Summary of front-end code writing specifications
Purpose of the specification: In order to improve work efficiency, facilitate back-end personnel to add functions and front-end post-optimization and maintenance, output high-quality documents, and make the structure clearer, the code concise and orderly, and have a better front-end architecture during website construction. .
Basic guidelines for specifications: comply with web standards, use semantic tags, separate structure, performance, and behavior, and have excellent compatibility. Page performance optimization, the code is concise, clear and orderly, reducing the load on the server as much as possible and ensuring the fastest parsing speed.
1. File specifications
1.1 HTML part
1.1.1 Package building issues
All files are archived in the agreed directory , the package building format is as follows:

Note: All css files are placed in the css folder, images are placed in the images folder, and js are placed in the js folder
1.1.2 HTML header writing
(1) Encoding: All encoding uses xhtml/html, tags must be closed, and encoding is unified to UTF-8. It is recommended to add it on multi-language websites , indicating that the content is based on Chinese display and reading
(2) Semanticization: Use tags correctly and make full use of html tags without compatibility issues
・ [[]]\head content of the file header:
• title: need to add a title
• Encoding: charset=UTF-8
• meta: You can add description and keywords content
1.2 CSS part
1.2.1 CSS types and naming
CSS style sheets can be divided into three categories: global style sheets and modules Universal style sheet and independent style sheet
• Commonly used naming for global style sheets: public.css
• • Universal style sheet naming for modules: module name_basic.css
• Independent Style sheet: module name_page name.css
1.2.2 CSS introduction
CSS file introduction can be introduced through external link or inline method
• External link method
• Inline method
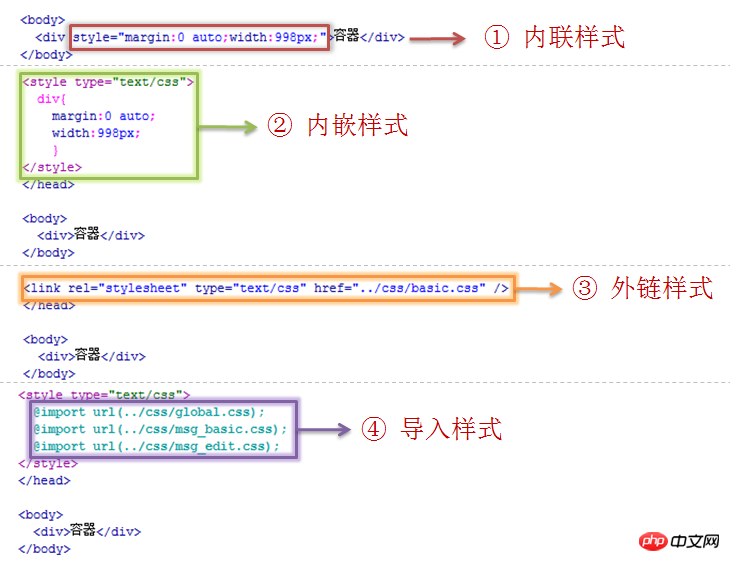
Note: Both link and style tags should be placed in the head. In principle, writing styles directly on HTML is not allowed. Avoid using @import in CSS and do not nest it more than one level.
