 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 HTML Tutorial
HTML Tutorial
 Introduction to the progress element of the progress bar in HTML5 and its compatibility processing
Introduction to the progress element of the progress bar in HTML5 and its compatibility processing
Introduction to the progress element of the progress bar in HTML5 and its compatibility processing
1. Basic understanding of progress element
1. Basic UI
The progress element belongs to the HTML5 family and refers to progress bar. Supported by IE10+ and other reliable browsers. The following is a simple code:
1.<progress>o(︶︿︶)o</progress>
is a very impressive progress bar. Some people are wondering: "Oh~ why do I see a character emoticon?" Well... I can only say to you: "I despise you, you are so reluctant to use a more reliable browser?!"
This default The effect is different under different browsers, as shown in the following screenshots (under window 7):
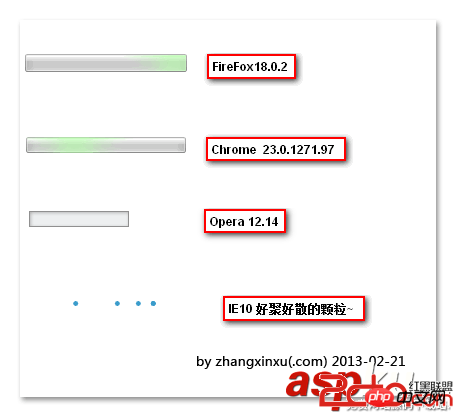
The slow-moving convergence effect of IE10 particles is still It's quite eye-catching.
2. Basic attributes
max, value, position, and labels.
(1) max refers to the maximum value. If it is defaulted, the progress value range is from 0.0~1.0. If set to max=100, the progress value range is from 0~100.
(2) value is the value. If max=100, value=50, the progress is just right. half. The presence or absence of the value attribute determines whether the progress progress bar is deterministic. What's the meaning? For example, has no value and is uncertain, so under the IE10 browser it looks like an infinite loop of dot animation; however, once there is a value attribute (even if it has no value), such as < progress value>, is also considered to be confirmed, and the virtual point animation enters the fairy mode——>The bar changes, as shown in the screenshot below:
(3) position is read-only Attribute, as the name implies, the current progress position is the value of value / max. If the progress bar is uncertain, the value is -1.
(4) labels is also a read-only attribute, and what is obtained is the label elements pointing to the progress element. For example, document.querySelector("progress").labels returns an HTMLCollection, and the following is a screenshot of one of my tests (taken from the Opera browser, currently FireFox18.0.2 and IE10 do not seem to support it).
2. Progress element compatibility processing example
html code
1.<progress max="100" value="20"><ie style="max-width:90%"></ie></progress>
css compatible code
CSS Code copy content to the clipboard
1.progress {
2. display: inline-block;
3. width: 160px;
4. height: 20px;
5. border: 1px solid #0064B4;
6. background-color:#e6e6e6;
7. color: #0064B4; /*IE10*/
8.}
9./*ie6-ie9*/
10.progress ie {
11. display:block;
12. height: 100%;
13. background: #0064B4;
14.}
15.progress::-moz-progress-bar { background: #0064B4; }
16.progress::-webkit-progress-bar { background: #e6e6e6; }
17.progress::-webkit-progress-value { background: #0064B4; }Basic It perfectly solves the differences between browsers.
The above is the detailed content of Introduction to the progress element of the progress bar in HTML5 and its compatibility processing. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 Table Border in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Table Border in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Guide to Table Border in HTML. Here we discuss multiple ways for defining table-border with examples of the Table Border in HTML.
 HTML margin-left
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:48 PM
HTML margin-left
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:48 PM
Guide to HTML margin-left. Here we discuss a brief overview on HTML margin-left and its Examples along with its Code Implementation.
 Nested Table in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Nested Table in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
This is a guide to Nested Table in HTML. Here we discuss how to create a table within the table along with the respective examples.
 HTML Table Layout
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
HTML Table Layout
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
Guide to HTML Table Layout. Here we discuss the Values of HTML Table Layout along with the examples and outputs n detail.
 HTML Input Placeholder
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
HTML Input Placeholder
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
Guide to HTML Input Placeholder. Here we discuss the Examples of HTML Input Placeholder along with the codes and outputs.
 Moving Text in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:45 PM
Moving Text in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:45 PM
Guide to Moving Text in HTML. Here we discuss an introduction, how marquee tag work with syntax and examples to implement.
 HTML Ordered List
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:43 PM
HTML Ordered List
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:43 PM
Guide to the HTML Ordered List. Here we also discuss introduction of HTML Ordered list and types along with their example respectively
 HTML onclick Button
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
HTML onclick Button
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Guide to HTML onclick Button. Here we discuss their introduction, working, examples and onclick Event in various events respectively.



