Detailed examples of Netty threading model
Netty Threading Model
Netty’s threading model is mainly based on React, and has evolved into multiple versions due to different application scenarios.
Single-threaded mode
That is, receiving service requests and performing IO operations are all completed by one thread. Since non-blocking IO operations such as IO multiplexing are used, the amount of requests increases. In small cases, single-threaded mode can also solve some scene problems.

Single receiving multi-worker thread mode
When the number of requests increases, the original one thread processing all IO operations becomes increasingly unsupportable Corresponding performance indicators, so the concept of a working thread pool is mentioned. At this time, receiving the service request is still a thread. After receiving the request, the thread receiving the request will be entrusted to the subsequent working thread pool and obtain a thread from the thread pool for execution. User request.
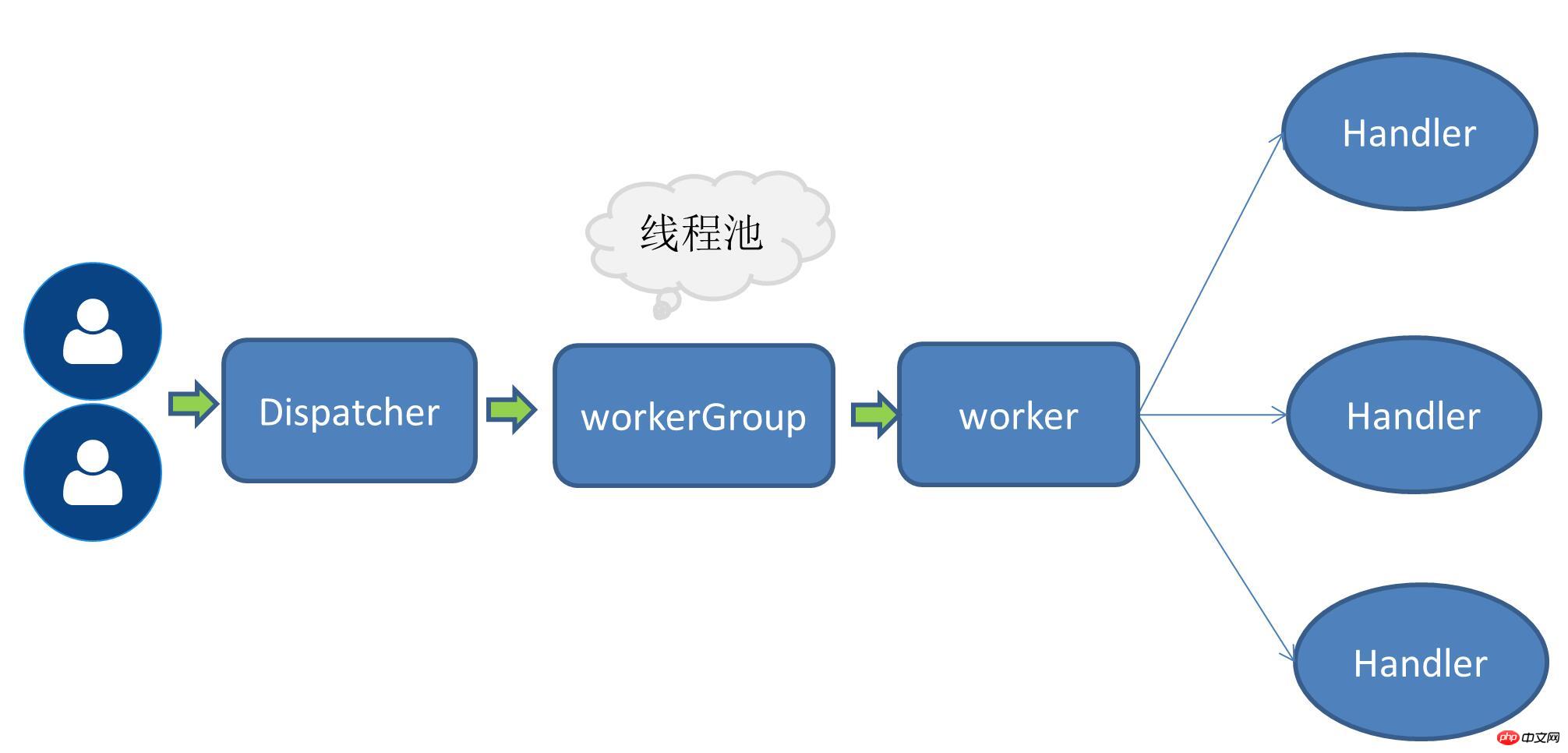
Multiple receiving and multi-worker thread mode
When the request volume further increases, a single thread that receives service requests cannot handle all client connections, so The thread pool that receives service requests is also expanded, and multiple threads are responsible for receiving client connections at the same time.
