Introduction to Struts2 framework and usage introduction
Original address: Click to go
1 What is ValueStack
It is called the value stack, the data structure of shared data provided by Struts
2 Why use ValueStack
Pass data from the controller to the browser
Store object information related to the request (session/application)
3 Life cycle of the ValueStack object
Request entry After reaching the server, a ValueStack object will be created in the memory; when the request processing is completed, the ValueStack object will be cleared
4 How to access the data in ValueStack
Using OGNL expression Expression acquisition
Use EL expression to obtain
5 Area division of data stored in ValueStack
Contents (stack structure) Use OGNL or EL to obtain data
Context (Map structure ) Use #key to obtain data
7 Case: Pass values from the controller to the browser and display the valueStack area
7.1 Guide package
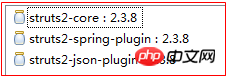


1 <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 "> 2 <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> 3 <groupId>cn.xiangxu</groupId> 4 <artifactId>ssh03</artifactId> 5 <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> 6 <packaging>war</packaging> 7 <dependencies> 8 <dependency> 9 <groupId>org.apache.struts</groupId>10 <artifactId>struts2-core</artifactId>11 <version>2.3.8</version>12 </dependency>13 <dependency>14 <groupId>org.apache.struts</groupId>15 <artifactId>struts2-spring-plugin</artifactId>16 <version>2.3.8</version>17 </dependency>18 <dependency>19 <groupId>org.apache.struts</groupId>20 <artifactId>struts2-json-plugin</artifactId>21 <version>2.3.8</version>22 </dependency>23 </dependencies>24 </project>
7.2 Configuration file
7.2.1 spring_context.xml
Configuring annotation scanning

 ##
##1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" 4 xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc" xmlns:jee="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee" 5 xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" 6 xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util" 7 xmlns:jpa="http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa" 8 xsi:schemaLocation=" 9 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd10 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd11 http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc/spring-jdbc-3.0.xsd12 http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee/spring-jee-3.0.xsd13 http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.0.xsd14 http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa/spring-jpa-1.3.xsd15 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd16 http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.0.xsd17 http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-3.0.xsd">18 19 <!-- 配置组件扫描 -->20 <context:component-scan base-package="cn.xiangxu" />21 22 </beans>
 ##
##1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 3 <!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC 4 "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN" 5 "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd"> 6 7 <struts> 8 9 <!-- 测试struts整合spring时用 -->10 <package name="test" namespace="/test" extends="json-default">11 <action name="demo">12 <result>13 /WEB-INF/jsp/msg.jsp14 </result>15 </action>16 </package>17 18 <package name="vs" namespace="/vs" extends="json-default">19 <action name="valueStack" class="valueStackAction" method="valueStaceMethod">20 <result name="success">21 /WEB-INF/jsp/valueStack.jsp22 </result>23 </action>24 </package>25 26 </struts>27 28

7.2.3 web.xml
Configure the spring listener
Configure the spring configuration file location
Configure the main controller

1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee " version="2.5"> 3 <display-name>ssh03</display-name> 4 <welcome-file-list> 5 <welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file> 6 <welcome-file>index.htm</welcome-file> 7 <welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file> 8 <welcome-file>default.html</welcome-file> 9 <welcome-file>default.htm</welcome-file>10 <welcome-file>default.jsp</welcome-file>11 </welcome-file-list>12 13 <!-- 配置spring监听14 目的:容器启动时自动加载一些东西到缓存中 -->15 <listener>16 <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>17 </listener>18 19 <!-- 配置Spring配置文件的位置 -->20 <context-param>21 <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>22 <param-value>classpath:spring_*.xml</param-value>23 </context-param>24 25 <!-- 配置主控制器和过滤条件 -->26 <filter>27 <filter-name>mvc</filter-name>28 <filter-class>org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter</filter-class>29 </filter>30 <filter-mapping>31 <filter-name>mvc</filter-name>32 <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>33 </filter-mapping>34 35 </web-app>

