Summary of Java programming ideas and methods
I always felt that the book was too wordy. After reading the summary, it would be easier to recall later. I wanted to be lazy and look for other people's summaries online, but I couldn't find a good one, so I had to do my best to summarize it as best as possible.
Introduction to Objects
I feel like this after seeing Introduction to Objects This book
Contents:
1.1 Abstraction process
1.2 Each object There is an interface
1.3 Each object provides services
1.4 Hidden concrete implementation
1.5 Reusing concrete implementation
1.6 Inheritance
1.7 Interchangeable objects with polymorphism
1.8 Single root inheritance structure
1.9 Container
1.10 Creation and lifetime of objects
1.11 Exception handling: handling errors
1.12 Concurrent programming
1.13 Java and the Internet
1.14 Summary
I feel like I will finally become proficient in Java after reading this. However, this chapter only introduces the basic concepts of OOP including an overview of development methods, and understands the importance of objects.
1.1 Abstraction process
Explain the orientation through the shortcomings of other languages Object language is good.
Assembly language is a slight abstraction of the underlying machine. Imperative languages (such as C and BASIC) are an abstraction of assembly language. Assembly language directly controls the computer's hardware. Imperative languages Languages are based on computer structures to solve problems. OOP languages solve problems based on the structure of the problem and are not restricted to any specific type of problem.
1.2 Each object has an interface
Interface: determines what can be issued to a specific object Request Object: Type name
Looking at the text description, it has risen to a philosophical issue. It is easy to understand from the following example.
Light lt = new Light(); //对象lt.on;//接口向对象发出请求
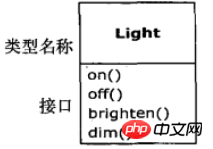
1.3 Each object provides services
Benefits: 1. Helps improve the cohesion of software 2. Each object can complete a task well, but it does not try to do more things.
Understanding: Design a music player that has lyrics display, playback, pause, and background display (service). At this time, don’t just provide an object (it doesn’t try to do more Things), can provide three objects to complete three services, and three objects provide three services to complete a music player (Cohesion).
1.4 Hidden specific implementation
Download a framework from Github, my goal is to achieve For rapid application development, the framework only needs to provide me with method calls, and hiding the others will not affect my calls.
Access permissions: public > protected (package + base class) > package access permissions (default when there is no keyword) > private
1.5 Specific implementation of reuse
Reuse refers to using inheritance or combination in a class.
- Inheritance----is the relationship of a Lychee is a fruit
- combination- ---Has a relationship There is a way to sleep on your stomach
Derive a subclass from the parent class. The subclass can absorb the data attributes and behaviors of the parent class, and can expand new capabilities.
1.7 Interchangeable objects with polymorphism
class Shape{
draw();
erase();
move();
getColor();
setColor();
}void doSomething(Shape shape){
shape.erase();//...shape.draw();
}
Circle circle = new Circle(); //父类为ShapeTriangle triangle = new Triangle(); //父类为ShapeLine line = new Triangle(); //父类为ShapedoSomething(circle);
doSomething(triangle);
doSomething(line);对doSomething的调用会自动地正确处理,而不管对象的确切类型(可互换对象)。
doSomething(Shape shape)的执行是指你是Shape类或者父类为Shape,而不是你是Circle类就执行这样,你是Triangle 类就执行那样。理解了可以去看设计模式之策略模式。
这里还涉及到向上转型,如下图:
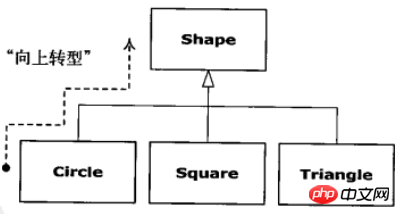
1.8 单根继承结构
1、所有类都继承自单一的基类
public class JianCheng extends Object {
}public class JianCheng { public static void main(String[] args) {
JianCheng jiancheng= new JianCheng();
System.out.println(JianCheng instanceof Object);
}
}Output: true //ExplanationJianCheng class inherits by defaultObject
2. Ensure that all objects have certain functions
Object methods will be inherited by subclasses, such as: clone(), equals( Object obj), toString() and other methods.
3. Garbage collection becomes easy
The object is guaranteed to have its (Object) Type information, so you don't get stuck in an inability to determine the type of an object. This is important for system-level operations (such as exception handling).
1.9 Container
holds access to other objects References are called containers (collections), such as List (used to store sequences), Map (also known as associative array, used to establish associations between objects), Set (only one of each object type is held), and such as Queues, trees, stacks and more.
Comparison between ArrayList and LinkedList, the former is the shape of an array, randomly accessing elements has a small overhead, but insertion and deletion operations have a high overhead. The latter is in the shape of a linked list, insertion and deletion operations are easy to operate.
1.10 Object Creation and Lifetime
Understanding The difference between objects placed on the stack and the heap
Allocation and release between stack-- are given priority Position,sacrifice flexibility, becausemust know the exact number, lifetime and type of objects.
##Heap--dynamically created objects in the memory pool at runtime Know the number, lifetime and type of objects. Dynamic management requires a lot of time to allocate storage space in the heap, but creating storage space and releasing storage space is very convenient.
#Java adopts By using the new keyword to create an object using dynamic memory allocation, the compiler can determine how long the object will survive and automatically destroy it through the "garbage collector mechanism".
##1.11 Exception handling: handling errors
Exception is an object that is thrown from the error location and is caught by a specific type of error exception handler, through try--catch or throw. Exception handling is like another path that is executed when an error occurs, parallel to the normal execution path of the program.If the Java code does not write the correct exception handling code, you will get a compile-time error message. For example: IOException, ClassCastException (class conversion exception), NullPointerException (null pointer exception), etc.
1.12 Concurrent ProgrammingProcess multiple processes at the same time The idea of tasks is to run in multiple threads.
There is a hidden danger in synchronous multi-threaded operation, shared resources. A originally wanted to use a=Love You, but a certain thread led to a=hate you and then A used it, so A's confession will definitely fail.
1.14 Summary
##The first chapter is all theoretical knowledge, and many knowledge points are obviously easy However, the long explanation makes it difficult to understand. There is some practical information but it is mixed with too much fluff.
The above is the detailed content of Summary of Java programming ideas and methods. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to Square Root in Java. Here we discuss how Square Root works in Java with example and its code implementation respectively.
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in Java. Here we discuss Functions in Java with examples and two different Generators with ther examples.
 Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to the Armstrong Number in Java. Here we discuss an introduction to Armstrong's number in java along with some of the code.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is