2. Comment specifications
2.1 Top document comments (recommended)
1 /* 2 * @description: 中文说明 3 * @author: name 4 * @update: name(xxxx-xx-xx xx:xx) 5 */
2.2 Attribute comments
1 /*Header*/ 2 /*Nav*/ 3 /*Container*/ 4 ... 5 /*Footer*/
2.3 Function module comments
1 /* module: module1 by 小王 */ 2 ... 3 /* module: module2 by 小李 */
2.4 Special comments
1 /*Color codes 2 -------------------------------- 3 Red: #e03d3d; 4 Dark: #424242; 5 Light: #c3c5c0; 6 blue #e03d3d; 7 */ 8 9 /* 10 默认宽度为1128px 11 */ 12 13 /*@group Reset Css*/ 14 /*@group General Definitions*/ 15 16 /*---------------Typography-----------------*/ 17 /*------------------Sprite--------------------*/
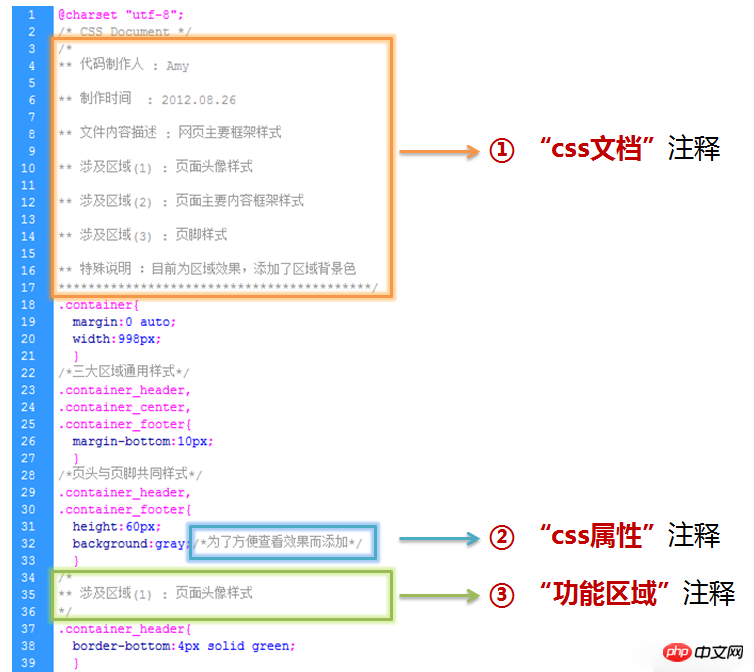
Note:
• Each document corresponds to a document comment (the main comment content includes: document creator, creation time, main content description, etc.)
• Attribute comment description: CSS attributes can be divided into names (such as: margin/padding value, CSS Hack, global Hover, etc.)
• Function module comment description: CSS styles can be written in modules (such as: Header, navigation, buttons, footer, etc.)
3. Naming specifications
3.1 How to name
• It is best to use class to name css and id to name js. The distinction has been made
• The naming of id and class should reflect the function of the element or use a common name instead of abstract and obscure naming
3.2 Naming example
- ##.div1{} /* Not recommended; meaningless */
- .a_green{} /* Not recommended; meaningless */
- .menu{} /* Recommended; special */
- .header{} /* Recommended ;Versatility*/
- .navigation{} /* Not recommended*/
- .login_box_inside_con{} /* Not recommended*/
- .nav{} /* Recommended*/
- ##.nav ul.list{} /* Not recommended*/
- ##.nav .list{} /* Recommendation*/
##3.5 Notes
When naming rules, always use lowercase letters and underscores
Try to avoid using Chinese pinyin when naming, and use more concise and semantic English words to combine
Pay attention to abbreviations when naming, but do not abbreviate blindly
It is not allowed to name by serial numbers such as 1, 2, 3 etc.
Avoid duplication of class and id names
id should be used to identify a certain parent container area of a module or page. The name must be unique. Do not create a new id at will.
class is used to identify a certain type of object. The naming must be concise and comprehensive.
Improve the reuse of code modules as much as possible, and try to use a combination of styles
The rule name should not contain color, positioning, etc. Information related to specific display effects should be named with meanings instead of result names
4.1 Typesetting specifications
Use 4tab for indentation
The rules can be written in a single line. Or multiple lines, but the rule formatting in the entire file must be unified
Writing style:
Each attribute value must be added with a semicolon
If multiple attributes share a style set, multiple attributes must be written in a multi-line format
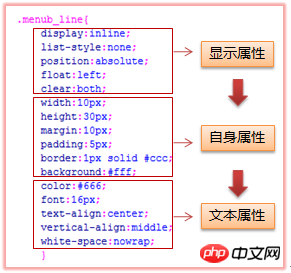
4.2 Attribute writing order (generally follow the display attributes- > Self attribute-> Text attribute-> Writing format of other attributes)
Display attributes: display/list-style/position/float/clear...
Self attributes (box model): width/height/margin/padding/border
Background: background
Line-height: line-height
Text attributes: color/font/text-decoration/text-align/text-indent/vertical-align/white-space/content.. .
- ##Others: cursor/z-index/zoom/overflow...