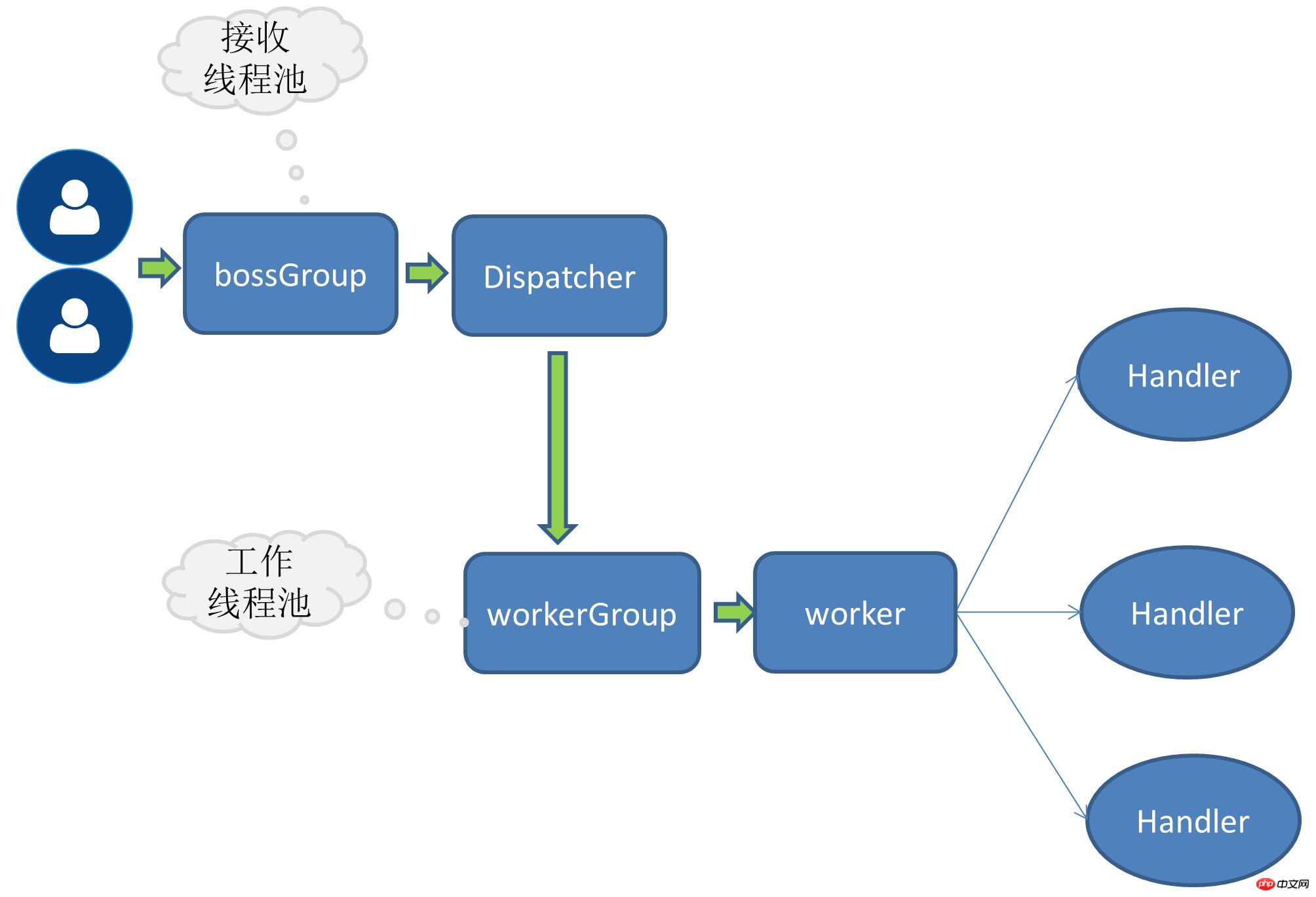
RPC Business Thread
The above mentioned are Netty’s own threading models, optimization strategies that have been continuously developed with the increase in request volume. For RPC requests, the most important thing for application systems is the processing of business logic, and this type of business may be computationally intensive or IO-intensive. For example, most applications are accompanied by database operations, redis or other connections. Network services, etc. If there are such time-consuming IO operations in the business request, it is recommended to allocate the task of processing the business request to an independent thread pool, otherwise netty's own threads may be blocked.
