 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 CSS Tutorial
CSS Tutorial
 Example of how to implement step-by-step registration login form with css3+html5
Example of how to implement step-by-step registration login form with css3+html5
Example of how to implement step-by-step registration login form with css3+html5
There are now many step-by-step login and registration forms, mainly to improve the user experience. Users can selectively fill in the corresponding form information, so that users will not be deterred by seeing a bunch of forms. What I share with you today is a step-by-step registration and login form based on HTML5 and CSS3. Needless to say, it looks very beautiful. You will know just by looking at the DEMO.
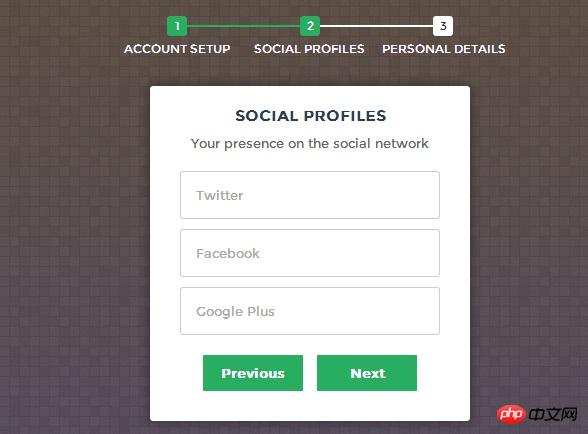
#Here is an online demonstration, you can see the effect first.
Next we will take a look at the implementation process. The code is a bit complicated and mainly consists of HTML code, CSS3 code and Javascript code.
HTML code:
<form id="msform">
<!-- progressbar -->
<ul id="progressbar">
<li>Account Setup</li>
<li>Social Profiles</li>
<li>Personal Details</li>
</ul>
<!-- fieldsets -->
<fieldset>
<h2 id="Create-nbsp-your-nbsp-account">Create your account</h2>
<h3 id="This-nbsp-is-nbsp-step-nbsp">This is step 1</h3>
<input type="text" name="email" placeholder="Email" />
<input type="password" name="pass" placeholder="Password" />
<input type="password" name="cpass" placeholder="Confirm Password" />
<input type="button" name="next" value="Next" />
</fieldset>
<fieldset>
<h2 id="Social-nbsp-Profiles">Social Profiles</h2>
<h3 id="Your-nbsp-presence-nbsp-on-nbsp-the-nbsp-social-nbsp-network">Your presence on the social network</h3>
<input type="text" name="twitter" placeholder="Twitter" />
<input type="text" name="facebook" placeholder="Facebook" />
<input type="text" name="gplus" placeholder="Google Plus" />
<input type="button" name="previous" value="Previous" />
<input type="button" name="next" value="Next" />
</fieldset>
<fieldset>
<h2 id="Personal-nbsp-Details">Personal Details</h2>
<h3 id="We-nbsp-will-nbsp-never-nbsp-sell-nbsp-it">We will never sell it</h3>
<input type="text" name="fname" placeholder="First Name" />
<input type="text" name="lname" placeholder="Last Name" />
<input type="text" name="phone" placeholder="Phone" />
<textarea name="address" placeholder="Address"></textarea>
<input type="button" name="previous" value="Previous" />
<input type="submit" name="submit" value="Submit" />
</fieldset></form>The HTML code looks like a lot, but it is very simple. It mainly describes a form.
CSS code:
/*form styles*/#msform {
width: 400px;
margin: 50px auto;
text-align: center;
position: relative;
}#msform fieldset {
background: white;
border: 0 none;
border-radius: 3px;
box-shadow: 0 0 15px 1px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.4);
padding: 20px 30px;
box-sizing: border-box;
width: 80%;
margin: 0 10%; /*stacking fieldsets above each other*/
position: absolute;
}/*Hide all except first fieldset*/#msform fieldset:not(:first-of-type) {
display: none;
}/*inputs*/#msform input, #msform textarea {
padding: 15px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 3px;
margin-bottom: 10px;
width: 100%;
box-sizing: border-box;
font-family: montserrat;
color: #2C3E50;
font-size: 13px;
}/*buttons*/#msform .action-button {
width: 100px;
background: #27AE60;
font-weight: bold;
color: white;
border: 0 none;
border-radius: 1px;
cursor: pointer;
padding: 10px 5px;
margin: 10px 5px;
}#msform .action-button:hover, #msform .action-button:focus {
box-shadow: 0 0 0 2px white, 0 0 0 3px #27AE60;
}/*headings*/.fs-title {
font-size: 15px;
text-transform: uppercase;
color: #2C3E50;
margin-bottom: 10px;
}.fs-subtitle {
font-weight: normal;
font-size: 13px;
color: #666;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}/*progressbar*/#progressbar {
margin-bottom: 30px;
overflow: hidden; /*CSS counters to number the steps*/
counter-reset: step;
}#progressbar li {
list-style-type: none;
color: white;
text-transform: uppercase;
font-size: 9px;
width: 33.33%;
float: left;
position: relative;
}#progressbar li:before {
content: counter(step);
counter-increment: step;
width: 20px;
line-height: 20px;
display: block;
font-size: 10px;
color: #333;
background: white;
border-radius: 3px;
margin: 0 auto 5px auto;
}/*progressbar connectors*/#progressbar li:after {
content: '';
width: 100%;
height: 2px;
background: white;
position: absolute;
left: -50%;
top: 9px;
z-index: -1; /*put it behind the numbers*/}#progressbar li:first-child:after { /*connector not needed before the first step*/
content: none;
}/*marking active/completed steps green*//*The number of the step and the connector before it = green*/#progressbar li.active:before, #progressbar li.active:after{
background: #27AE60;
color: white;
}Here we just posted the CSS code for rendering the form, which makes our form look very fresh and natural. Another point to note is that here we use the :before attribute of CSS3.