- CSS3 properties: transform/transition/animation/box- shadow/border-radius
- If you use CSS3 attributes, if it is necessary to add a browser prefix, follow -webkit-/-moz-/-ms-/-o-/std Add them in the order in which the standard attributes are written at the end
- Please add the link style in strict accordance with the following order: a:link -> a:visited -> a:hover -> a:active ##
- 4.3 Code performance optimization
 Merge margin, padding, border-top/ For -right/-bottom/-left settings, try to use short names
Merge margin, padding, border-top/ For -right/-bottom/-left settings, try to use short names
- The selector should be as short as possible on the basis of satisfying the function to reduce selector nesting and query consumption. But be sure to avoid overriding global style settings
- It is forbidden to use the * selector in css
- 0 does not need to be followed separately, for example, 0px can be omitted 0, 0.8px can be omitted to .8px
- If possible, use three characters to express the color, such as #ccc
- If there is no border Do not write border:0; should write border:none
- On the premise of preserving code decoupling, try to merge repeated styles
- background, font and other attributes that can be abbreviated, try to use the abbreviated form
- Images that can be presented in the form of background, try to write them in the CSS style
- 4.4 Use of CSS Hack
-
Try to use browser detection and CSS Hacks as little as possible, and try other solutions first. Considering the efficiency and manageability of the code, although these two methods can quickly resolve browser parsing differences, they should be regarded as a last resort. In long-term projects, allowing the use of hacks will only lead to more hacks, so try to use them as little as possible
IE6: _property:value
IE6/7: *property:value
IE6/7/8/9: property:value\9
4.5 IE Compatibility
IE supports using specific tags to determine the IE version that should be used to draw the current page. Unless there are strong special needs, it is best to set edge mode to notify IE to use the IE version it supports. The latest mode
Note: X-UA-Compatible is a special tag for IE8, which is used to specify the IE8 browser to simulate the rendering method of a specific version of IE browser
The effect of chrome=1 in is that if GCF is installed, GCF will be used to render the page. If If GCF is not installed, use the highest version of IE kernel for rendering
4.6 Font rules
In order to prevent problems caused by file merging and encoding conversion, it is recommended to change the style Chinese font Change the name to the corresponding English name, such as: SimHei, SimSun, Microsoft Yahei
The font thickness uses a specific value, bold bold is written as 700 , normal normal is written as 400
font-size must be in px units
In order to unify the font-family values, better Supports the compatibility of various browsers on various operating systems. Font-family is not allowed to be set arbitrarily in the business code

5. Other specifications
Do not change site-wide CSS and general CSS libraries easily. After changes, they must be fully tested
-
Avoid using filter
Avoid using expression in CSS
- ##Avoid tiling of background images that are too small
- Try not to use !important in CSS
- Never use the "*" selector in CSS ##Level (z-index) must be clear and clear. Page pop-ups and bubbles are the highest level (the highest level is 999). Different pop-up bubbles can be adjusted between three digits. Ordinary blocks are multiples of 10 within 10-90. ;Block expansion and pop-up will increase the number of bits above the current parent level. Blind comparison between levels is prohibited.
- Background image. If possible, use sprite technology as much as possible to reduce http requests. Consider For multi-person collaborative development, sprites are divided according to modules, businesses, and pages.
- Try to avoid using the style attribute inside the page. CSS is placed in the head tag and introduced by the link tag to make the page Separation of structure and performance
- Try to reduce the use of float, position and other properties that affect performance, so as to avoid confusion caused by novices during layout