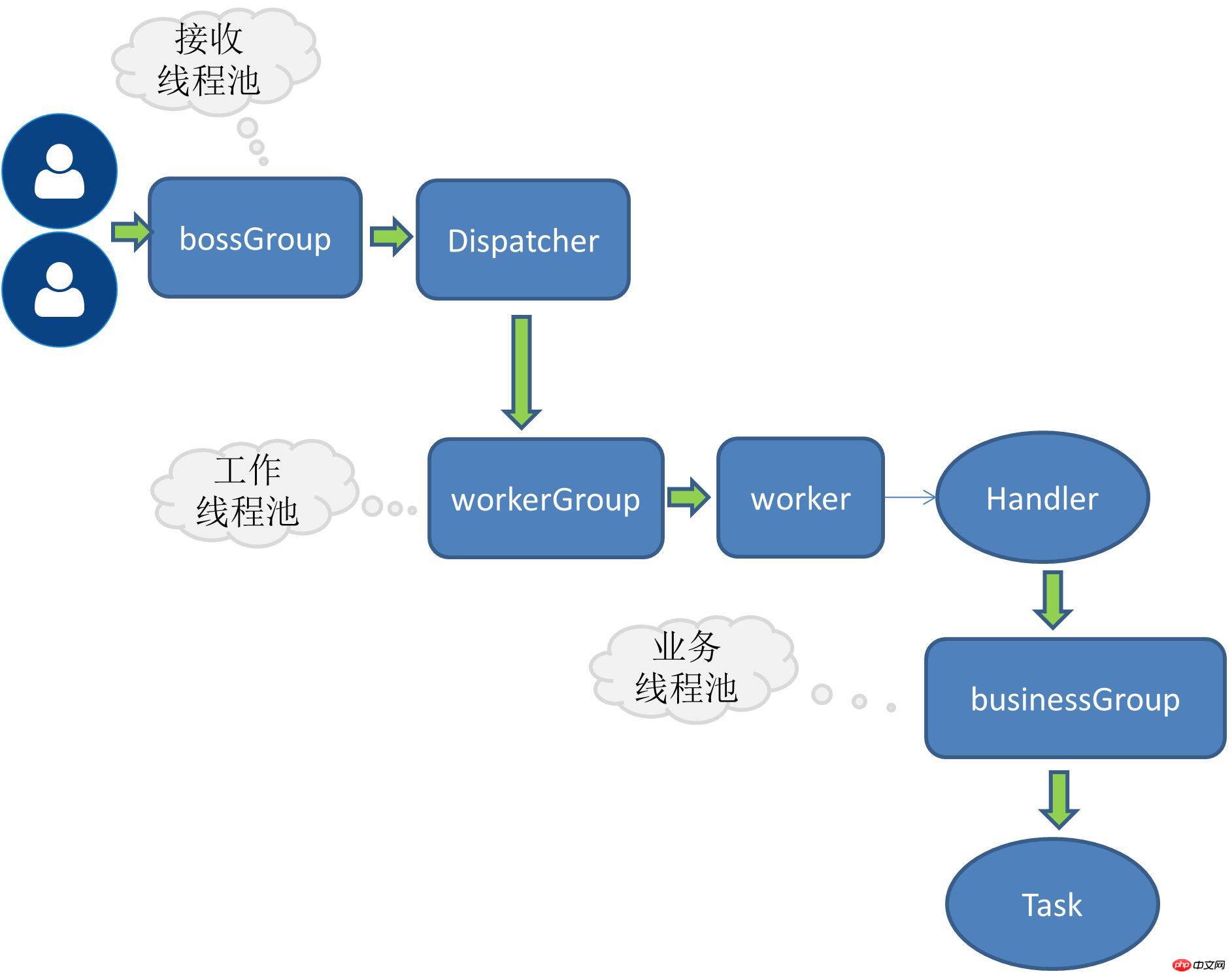
Division of work between the receiving request thread and the working thread
The receiving request thread is mainly responsible for creating the link, and then Delegate the request to the worker thread
The worker thread is responsible for encoding, decoding, reading IO and other operations
Solution implementation
Currently I The implemented RPC adopts the multi-receiving and multi-worker thread mode. The port is bound on the server side like this:
public void bind(ServiceConfig serviceConfig) {EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();try {ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(this.rpcServerInitializer)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE,true)
;try {ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.bind(serviceConfig.getHost(),serviceConfig.getPort()).sync();//...channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RpcException(e);
}
}finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}To add business threads, you only need to further delegate the handle operations to the thread pool. For expansion, an interface needs to be defined here: Define thread pool interfaceboosGroup is a group of ## used to receive service requests. #workerGroup is a group of people specifically responsible for IO operations.
public interface RpcThreadPool {Executor getExecutor(int threadSize,int queues);
}Refer to dubbo thread pool
@Qualifier("fixedRpcThreadPool")@Componentpublic class FixedRpcThreadPool implements RpcThreadPool {private Executor executor;@Overridepublic Executor getExecutor(int threadSize,int queues) {if(null==executor) {synchronized (this) {if(null==executor) {
executor= new ThreadPoolExecutor(threadSize, threadSize, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
queues == 0 ? new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>() :(queues < 0 ? new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(): new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(queues)),new RejectedExecutionHandler() {@Overridepublic void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) { //...}
