 Backend Development
Backend Development
 PHP Tutorial
PHP Tutorial
 Detailed explanation of the definition and usage of abstract class and interface in php
Detailed explanation of the definition and usage of abstract class and interface in php
Detailed explanation of the definition and usage of abstract class and interface in php
Abstract classabstract class1. An abstract class refers to a class with the abstract keyword in front of the class and an abstract method (the abstract keyword in front of the class method function keyword).
2. Abstract classes cannot be instantiated directly. The abstract class only defines (or partially implements) the methods required by the subclass. Subclasses can make an abstract class concrete by inheriting it and by implementing all the abstract methods in the abstract class.
3. If a subclass needs to be instantiated, it must implement all abstract methods in the abstract class. If the subclass does not implement all abstract methods in the abstract class, then the subclass is also an abstract class. The abstract keyword must be added in front of the class and cannot be instantiated.
abstract class A
{
/** 抽象类中可以定义变量 */
protected $value1 = 0;
private $value2 = 1;
public $value3 = 2;
/** 也可以定义非抽象方法 */
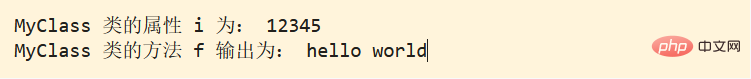
public function my_print()
{
echo "hello,world/n";
}
/**
* 大多数情况下,抽象类至少含有一个抽象方法。抽象方法用abstract关键字声明,其中不能有具体内容。
* 可以像声明普通类方法那样声明抽象方法,但是要以分号而不是方法体结束。也就是说抽象方法在抽象类中不能被实现,也就是没有函数体“{some codes}”。
*/
abstract protected function abstract_func1();
abstract protected function abstract_func2();
}
abstract class B extends A
{
public function abstract_func1()
{
echo "implement the abstract_func1 in class A/n";
}
/** 这么写在zend studio 8中会报错*/
//abstract protected function abstract_func2();
}
class C extends B
{
public function abstract_func2()
{
echo "implement the abstract_func2 in class A/n";
}
}4. If you create a subclass B that inherits from A as shown below, but does not implement the abstract method abstract_func():
Class B extends A{};, then the program will have the following error:
Fatal error: Class B contains 1 abstract method and must therefore be declared abstract or implement the remaining methods (A::abstract_func)
5. If B implements the abstract method abstract_func(), then the access control of the abstract_func() method in B cannot be stricter than the access control of abstract_func() in A, that is to say:
(1) If abstract_func() in A is declared as public, then the declaration of abstract_func() in B can only be public, not protected or private
(2) If abstract_func() in A is declared protected, then the declaration of abstract_func() in B can be public or protected, but cannot be private
(3) If abstract_func() in A Declared as private, hehe, it cannot be defined as private! (Fatal error: Abstract function A::abstract_func() cannot be
declared private) 2.
interface interface1. Abstract classes provide standards for concrete implementation, while interfaces are pure templates. Interfaces only define functions, not implementation content. Interfaces are declared with the keyword interface. 2. Interface is completely abstract. It can only declare methods, and only public methods. It cannot declare private and protected methods, cannot define method bodies, and cannot declare instance variables. However, interface can declare
constantsvariables. However, placing constant variables in an interface violates its purpose of existing as an interface, and also confuses the different values of interfaces and classes. If you really need it, you can put it in the corresponding abstract class or Class.