- Use
- Do not appear multiple (spaces) in a row, and use full-width spaces as little as possible (under the English character set, full-width spaces will become garbled characters) ), you should try to use text-indent, maring/padding and other methods to achieve
- typesetting. If you encounter a need to indent the first line, you can use text-indent:2em;
- If the image needs to be loaded, use the img tag to write it on the page, and specify the width and height. Important images must be added with alt attributes, and important elements and truncated elements must be added. title
- If there is a jump, use the a tag, , if you need to jump to a new page, then also You need to add the target="_blank" attribute. If you click an empty link (#), the current page will be automatically reset to the head end. You can use "javascript:void()" to replace the original "#"
- Clearly distinguish under what circumstances jpg/gif/png pictures
to break lines as little as possible6.1 Layout details
- First add a new meta tag to the head
- position: Absolute positioning cannot be used
- width/height/margin/padding: You cannot use px, you should use percentage, auto or em
- font: You cannot use absolute size, you should use em
- 6.2 The Media Query module introduced by CSS3 can automatically detect the screen width
Load the corresponding CSS file. It is recommended to apply different CSS rules according to different screen resolutions, such as: @media screen and (max-width:799px) {...}
Image adaptive: img{max-width:100%;}
##7. Help documentation
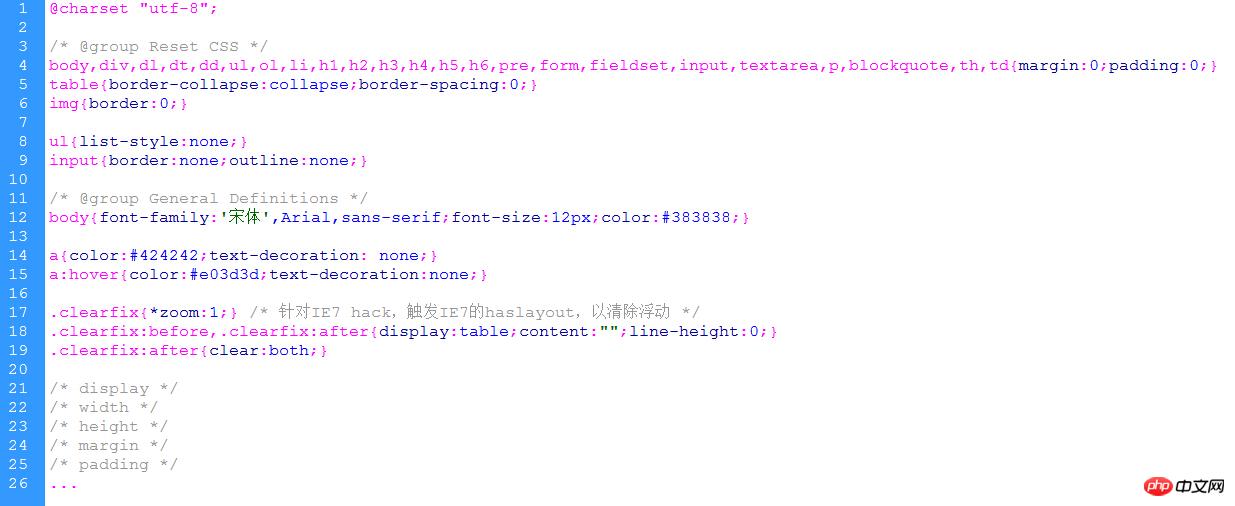
7.1 Global style writing (reset css) ##7.2 Clear floats
##7.2 Clear floatsThe places where floats need to be cleared are:
- If the child element floats and the content of the parent element collapses (that is, it is not wrapped)
- ##The layout will be chaotic, for example, the next layer will run to the previous one The layer is gone
- Solution (four methods)
- Use overflow:hidden correctly; as we all know, overflow:hidden mainly means overflow and hiding, but it also has the effect of clearing and floating
- Add below the required elements, in CSS: clear{clear:both;} (not recommended, add code, redundant)
- Use clearfix to clear floats (recommended), which is equivalent to creating an invisible target element with an empty content block to clear floats
- .clearfix{ *zoom:1;} /* For IE7 hack, trigger IE7's haslayout to clear floats*/ .clearfix:before,.clearfix:after{display:table;content:"";line-height:0; }
Google: font-family:arial, sans- serif;
7.3 Font styles of major websites:- Yahoo: font:13px/1.25 "Helvetica Neue",Helvetica,Arial;
##Apple: font:12px/18px " Lucida Grande", "Lucida Sans Unicode",Helvetica,Arial,Verdana,sans-serif;
Baidu: font:12px arial;
taobao: font:12px/1.5 tahoma,arial,'Hiragino Sans GB',\5b8b\4f53,sans-serif;
Weibo: font:12px/1.125 Arial,Helvetica, sans-serif;
Tencent: font:12px "宋体","Arial Narrow",HELVETICA;
Sina Weibo: font:12px /1.3 "Arial","Microsoft YaHei";
Sina: font:12px/20px "SimSun","宋体","Arial Narrow",HELVETICA;
JD: font:12px/150% Arial,Verdana,"宋体";
- ##zhihu: font-family:'Helvetica Neue', Helvetiva,Arial, Sans-serif;
- Default font style:
- Closer to the design: font-family:Geogia,"Times New Roman",Times,serif;
- 7.4 Multi-line text display added Ellipses (text overflow omission)Add specific width restrictions to the required labels, white-space:nowrap;text-overflow:ellipsis;overflow:hidden;
The above is the detailed content of Summary of front-end code writing specifications. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1389
1389
 52
52
 Summarize the usage of system() function in Linux system
Feb 23, 2024 pm 06:45 PM
Summarize the usage of system() function in Linux system
Feb 23, 2024 pm 06:45 PM
Summary of the system() function under Linux In the Linux system, the system() function is a very commonly used function, which can be used to execute command line commands. This article will introduce the system() function in detail and provide some specific code examples. 1. Basic usage of the system() function. The declaration of the system() function is as follows: intsystem(constchar*command); where the command parameter is a character.