});
}
}
}return executor;
}
}Interlude:Thread Pool FactoryWhen there are multiple thread pool implementations, the thread pool is dynamically selected through the thread pool name.I remember once a friend suddenly asked what the coreSize in the java thread pool meant? I was suddenly short-circuited, because I don't usually write multi-threading. When I think of the database thread pool that I usually use a lot, I am quite impressed by the parameters in it, but I just can't remember coreSize. Later, I took a closer look at some parameters of the thread pool. Now I can take this opportunity to take a closer look to avoid short-circuiting again.
@Componentpublic class RpcThreadPoolFactory {@Autowiredprivate Map<String,RpcThreadPool> rpcThreadPoolMap;public RpcThreadPool getThreadPool(String threadPoolName){return this.rpcThreadPoolMap.get(threadPoolName);
}
}@Overrideprotected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, RpcRequest rpcRequest) {this.executor.execute(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {RpcInvoker rpcInvoker=RpcServerInvoker.this.buildInvokerChain(RpcServerInvoker.this);RpcResponse response=(RpcResponse) rpcInvoker.invoke(RpcServerInvoker.this.buildRpcInvocation(rpcRequest));
channelHandlerContext.writeAndFlush(response);
}
});
}The above is the detailed content of Detailed examples of Netty threading model. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of commercial support for Java frameworks
Jun 05, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
How to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of commercial support for Java frameworks
Jun 05, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
Evaluating the cost/performance of commercial support for a Java framework involves the following steps: Determine the required level of assurance and service level agreement (SLA) guarantees. The experience and expertise of the research support team. Consider additional services such as upgrades, troubleshooting, and performance optimization. Weigh business support costs against risk mitigation and increased efficiency.