1 package cn.xiangxu.action; 2 3 import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope; 4 import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; 5 6 import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext; 7 import com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack; 8 9 import cn.xiangxu.entity.Person;10 11 @Controller12 @Scope("prototype")13 public class ValueStackAction {14 15 private String message;16 17 public String valueStaceMethod() {18 System.out.println("跟valueStack相关的action类");19 20 message = "我是控制类中的属性message";21 22 // 利用工厂方法来获取session对象时就使用下面两行代码23 ActionContext context = ActionContext.getContext();24 context.getSession().put("loginName", "warrior"); // 向session中插入数据25 26 context.getSession().put("password", "123456"); // 向session中插入数据27 28 // 利用上下文对象来获取ValueStack对象29 ValueStack valueStack = context.getValueStack();30 31 Person person = new Person();32 person.setId("333");33 person.setName("fury");34 person.setMessage("hello fury");35 valueStack.push(person); // 将数据插入到对象栈中36 37 return "success";38 }39 40 public String getMessage() {41 return message;42 }43 44 public void setMessage(String message) {45 this.message = message;46 }47 48 } ValueStackAction.java
ValueStackAction.java Entity classes that need to be used in the control class
Entity classes that need to be used in the control class
1 package cn.xiangxu.entity; 2 3 import java.io.Serializable; 4 5 public class Person implements Serializable { 6 7 private static final long serialVersionUID = -7221161390673280278L; 8 private String id; 9 private String name;10 private String message;11 public Person() {12 super();13 // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub14 }15 public Person(String id, String name, String message) {16 super();17 this.id = id;18 this.name = name;19 this.message = message;20 }21 @Override22 public int hashCode() {23 final int prime = 31;24 int result = 1;25 result = prime * result + ((id == null) ? 0 : id.hashCode());26 return result;27 }28 @Override29 public boolean equals(Object obj) {30 if (this == obj)31 return true;32 if (obj == null)33 return false;34 if (getClass() != obj.getClass())35 return false;36 Person other = (Person) obj;37 if (id == null) {38 if (other.id != null)39 return false;40 } else if (!id.equals(other.id))41 return false;42 return true;43 }44 public String getId() {45 return id;46 }47 public void setId(String id) {48 this.id = id;49 }50 public String getName() {51 return name;52 }53 public void setName(String name) {54 this.name = name;55 }56 public String getMessage() {57 return message;58 }59 public void setMessage(String message) {60 this.message = message;61 }62 @Override63 public String toString() {64 return "Person [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", message=" + message + "]";65 }66 67 68 } Person.java
Person.java
7.4 编写jsp页面
7.4.1 利用EL表达式访问ValueStack中的数据的格式
${变量名}
7.4.2 利用OGNL表达式访问ValueStack中的数据的格式
注意:为什么访问sesseion中的数据时需要在前面加 #session. 是因为....【自己百度去,或者参见本博客顶端的连接;三少能力有限,讲不清楚】
注意:在读取栈结构中的数据时是从栈顶开始读的,如果有两个变量的名字相同,那么读取到的只会是相对前面的那个变量的值
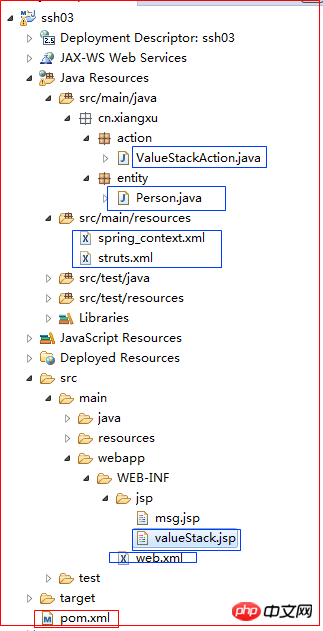
1 <%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=utf-8" 2 pageEncoding="utf-8"%> 3 4 <!-- 引入struts2标签库 --> 5 <%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags" %> 6 7 <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> 8 <html> 9 <head>10 <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8">11 <title>Insert title here</title>12 </head>13 <body>14 <h2>跟valueStack有关的页面</h2>15 <hr /><hr />16 17 <h2>利用EL表达式从valuesStack中获取数据</h2>18 <h3>${message }</h3>19 <hr />20 <h3>${loginName }</h3>21 <hr />22 <h3>${password }</h3>23 <hr /><hr />24 25 <h2>利用OGNL表达式获取valueStack中的数据</h2>26 <h3><s:property value="message"/></h3>27 <hr />28 <h3><s:property value="#session.loginName"/></h3>29 <hr />30 <h3><s:property value="#session.password"/></h3>31 32 <hr /><hr />33 34 <s:debug></s:debug>35 </body>36 </html>7.5 项目结构图
The above is the detailed content of Introduction to Struts2 framework and usage introduction. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 How to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of commercial support for Java frameworks
Jun 05, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
How to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of commercial support for Java frameworks
Jun 05, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
Evaluating the cost/performance of commercial support for a Java framework involves the following steps: Determine the required level of assurance and service level agreement (SLA) guarantees. The experience and expertise of the research support team. Consider additional services such as upgrades, troubleshooting, and performance optimization. Weigh business support costs against risk mitigation and increased efficiency.
