 Java
Java
 javaTutorial
javaTutorial
 Kubernetes service--a brief example of running a single-instance stateful service
Kubernetes service--a brief example of running a single-instance stateful service
Kubernetes service--a brief example of running a single-instance stateful service
Goal
Create a PV in your environment
Create a Deployment of MySQl
Start by exposing MySQL to other pods using DNS names in the cluster
Previously
You need aKubernetes cluster and a kubectl command line tool that can connect to the cluster. If you don't have a cluster, you can use Minikube to create one.
We will create a PV (PersistentVolume) for data storage. Click here to view the supported PV types. This guide will use GCEPersistentDisk to demonstrate, but any PV type will work normally. GCEPersistentDisk only works on Google Compute Engine (GCE).
Create the disk in your environment
## In Google Compute Engine, run:
gcloud compute disks create --size=20GB mysql-disk
Then create a PV pointing to the mysql-disk just created. The following is a configuration file for creating a PV, pointing to the GCE disk mentioned above:
apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolume metadata: name: mysql-pv spec: capacity: storage: 20Gi accessModes:- ReadWriteOnce gcePersistentDisk: pdName: mysql-disk fsType: ext4
Note that the line pdName: mysql-disk matches the GCE environment creation disk above The name. If you want to create PVs in other environments, you can check out Persistent Volumes for details.
Create PV:
kubectl create -f https://k8s.io/docs/tasks/run-application/gce-volume.yaml
Deploy MySQL
You can create a stateful service through Kubernetes Deployment, and then use PVC (PersistentVolumeClaim) to connect to the existing PV. For example, the following YAML file describes a Deployment that runs MySQL and uses PVC. The file defines a volume mounted to /var/lib/mysql and creates a PVC that requires a 20G volume size.
Note: The password is defined in the YAML configuration file, which is not safe. Check out Kubernetes Secrets for more secure solutions.
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: mysql spec: ports:- port: 3306 selector: app: mysql clusterIP: None---apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolumeClaim metadata: name: mysql-pv-claim spec: accessModes:- ReadWriteOnce resources: requests: storage: 20Gi---apiVersion: apps/v1beta1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: mysql spec: strategy: type: Recreate template: metadata: labels: app: mysql spec: containers: - image: mysql:5.6name: mysql env: # Use secret in real usage- name: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD value: password ports:- containerPort: 3306 name: mysql volumeMounts:- name: mysql-persistent-storage mountPath: /var/lib/mysql volumes: - name: mysql-persistent-storage persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: mysql-pv-claim
1. Deploy the content in the YAML file.
kubectl create -f https://k8s.io/docs/tasks/run-application/mysql-deployment.yaml
2. Display Deployment information.
kubectl describe deployment mysql
Name: mysql
Namespace: default
CreationTimestamp: Tue, 01 Nov 2016 11:18:45 -0700
Labels: app=mysql
Selector: app=mysql
Replicas: 1 updated | 1 total | 0 available | 1 unavailable
StrategyType: Recreate
MinReadySeconds: 0
OldReplicaSets: <none>
NewReplicaSet: mysql-63082529 (1/1 replicas created)
Events:
FirstSeen LastSeen Count From SubobjectPath Type Reason Message --------- -------- ----- ---- ------------- -------- ------ -------
33s 33s 1 {deployment-controller } Normal ScalingReplicaSet Scaled up replica set mysql-63082529 to 13. Display the pods created by Deployment.
kubectl get pods -l app=mysql NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE mysql-63082529-2z3ki 1/1 Running 0 3m
4. Check PV.
kubectl describe pv mysql-pv Name: mysql-pv Labels: <none> Status: Bound Claim: default/mysql-pv-claim Reclaim Policy: Retain Access Modes: RWO Capacity: 20Gi Message: Source: Type: GCEPersistentDisk (a Persistent Disk resource in Google Compute Engine) PDName: mysql-disk FSType: ext4 Partition: 0 ReadOnly: false No events.
5. Check the PVC.
kubectl describe pvc mysql-pv-claim Name: mysql-pv-claim Namespace: default Status: Bound Volume: mysql-pv Labels: <none> Capacity: 20Gi Access Modes: RWO No events.
Access MySQL instance
Previous YAML file Created a service that allows other Pods in the cluster to access the database. The service option clusterIP:None causes the service's DNS name to be resolved directly to the Pod's IP address. This is the best way to use it when your service only has one Pod and you don't plan to increase the number of Pods.
Run a Mysql client to connect to the Mysql service:
kubectl run -it --rm --image=mysql:5.6 mysql-client -- mysql -h <pod-ip> -ppassword
The above command creates a new Pod in the cluster , the Pod runs a mysql client and is connected to the Mysql Server served above. If it connects successfully, it means that the stateful MySQL database is successfully up and running.
Waiting for pod default/mysql-client-274442439-zyp6i to be running, status is Pending, pod ready: falseIf you don't see a command prompt, try pressing enter.mysql>
Update
Update the image or other parts of the Deployment and you can use it as usual kubectl apply command to complete. The following are things to note when using stateful applications:
Do not expand the application. This application is only for singleton applications. The following PV can only be mapped to one Pod. For clustered stateful applications, check out the StatefulSet documentation.
Use strategy: type: Recreate in the Deployment’s YAML configuration document. It will tell Kubernetes not to use rolling update. Because Rolling update won't work, there won't be multiple Pods running at the same time. The strategy Recreate will delete the previous Pod when creating a new Pod with updated configuration.
