How to use native JDBC?
JDBC
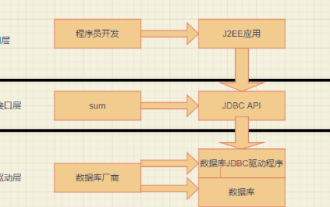
Java DataBase Connectivity, java database connection, is a Java API used to execute SQL statements.
JDBC is the standard specification for Java to access databases. It can provide unified access to different relational databases. It consists of a set of interfaces and classes written in Java language.
Driver
JDBC needs to connect to the driver. The driver is for two devices to communicate and meet a certain communication data format. The data format is specified by the equipment provider, and the equipment provider provides it for the device. Driver software, through which the device can communicate.
JDBC specification (mastering four core objects)
DriverManager: used to register the driver
Connection: represents the connection created with the database
Statement: operates the database sql statement Object
ResultSet: result set or a virtual table
Use JDBC technology, through the driver provided by mysql, to operate the database implementation steps:
1. Register the driver
Inform the JVM that we use What is the driver (mysql, oracle....)
DriverManager.registerDriver(new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver()); It is not recommended to use
There are 2 reasons:
>Cause The driver was registered twice.
>Driver jar that strongly relies on the database
Solution:
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
2. Get the connection to the database
The database is TCP Program server, connection server (through 3-way handshake)
is equivalent to establishing a connection path from the java program to the database server
static Connection getConnection(String url, String user, String password)
Try to establish A connection to the given database URL.
Parameter description: url The location where the database needs to be connected (web address) user user name password password
For example: getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/day06", "root", "root");
URL: An agreement between SUN and the database manufacturer.
jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/day06
Protocol sub-protocol IP: port number database
mysql: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/day04 or jdbc:mysql:///day14 (Default local connection)
oracle database: jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:sid
3. Get the executor object
The object that executes the SQL statement, its function is to execute the SQL
interface The implementation is in the database driver. All interactions with the database are based on connection objects.
Statement createStatement(); //Create an object for operating sql statements
4. Execute the SQL statement and obtain the result set
Use the executor object to execute the SQL statement
Obtain the result set of the SQL statement (add, delete, modify) : Integer, number of valid rows to execute Query: What is returned is a result set)
Commonly used methods:
? int executeUpdate(String sql); --Execute insert update delete statement.
? ResultSet executeQuery(String sql ); --Execute the select statement.
? boolean execute(String sql); --Return true only when the select is executed and there is a result, and false is returned when executing other statements.
5. Process the result set
ResultSet is actually a two-dimensional table. We can call its boolean next() method to point to a certain row of records. When the next() method is called for the first time, it points to the location of the first row of records. At this time, ResultSet can be used Provided getXXX(int col) method (different from index starting from 0, column starting from 1) to get the data of the specified column:
rs.next();//Point to the first row
rs.getInt (1);//Get the data of the first row and the first column
Common methods:
? Object getObject(int index) / Object getObject(String name) Get any object
? String getString(int index )/ String getString(String name) Get the string
? int getInt(int index)/int getInt(String name) Get the integer
? double getDouble(int index)/ double getDouble(String name) Get the double precision Floating point type
6. Release resources
Like IO streams, everything needs to be closed after use! The order of closing is to get it first and then close it, and to get it later and close it first.
Using JDBC to add, delete, modify and query the database code demonstration:
1 2 3 4 |
|
1 |
|
sql injection problem
SQL injection: The content entered by the user is used as part of the SQL statement syntax, changing the true meaning of the original SQL.
Assume there is a login case and the SQL statement is as follows:
SELECT * FROM user table WHERE NAME = User name entered by the user AND PASSWORD = Password entered by the user;
At this time, when the user enters the correct account number and password , and the user is allowed to log in after the information is queried. But when the user enters the account number XXX and the password: XXX' OR 'a'='a, the actually executed code becomes:
SELECT * FROM user table WHERE NAME = 'XXX' AND PASSWORD =' OR 'a'='a';
At this time, the above query statement can always produce results. Then the user logs in successfully directly. Obviously we don't want to see such a result. This is a SQL injection problem.
To this end, we use PreparedStatement to solve the corresponding problem.
preparedStatement: Precompiled object, which is a subclass of Statement object.
Features:
High performance
Will compile the sql statement first
Can filter out the keywords entered by the user.
PreparedStatement preprocessing object, all actual parameters in each SQL statement processed must be replaced with placeholders?.
String sql = "select * from user where username = ? and password = ?";
To use PreparedStatement, you need to complete the following 3 steps:
1.PreparedStatement preprocessing object code:
Obtain pre-processing To process the object, you need to provide the SQL statement that has been processed using placeholders
PreparedStatement psmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql)
2. Set the actual parameters
void setXxx(int index, Xxx xx) will specify the parameters Set the value of the specified type
Parameter 1: index Actual parameter sequence number, starting from 1.
Parameter 2: xxx actual parameter value, xxx represents the specific type.
For example:
setString(2, "1234") Replace the placeholder at the second position in the SQL statement with the actual parameter "1234"
3. Execute the SQL statement:
int executeUpdate (); --Execute insert update delete statement.
ResultSet executeQuery(); --Execute select statement.
boolean execute(); --Execute select and return true. Execute other statements and return false.