interface iA
{
const AVAR=3;
public function iAfunc1();
public function iAfunc2();
}
echo iA:: AVAR;3. Any class that implements an interface must implement all methods defined in the interface class E implements iA
{
public function iAfunc1(){echo "in iAfunc1";}
public function iAfunc2(){echo "in iAfunc2";}
}
abstract class E implements iA{}4.一个类可以在声明中使用implements关键字来实现某个接口。这么做之后,实现接口的具体过程和继承一个仅包含抽象方法的抽象类是一样的。一个类可以同时继承一个父类和实现任意多个接口。extends子句应该在implements子句之前。PHP只支持继承自一个父类,因此extends关键字后只能跟一个类名。
interface iB
{
public function iBfunc1();
public function iBfunc2();
}
class D extends A implements iA,iB
{
public function abstract_func1()
{
echo "implement the abstract_func1 in class A/n";
}
public function abstract_func2()
{
echo "implement the abstract_func2 in class A/n";
}
public function iAfunc1(){echo "in iAfunc1";}
public function iAfunc2(){echo "in iAfunc2";}
public function iBfunc1(){echo "in iBfunc1";}
public function iBfunc2(){echo "in iBfunc2";}
}
class D extends B implements iA,iB
{
public function abstract_func1()
{
parent::abstract_func1();
echo "override the abstract_func1 in class A/n";
}
public function abstract_func2()
{
echo "implement the abstract_func2 in class A/n";
}
public function iAfunc1(){echo "in iAfunc1";}
public function iAfunc2(){echo "in iAfunc2";}
public function iBfunc1(){echo "in iBfunc1";}
public function iBfunc2(){echo "in iBfunc2";}
}5.接口不可以实现另一个接口,但可以继承多个
interface iC extends iA,iB{}
class F implements iC
{
public function iAfunc1(){echo "in iAfunc1";}
public function iAfunc2(){echo "in iAfunc2";}
public function iBfunc1(){echo "in iBfunc1";}
public function iBfunc2(){echo "in iBfunc2";}
}三、抽象类和接口的异同
1.相同点:
(1) 两者都是抽象类,都不能实例化。
(2) interface实现类及abstract class的子类都必须要实现已经声明的抽象方法。
2. 不同点:
(1) interface需要实现,要用implements,而abstract class需要继承,要用extends。
(2) 一个类可以实现多个interface,但一个类只能继承一个abstract class。
(3) interface强调特定功能的实现,而abstract class强调所属关系。
(4) 尽管interface实现类及abstract class的子类都必须要实现相应的抽象方法,但实现的形式不同。interface中的每一个方法都是抽象方法,都只是声明的 (declaration, 没有方法体),实现类必须要实现。而abstract class的子类可以有选择地实现。这个选择有两点含义:a) abstract class中并非所有的方法都是抽象的,只有那些冠有abstract的方法才是抽象的,子类必须实现。那些没有abstract的方法,在 abstract class中必须定义方法体;b) abstract class的子类在继承它时,对非抽象方法既可以直接继承,也可以覆盖;而对抽象方法,可以选择实现,也可以留给其子类来实现,但此类必须也声明为抽象类。既是抽象类,当然也不能实例化。
(5) abstract class是interface与class的中介。abstract class在interface及class中起到了承上启下的作用。一方面,abstract class是抽象的,可以声明抽象方法,以规范子类必须实现的功能;另一方面,它又可以定义缺省的方法体,供子类直接使用或覆盖。另外,它还可以定义自己的实例变量,以供子类通过继承来使用。
(6) 接口中的抽象方法前不用也不能加abstract关键字,默认隐式就是抽象方法,也不能加final关键字来防止抽象方法的继承。而抽象类中抽象方法前则必须加上abstract表示显示声明为抽象方法。
(7) 接口中的抽象方法默认是public的,也只能是public的,不能用private,protected修饰符修饰。而抽象类中的抽象方法则可以用public,protected来修饰,但不能用private。
3. interface的应用场合
(1) 类与类之间需要特定的接口进行协调,而不在乎其如何实现。
(2) 作为能够实现特定功能的标识存在,也可以是什么接口方法都没有的纯粹标识。
(3) 需要将一组类视为单一的类,而调用者只通过接口来与这组类发生联系。
(4) 需要实现特定的多项功能,而这些功能之间可能完全没有任何联系。
4. abstract class的应用场合
一句话,在既需要统一的接口,又需要实例变量或缺省的方法的情况下,就可以使用它。最常见的有:
(1) 定义了一组接口,但又不想强迫每个实现类都必须实现所有的接口。可以用abstract class定义一组方法体,甚至可以是空方法体,然后由子类选择自己所感兴趣的方法来覆盖。
(2) 某些场合下,只靠纯粹的接口不能满足类与类之间的协调,还必需类中表示状态的变量来区别不同的关系。abstract的中介作用可以很好地满足这一点。
(3) Standardizes a set of mutually coordinated methods, some of which are common, state-independent, and can be shared without the need for subclasses to implement them separately; while other methods require individual implementation Subclasses implement specific functions based on their own specific status .