Delete Deployment
Delete the Deployment object by name:
kubectl delete deployment,svc mysql kubectl delete pvc mysql-pv-claim kubectl delete pv mysql-pv
另外,如果你使用的是GCE disk,还需要删除对应的disk:
gcloud compute disks delete mysql-disk
文章转自:
The above is the detailed content of Kubernetes service--a brief example of running a single-instance stateful service. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
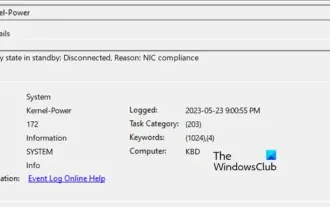 Connection status in standby: Disconnected, reason: NIC Compliance
Feb 19, 2024 pm 03:15 PM
Connection status in standby: Disconnected, reason: NIC Compliance
Feb 19, 2024 pm 03:15 PM
"The connection status in the event log message shows Standby: Disconnected due to NIC compliance. This means that the system is in standby mode and the network interface card (NIC) has been disconnected. Although this is usually a network issue , but can also be caused by software and hardware conflicts. In the following discussion, we will explore how to solve this problem." What is the reason for standby connection disconnection? NIC compliance? If you see the "ConnectivityStatusinStandby:DisConnected,Reason:NICCompliance" message in Windows Event Viewer, this indicates that there may be a problem with your NIC or network interface controller. This situation is usually
 SVM examples in Python
Jun 11, 2023 pm 08:42 PM
SVM examples in Python
Jun 11, 2023 pm 08:42 PM
Support Vector Machine (SVM) in Python is a powerful supervised learning algorithm that can be used to solve classification and regression problems. SVM performs well when dealing with high-dimensional data and non-linear problems, and is widely used in data mining, image classification, text classification, bioinformatics and other fields. In this article, we will introduce an example of using SVM for classification in Python. We will use the SVM model from the scikit-learn library
 How to set Momo status
Mar 01, 2024 pm 12:10 PM
How to set Momo status
Mar 01, 2024 pm 12:10 PM
Momo, a well-known social platform, provides users with a wealth of functional services for their daily social interactions. On Momo, users can easily share their life status, make friends, chat, etc. Among them, the setting status function allows users to show their current mood and status to others, thereby attracting more people's attention and communication. So how to set your own Momo status? The following will give you a detailed introduction! How to set status on Momo? 1. Open Momo, click More in the lower right corner, find and click Daily Status. 2. Select the status. 3. The setting status will be displayed.
 How to check server status
Oct 09, 2023 am 10:10 AM
How to check server status
Oct 09, 2023 am 10:10 AM
Methods to view server status include command line tools, graphical interface tools, monitoring tools, log files, and remote management tools. Detailed introduction: 1. Use command line tools. On Linux or Unix servers, you can use command line tools to view the status of the server; 2. Use graphical interface tools. For server operating systems with graphical interfaces, you can use the graphics provided by the system. Use interface tools to view server status; 3. Use monitoring tools. You can use special monitoring tools to monitor server status in real time, etc.
 How to show up offline on WhatsApp on Android phone
Jul 14, 2023 am 08:21 AM
How to show up offline on WhatsApp on Android phone
Jul 14, 2023 am 08:21 AM
Want to appear "offline" or don't want to share your current status with your friends on WhatsApp? There is a simple but clever trick to do this. You can adjust your WhatsApp settings so that your current status (offline or last seen) is not visible to your friends or others there. How to show offline status on your WhatsApp status bar? This is a very simple and streamlined process. So, follow the steps below now. Step 1 – Open WhatsApp on your phone. Step 2 – Tap ⋮ and choose to open Settings. Step 3 – Open Privacy settings to access it. Step 4 – On that privacy page, open the “Last Viewed & Online” setting to access it. Step 5 – Change the “Who can
 The practice of go-zero and Kubernetes: building a containerized microservice architecture with high availability, high performance, and high scalability
Jun 22, 2023 am 09:26 AM
The practice of go-zero and Kubernetes: building a containerized microservice architecture with high availability, high performance, and high scalability
Jun 22, 2023 am 09:26 AM
As the scale of the Internet continues to expand and user needs continue to increase, the advantages of microservice architecture are receiving more and more attention. Subsequently, the containerized microservice architecture has become particularly important, which can better meet the needs of high availability, high performance, high scalability and other aspects. Under this trend, go-zero and Kubernetes have become the most popular containerized microservice frameworks. This article will introduce how to use the go-zero framework and Kubernetes container orchestration tools to build high-availability, high-performance
 Detailed explanation of the five states of Java threads and state transition rules
Feb 19, 2024 pm 05:03 PM
Detailed explanation of the five states of Java threads and state transition rules
Feb 19, 2024 pm 05:03 PM
In-depth understanding of the five states of Java threads and their conversion rules 1. Introduction to the five states of threads In Java, the life cycle of a thread can be divided into five different states, including new state (NEW), ready state (RUNNABLE), Running status (RUNNING), blocking status (BLOCKED) and termination status (TERMINATED). New state (NEW): When the thread object is created, it is in the new state. At this point, the thread object has allocated enough resources to perform the task
 Production deployment and management using Docker and Kubernetes in Beego
Jun 23, 2023 am 08:58 AM
Production deployment and management using Docker and Kubernetes in Beego
Jun 23, 2023 am 08:58 AM
With the rapid development of the Internet, more and more enterprises have begun to migrate their applications to cloud platforms. Docker and Kubernetes have become two very popular and powerful tools for application deployment and management on cloud platforms. Beego is a web framework developed using Golang. It provides rich functions such as HTTP routing, MVC layering, logging, configuration management, Session management, etc. In this article we will cover how to use Docker and Kub





