.html')20 else:21 user_name = request.POST.get('user') # 获取用户名22 user_pwd = request.POST.get('pwd') # 获取用户密码23 if user_name == 'jack' and user_pwd == '123': # 若用户名和密码匹配24 request.session['user'] = user_name # 写当前用户至session中25 request.session.set_expiry(3600) # 设置session,有效期1小时26 return redirect('/index.html/')27 else:28 return HttpResponse('密码错误')29 30 31 @auth32 def index(request):33 return HttpResponse('welcome to index')The above is the detailed content of Examples of Cookies and Sessions. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