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of the definition and usage of abstract class and interface in php. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to use classes and methods in Python
Apr 21, 2023 pm 02:28 PM
How to use classes and methods in Python
Apr 21, 2023 pm 02:28 PM
Concepts and instances of classes and methods Class (Class): used to describe a collection of objects with the same properties and methods. It defines the properties and methods common to every object in the collection. Objects are instances of classes. Method: Function defined in the class. Class construction method __init__(): The class has a special method (construction method) named init(), which is automatically called when the class is instantiated. Instance variables: In the declaration of a class, attributes are represented by variables. Such variables are called instance variables. An instance variable is a variable modified with self. Instantiation: Create an instance of a class, a specific object of the class. Inheritance: that is, a derived class (derivedclass) inherits the base class (baseclass)
 Replace the class name of an element using jQuery
Feb 24, 2024 pm 11:03 PM
Replace the class name of an element using jQuery
Feb 24, 2024 pm 11:03 PM
jQuery is a classic JavaScript library that is widely used in web development. It simplifies operations such as handling events, manipulating DOM elements, and performing animations on web pages. When using jQuery, you often encounter situations where you need to replace the class name of an element. This article will introduce some practical methods and specific code examples. 1. Use the removeClass() and addClass() methods jQuery provides the removeClass() method for deletion
 What does class mean in python?
May 21, 2019 pm 05:10 PM
What does class mean in python?
May 21, 2019 pm 05:10 PM
Class is a keyword in Python, used to define a class. The method of defining a class: add a space after class and then add the class name; class name rules: capitalize the first letter. If there are multiple words, use camel case naming, such as [class Dog()].
 Detailed explanation of PHP Class usage: Make your code clearer and easier to read
Mar 10, 2024 pm 12:03 PM
Detailed explanation of PHP Class usage: Make your code clearer and easier to read
Mar 10, 2024 pm 12:03 PM
When writing PHP code, using classes is a very common practice. By using classes, we can encapsulate related functions and data in a single unit, making the code clearer, easier to read, and easier to maintain. This article will introduce the usage of PHPClass in detail and provide specific code examples to help readers better understand how to apply classes to optimize code in actual projects. 1. Create and use classes In PHP, you can use the keyword class to define a class and define properties and methods in the class.
 Vue error: Unable to use v-bind to bind class and style correctly, how to solve it?
Aug 26, 2023 pm 10:58 PM
Vue error: Unable to use v-bind to bind class and style correctly, how to solve it?
Aug 26, 2023 pm 10:58 PM
Vue error: Unable to use v-bind to bind class and style correctly, how to solve it? In Vue development, we often use the v-bind instruction to dynamically bind class and style, but sometimes we may encounter some problems, such as being unable to correctly use v-bind to bind class and style. In this article, I will explain the cause of this problem and provide you with a solution. First, let’s understand the v-bind directive. v-bind is used to bind V
 How to determine whether an element has a class in jquery
Mar 21, 2023 am 10:47 AM
How to determine whether an element has a class in jquery
Mar 21, 2023 am 10:47 AM
How jquery determines whether an element has a class: 1. Determine whether an element has a certain class through the "hasClass('classname')" method; 2. Determine whether an element has a certain class through the "is('.classname')" method.
![How to solve the '[Vue warn]: v-bind:class/ :class' error](https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/465/014/169300902772563.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_207,w_330) How to solve the '[Vue warn]: v-bind:class/ :class' error
Aug 26, 2023 am 08:17 AM
How to solve the '[Vue warn]: v-bind:class/ :class' error
Aug 26, 2023 am 08:17 AM
How to solve the "[Vuewarn]:v-bind:class/:class" error During the development process of using Vue, we often encounter some error prompts. One of the common errors is "[Vuewarn]:v-bind:class" /:class" error. This error message usually appears when we use v-bind:class or :class attribute, indicating that Vue cannot correctly parse the class value we set. Then, if
 How SpringBoot encrypts and protects class files through custom classloader
May 11, 2023 pm 09:07 PM
How SpringBoot encrypts and protects class files through custom classloader
May 11, 2023 pm 09:07 PM
Background Recently, key business codes have been encrypted for the company framework to prevent the engineering code from being easily restored through decompilation tools such as jd-gui. The configuration and use of the related obfuscation scheme are relatively complex and there are many problems for the springboot project, so the class files are encrypted and then passed The custom classloder is decrypted and loaded. This solution is not absolutely safe. It only increases the difficulty of decompilation. It prevents gentlemen but not villains. The overall encryption protection flow chart is shown in the figure below. Maven plug-in encryption uses custom maven plug-in to compile. The class file specified is encrypted, and the encrypted class file is copied to the specified path. Here, it is saved to resource/corecla.