 How do the lightweight options of PHP frameworks affect application performance?
Jun 06, 2024 am 10:53 AM
How do the lightweight options of PHP frameworks affect application performance?
Jun 06, 2024 am 10:53 AM
The lightweight PHP framework improves application performance through small size and low resource consumption. Its features include: small size, fast startup, low memory usage, improved response speed and throughput, and reduced resource consumption. Practical case: SlimFramework creates REST API, only 500KB, high responsiveness and high throughput
 How does the learning curve of PHP frameworks compare to other language frameworks?
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:41 PM
How does the learning curve of PHP frameworks compare to other language frameworks?
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:41 PM
The learning curve of a PHP framework depends on language proficiency, framework complexity, documentation quality, and community support. The learning curve of PHP frameworks is higher when compared to Python frameworks and lower when compared to Ruby frameworks. Compared to Java frameworks, PHP frameworks have a moderate learning curve but a shorter time to get started.
 Performance comparison of Java frameworks
Jun 04, 2024 pm 03:56 PM
Performance comparison of Java frameworks
Jun 04, 2024 pm 03:56 PM
According to benchmarks, for small, high-performance applications, Quarkus (fast startup, low memory) or Micronaut (TechEmpower excellent) are ideal choices. SpringBoot is suitable for large, full-stack applications, but has slightly slower startup times and memory usage.
 Golang framework documentation best practices
Jun 04, 2024 pm 05:00 PM
Golang framework documentation best practices
Jun 04, 2024 pm 05:00 PM
Writing clear and comprehensive documentation is crucial for the Golang framework. Best practices include following an established documentation style, such as Google's Go Coding Style Guide. Use a clear organizational structure, including headings, subheadings, and lists, and provide navigation. Provides comprehensive and accurate information, including getting started guides, API references, and concepts. Use code examples to illustrate concepts and usage. Keep documentation updated, track changes and document new features. Provide support and community resources such as GitHub issues and forums. Create practical examples, such as API documentation.
 How to choose the best golang framework for different application scenarios
Jun 05, 2024 pm 04:05 PM
How to choose the best golang framework for different application scenarios
Jun 05, 2024 pm 04:05 PM
Choose the best Go framework based on application scenarios: consider application type, language features, performance requirements, and ecosystem. Common Go frameworks: Gin (Web application), Echo (Web service), Fiber (high throughput), gorm (ORM), fasthttp (speed). Practical case: building REST API (Fiber) and interacting with the database (gorm). Choose a framework: choose fasthttp for key performance, Gin/Echo for flexible web applications, and gorm for database interaction.
 Detailed practical explanation of golang framework development: Questions and Answers
Jun 06, 2024 am 10:57 AM
Detailed practical explanation of golang framework development: Questions and Answers
Jun 06, 2024 am 10:57 AM
In Go framework development, common challenges and their solutions are: Error handling: Use the errors package for management, and use middleware to centrally handle errors. Authentication and authorization: Integrate third-party libraries and create custom middleware to check credentials. Concurrency processing: Use goroutines, mutexes, and channels to control resource access. Unit testing: Use gotest packages, mocks, and stubs for isolation, and code coverage tools to ensure sufficiency. Deployment and monitoring: Use Docker containers to package deployments, set up data backups, and track performance and errors with logging and monitoring tools.
 What are the common misunderstandings in the learning process of Golang framework?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 09:59 PM
What are the common misunderstandings in the learning process of Golang framework?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 09:59 PM
There are five misunderstandings in Go framework learning: over-reliance on the framework and limited flexibility. If you don’t follow the framework conventions, the code will be difficult to maintain. Using outdated libraries can cause security and compatibility issues. Excessive use of packages obfuscates code structure. Ignoring error handling leads to unexpected behavior and crashes.