 How does the learning curve of PHP frameworks compare to other language frameworks?
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:41 PM
How does the learning curve of PHP frameworks compare to other language frameworks?
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:41 PM
The learning curve of a PHP framework depends on language proficiency, framework complexity, documentation quality, and community support. The learning curve of PHP frameworks is higher when compared to Python frameworks and lower when compared to Ruby frameworks. Compared to Java frameworks, PHP frameworks have a moderate learning curve but a shorter time to get started.
 How do the lightweight options of PHP frameworks affect application performance?
Jun 06, 2024 am 10:53 AM
How do the lightweight options of PHP frameworks affect application performance?
Jun 06, 2024 am 10:53 AM
The lightweight PHP framework improves application performance through small size and low resource consumption. Its features include: small size, fast startup, low memory usage, improved response speed and throughput, and reduced resource consumption. Practical case: SlimFramework creates REST API, only 500KB, high responsiveness and high throughput
 Performance comparison of Java frameworks
Jun 04, 2024 pm 03:56 PM
Performance comparison of Java frameworks
Jun 04, 2024 pm 03:56 PM
According to benchmarks, for small, high-performance applications, Quarkus (fast startup, low memory) or Micronaut (TechEmpower excellent) are ideal choices. SpringBoot is suitable for large, full-stack applications, but has slightly slower startup times and memory usage.
 Golang framework documentation best practices
Jun 04, 2024 pm 05:00 PM
Golang framework documentation best practices
Jun 04, 2024 pm 05:00 PM
Writing clear and comprehensive documentation is crucial for the Golang framework. Best practices include following an established documentation style, such as Google's Go Coding Style Guide. Use a clear organizational structure, including headings, subheadings, and lists, and provide navigation. Provides comprehensive and accurate information, including getting started guides, API references, and concepts. Use code examples to illustrate concepts and usage. Keep documentation updated, track changes and document new features. Provide support and community resources such as GitHub issues and forums. Create practical examples, such as API documentation.
 How to choose the best golang framework for different application scenarios
Jun 05, 2024 pm 04:05 PM
How to choose the best golang framework for different application scenarios
Jun 05, 2024 pm 04:05 PM
Choose the best Go framework based on application scenarios: consider application type, language features, performance requirements, and ecosystem. Common Go frameworks: Gin (Web application), Echo (Web service), Fiber (high throughput), gorm (ORM), fasthttp (speed). Practical case: building REST API (Fiber) and interacting with the database (gorm). Choose a framework: choose fasthttp for key performance, Gin/Echo for flexible web applications, and gorm for database interaction.
 What are the common misunderstandings in the learning process of Golang framework?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 09:59 PM
What are the common misunderstandings in the learning process of Golang framework?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 09:59 PM
There are five misunderstandings in Go framework learning: over-reliance on the framework and limited flexibility. If you don’t follow the framework conventions, the code will be difficult to maintain. Using outdated libraries can cause security and compatibility issues. Excessive use of packages obfuscates code structure. Ignoring error handling leads to unexpected behavior and crashes.
 Detailed practical explanation of golang framework development: Questions and Answers
Jun 06, 2024 am 10:57 AM
Detailed practical explanation of golang framework development: Questions and Answers
Jun 06, 2024 am 10:57 AM
In Go framework development, common challenges and their solutions are: Error handling: Use the errors package for management, and use middleware to centrally handle errors. Authentication and authorization: Integrate third-party libraries and create custom middleware to check credentials. Concurrency processing: Use goroutines, mutexes, and channels to control resource access. Unit testing: Use gotest packages, mocks, and stubs for isolation, and code coverage tools to ensure sufficiency. Deployment and monitoring: Use Docker containers to package deployments, set up data backups, and track performance and errors with logging and monitoring tools.




