Detailed explanation of Future pattern in java
The following editor will bring you a cliché about the Future mode in Java. The editor thinks it’s pretty good, so I’ll share it with you now and give it as a reference. Let’s follow the editor and take a look.
##jdk1.7.0_79
This article is actually a continuation or supplement to the above "Briefly talk about the submit method of ThreadPoolExecutor thread pool". FutureTask appeared in the submit method mentioned above, which forced me to stop and turn to Java's Future mode.
Future is aExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(); Future<String> future = executor.submit(callable); //主线程需要callable线程的结果,先拿到一个未来的Future System.out.println(future.get()); //有了结果后再根据get方法取真实的结果,当然如果此时callable线程如果没有执行完get方法会阻塞执行完,如果执行完则直接返回结果或抛出异常
package com.future;
/**
* 数据结果
* Created by yulinfeng on 6/18/17.
*/
public interface Data {
String getResult() throws InterruptedException;
}package com.future;
/**
* 结果的真实计算过程
* Created by yulinfeng on 6/18/17.
*/
public class RealData implements Data {
protected String data;
public RealData(String data) {
try {
System.out.println("正在计算结果");
Thread.sleep(3000); //模拟计算
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
this.data = data + “ world”;
}
public String getResult() throws InterruptedException {
return data;
}
}package com.future;
/**
* 真实结果RealData的代理
* Created by yulinfeng on 6/18/17.
*/
public class FutureData implements Data {
RealData realData = null; //对RealData的封装,代理了RealData
boolean isReady = false; //真实结果是否已经准备好
public synchronized void setResultData(RealData realData) {
if (isReady) {
return;
}
this.realData = realData;
isReady = true;
notifyAll(); //realData已经被注入到了futureData中,通知getResult方法
}
public synchronized String getResult() throws InterruptedException {
if (!isReady) {
wait(); //数据还未计算好,阻塞等待
}
return realData.getResult();
}
}package com.future;
/**
* Client主要完成的功能包括:1. 返回一个FutureData;2.开启一个线程用于构造RealData
* Created by yulinfeng on 6/18/17.
*/
public class Client {
public Data request(final String string) {
final FutureData futureData = new FutureData();
/*计算过程比较慢,单独放到一个线程中去*/
new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
RealData realData = new RealData(string);
futureData.setResultData(realData);
}
}).start();
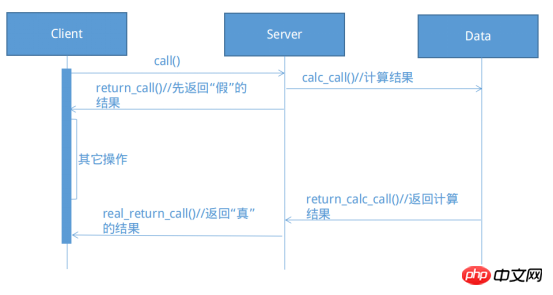
return futureData; //先返回一个“假”的futureData
}
}/**
* 负责调用Client发起请求,并使用返回的数据。
* Created by yulinfeng on 6/18/17.
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Client client = new Client();
System.out.println("准备计算结果");
Data data = client.request("hello"); //立即返回一个“假”的futureData,可以不用阻塞的等待数据返回,转而执行其它任务
System.out.println("执行其它任务");
Thread.sleep(3000); //模拟执行其它任务
System.out.println("数据的计算结果为:" + data.getResult());
}
}Proxy mode. Of course, the Future mode has been implemented for us in the JDK.
Modify the RealData class:
package com.future;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
/**
* 结果的真实计算过程
* Created by yulinfeng on 6/18/17.
*/
public class RealData2 implements Callable<String> {
protected String data;
public RealData2(String data) {
this.data = data;
}
public String call() throws Exception {
try {
System.out.println("正在计算结果");
Thread.sleep(2000); //模拟计算结果
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
this.data = data + " world";
return data;
}
}package com.future;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
/**
* 负责调用Executor的submit,并使用返回的数据。
* Created by yulinfeng on 6/18/17.
*/
public class Main2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
ExecutorService client = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(); //类似Client
System.out.println("准备计算结果");
Future<String> data = client.submit(new RealData2("hello")); //类似Client.request
System.out.println("执行其它任务");
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println("数据的计算结果为:" + data.get());
}
}ThreadPoolExecutor thread pool principle and its execute method" we explained the execute method. Line 1145 of the ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker#runWorker method is the call to the task task:
//ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker#runWorker task.run();
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of Future pattern in java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and the choice should be based on project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, with simple syntax and high execution efficiency. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and rich libraries.