The above is the detailed content of How to use native JDBC?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1653
1653
 14
14
 1413
1413
 52
52
 1304
1304
 25
25
 1251
1251
 29
29
 1224
1224
 24
24
 After Java8 (291), TLS1.1 is disabled and JDBC cannot connect to SqlServer2008 using SSL. How to solve the problem?
May 16, 2023 pm 11:55 PM
After Java8 (291), TLS1.1 is disabled and JDBC cannot connect to SqlServer2008 using SSL. How to solve the problem?
May 16, 2023 pm 11:55 PM
After Java8-291, TLS1.1 is disabled, so that JDBC cannot connect to SqlServer2008 using SSL. What should I do? The following is the solution to modify the java.security file 1. Find the java.security file of jre. If it is jre, go to {JAVA_HOME}/jre/ In lib/security, for example????C:\ProgramFiles\Java\jre1.8.0_301\lib\security. If it is the Eclipse green installation-free portable version, search for java.security in the installation folder, such as????xxx\plugins \org
 Java Errors: JDBC Errors, How to Solve and Avoid
Jun 24, 2023 pm 02:40 PM
Java Errors: JDBC Errors, How to Solve and Avoid
Jun 24, 2023 pm 02:40 PM
With the widespread application of Java, JDBC errors often occur when Java programs connect to databases. JDBC (JavaDatabaseConnectivity) is a programming interface in Java used to connect to a database. Therefore, a JDBC error is an error encountered when a Java program interacts with a database. Here are some of the most common JDBC errors and how to solve and avoid them. ClassNotFoundException This is the most common JDBC
 How to implement JDBC batch insert in Java
May 18, 2023 am 10:02 AM
How to implement JDBC batch insert in Java
May 18, 2023 am 10:02 AM
1. Explain that in JDBC, the executeBatch method can execute multiple dml statements in batches, and the efficiency is much higher than executing executeUpdate individually. What is the principle? How to implement batch execution in mysql and oracle? This article will introduce to you the principle behind this. 2. Experiment introduction This experiment will be carried out through the following three steps: a. Record the time consuming of jdbc batch execution and single execution in mysql; b. Record the time consuming of jdbc batch execution and single execution in oracle; c. Record the batch execution and single execution of oracleplsql. The execution time-consuming related java and database versions are as follows: Java17, Mysql8, Oracle
 How to analyze JDBC programming in MySQL
May 30, 2023 pm 10:19 PM
How to analyze JDBC programming in MySQL
May 30, 2023 pm 10:19 PM
1. Prerequisites for database programming Programming languages, such as Java, C, C++, Python and other databases, such as Oracle, MySQL, SQLServer and other database driver packages: Different databases provide different database driver packages corresponding to different programming languages. For example: MySQL provides the Java driver package mysql-connector-java, which is required to operate MySQL based on Java. Similarly, to operate Oracle database based on Java, Oracle's database driver package ojdbc is required. 2. Java database programming: JDBCJDBC, JavaDatabaseConnectiv
 Common problems encountered in Java using JDBC API to connect to MySQL database
Jun 10, 2023 am 09:55 AM
Common problems encountered in Java using JDBC API to connect to MySQL database
Jun 10, 2023 am 09:55 AM
In recent years, the application of Java language has become more and more widespread, and JDBCAPI is a creative method for Java applications to interact with databases. JDBC is based on an open database connection standard called ODBC, which enables Java applications to connect to any database. management system (DBMS). Among them, MySQL is a popular database management system. However, developers will also encounter some common problems when connecting to MySQL databases. This article aims to introduce the JDBCAPI connection M
 CSS native nested syntax is here! Quick guide!
Feb 08, 2023 pm 03:31 PM
CSS native nested syntax is here! Quick guide!
Feb 08, 2023 pm 03:31 PM
Currently, the CSS native nesting syntax is in developer trial status, and the CSS working group is formulating relevant specifications. The Chrome browser is expected to officially launch the CSS native nesting function in version 112.
 What is the difference between Hibernate framework and JDBC?
Apr 17, 2024 am 10:33 AM
What is the difference between Hibernate framework and JDBC?
Apr 17, 2024 am 10:33 AM
Differences between Hibernate and JDBC: Abstraction level: Hibernate provides high-level object mapping and query generation, while JDBC requires manual coding. Object-relational mapping: Hibernate maps Java objects and database tables, while JDBC does not provide this functionality. Query generation: Hibernate uses HQL to simplify query generation, while JDBC requires writing complex SQL queries. Transaction management: Hibernate automatically manages transactions, while JDBC requires manual management.
 How MySQL implements JDBC
May 27, 2023 am 11:06 AM
How MySQL implements JDBC
May 27, 2023 am 11:06 AM
Basic introductory concepts of JDBC JDBC (JavaDataBaseConnectivity, java database connection) is a Java API used to execute SQL statements and can provide unified access to a variety of relational databases. It is composed of a set of classes and interfaces written in the Java language. The JDBC specification defines the interface, and the specific implementation is implemented by major database vendors. JDBC is the standard specification for Java to access databases. How to actually operate the database requires specific implementation classes, that is, database drivers. Each database manufacturer writes its own database driver according to the communication format of its own database. So we just need to be able to call J