 Variable naming conventions required in Python learning
Jan 20, 2024 am 09:03 AM
Variable naming conventions required in Python learning
Jan 20, 2024 am 09:03 AM
Variable naming conventions you need to know when learning Python An important aspect when learning the Python programming language is learning how to name and use variables correctly. Variables are identifiers used to store and represent data. Good variable naming conventions not only improve the readability of your code, but also reduce the possibility of errors. This article will introduce some commonly used variable naming conventions and give corresponding code examples. Use Meaningful Names Variable names should have a clear meaning and be able to describe the data stored in the variable. Using meaningful names allows it to
 How can you understand the design principles and goals behind the latest PHP code specification by reading its source code?
Sep 05, 2023 pm 02:46 PM
How can you understand the design principles and goals behind the latest PHP code specification by reading its source code?
Sep 05, 2023 pm 02:46 PM
How can you understand the design principles and goals behind the latest PHP code specification by reading its source code? Introduction: When writing high-quality PHP code, it is very important to follow certain coding standards. Through code specifications, the readability, maintainability and scalability of the code can be improved. For the PHP language, there is a widely adopted code specification, namely PSR (PHPStandardsRecommendations). This article will introduce how to read the source code of the latest PHP code specification
 What is the standard for API interface?
Feb 23, 2024 pm 08:15 PM
What is the standard for API interface?
Feb 23, 2024 pm 08:15 PM
API (Application Programming Interface) interface specification refers to a series of guidelines and specifications that define and specify API interfaces in software development. The purpose of the API interface specification is to ensure interoperability and consistency between different software components. This article will introduce several important aspects of API interface specifications. Interface naming convention The name of an API interface should be clear, concise, and consistent, and can accurately express its function and purpose. Naming conventions should follow industry practices and internal conventions of the development team, and avoid using vague and confusing terms. this
 PyCharm formatting shortcut key analysis: how to quickly unify code style
Jan 27, 2024 am 10:38 AM
PyCharm formatting shortcut key analysis: how to quickly unify code style
Jan 27, 2024 am 10:38 AM
Quickly standardize code style: The readability and consistency of PyCharm formatted shortcut key parsing code is very important for programmers. Under the premise of following certain coding style specifications, writing clean code can make the project easier to maintain and understand. As a powerful integrated development environment, PyCharm provides shortcut keys to help us quickly format code. This article will introduce several commonly used shortcut keys in PyCharm, as well as their specific usage and effects. 1. Code automatic indentation (Ctrl
 How to solve the problem of irregular use of indented spaces in Python code?
Jun 24, 2023 pm 09:03 PM
How to solve the problem of irregular use of indented spaces in Python code?
Jun 24, 2023 pm 09:03 PM
Python is a very popular programming language. It is favored by more and more people because of its simplicity, ease of understanding, and ease of learning. In Python, indentation and code format are very important. If used irregularly, it will greatly affect the readability and maintainability of the code. This article aims to introduce several methods to solve the problem of irregular indentation spaces in Python code. Using automated tools In Python programming, it is very important to adhere to coding standards. Each indentation in the code should use the same number of spaces. If you manually modify line by line
 Recommended PyCharm theme: customize exclusive programming style
Feb 26, 2024 pm 10:27 PM
Recommended PyCharm theme: customize exclusive programming style
Feb 26, 2024 pm 10:27 PM
In the field of modern programming, the choice of programming tools plays a vital role in a programmer's productivity and comfort. As a powerful and popular integrated development environment, PyCharm has a high reputation in the field of Python development. However, in addition to functional requirements, PyCharm's theme selection is also an important part of programmers in customizing their personalized programming style. A beautiful and comfortable theme can not only increase the joy of programming, but also reduce visual fatigue and improve concentration. therefore,
 Common coding practices and norms in Go language
Jun 01, 2023 am 09:51 AM
Common coding practices and norms in Go language
Jun 01, 2023 am 09:51 AM
With the gradual popularization and application of Go language, the coding practices and specifications of Go language have also received more and more attention and attention. This article will introduce common coding practices and specifications in the Go language to help developers write high-quality Go code. Code formatting Code formatting in Go language is a very important specification and practice. Go language provides an official code formatting tool - goimports, which can automatically adjust the indentation, spaces, quotation marks, etc. of the code, and can also automatically import unimported packages. Use goimpo





 ##7.2 Clear floats
##7.2 Clear floats