The last is the Javascript code, which can realize the step jump of the registration form.
Javascript code:
var current_fs, next_fs, previous_fs; //fieldsets
var left, opacity, scale; //fieldset properties which we will animate
var animating; //flag to prevent quick multi-click glitches
$(".next").click(function(){ if(animating) return false;
animating = true;
current_fs = $(this).parent();
next_fs = $(this).parent().next(); //activate next step on progressbar using the index of next_fs
$("#progressbar li").eq($("fieldset").index(next_fs)).addClass("active"); //show the next fieldset next_fs.show();
//hide the current fieldset with style
current_fs.animate({opacity: 0}, {
step: function(now, mx) { //as the opacity of current_fs reduces to 0 - stored in "now"
//1. scale current_fs down to 80%
scale = 1 - (1 - now) * 0.2; //2. bring next_fs from the right(50%)
left = (now * 50)+"%"; //3. increase opacity of next_fs to 1 as it moves in
opacity = 1 - now;
current_fs.css({'transform': 'scale('+scale+')'});
next_fs.css({'left': left, 'opacity': opacity});
},
duration: 800,
complete: function(){
current_fs.hide();
animating = false;
},
//this comes from the custom easing plugin
easing: 'easeInOutBack'
});
});
$(".previous").click(function(){ if(animating) return false;
animating = true;
current_fs = $(this).parent();
previous_fs = $(this).parent().prev(); //de-activate current step on progressbar
$("#progressbar li").eq($("fieldset").index(current_fs)).removeClass("active"); //show the previous fieldset previous_fs.show();
//hide the current fieldset with style
current_fs.animate({opacity: 0}, {
step: function(now, mx) { //as the opacity of current_fs reduces to 0 - stored in "now"
//1. scale previous_fs from 80% to 100%
scale = 0.8 + (1 - now) * 0.2; //2. take current_fs to the right(50%) - from 0%
left = ((1-now) * 50)+"%"; //3. increase opacity of previous_fs to 1 as it moves in
opacity = 1 - now;
current_fs.css({'left': left});
previous_fs.css({'transform': 'scale('+scale+')', 'opacity': opacity});
},
duration: 800,
complete: function(){
current_fs.hide();
animating = false;
},
//this comes from the custom easing plugin
easing: 'easeInOutBack'
});
});
$(".submit").click(function(){ return false;
})Here we can see that using jQuery code becomes very simple. There are mainly 3 events: next, previous, and submit. At the same time, jQuery is used to achieve the fade-in and fade-out animation effect during next and previous.
The above is the detailed content of Example of how to implement step-by-step registration login form with css3+html5. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What does placeholder mean in vue
May 07, 2024 am 09:57 AM
What does placeholder mean in vue
May 07, 2024 am 09:57 AM
In Vue.js, the placeholder attribute specifies the placeholder text of the input element, which is displayed when the user has not entered content, provides input tips or examples, and improves form accessibility. Its usage is to set the placeholder attribute on the input element and customize the appearance using CSS. Best practices include being relevant to the input, being short and clear, avoiding default text, and considering accessibility.
 What does span mean in js
May 06, 2024 am 11:42 AM
What does span mean in js
May 06, 2024 am 11:42 AM
The span tag can add styles, attributes, or behaviors to text. It is used to: add styles, such as color and font size. Set attributes such as id, class, etc. Associated behaviors such as clicks, hovers, etc. Mark text for further processing or citation.
 What does rem mean in js
May 06, 2024 am 11:30 AM
What does rem mean in js
May 06, 2024 am 11:30 AM
REM in CSS is a relative unit relative to the font size of the root element (html). It has the following characteristics: relative to the root element font size, not affected by the parent element. When the root element's font size changes, elements using REM will adjust accordingly. Can be used with any CSS property. Advantages of using REM include: Responsiveness: Keep text readable on different devices and screen sizes. Consistency: Make sure font sizes are consistent throughout your website. Scalability: Easily change the global font size by adjusting the root element font size.
 What is node in js
May 07, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
What is node in js
May 07, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
Nodes are entities in the JavaScript DOM that represent HTML elements. They represent a specific element in the page and can be used to access and manipulate that element. Common node types include element nodes, text nodes, comment nodes, and document nodes. Through DOM methods such as getElementById(), you can access nodes and operate on them, including modifying properties, adding/removing child nodes, inserting/replacing nodes, and cloning nodes. Node traversal helps navigate within the DOM structure. Nodes are useful for dynamically creating page content, event handling, animation, and data binding.
 What language is the browser plug-in written in?
May 08, 2024 pm 09:36 PM
What language is the browser plug-in written in?
May 08, 2024 pm 09:36 PM
Browser plug-ins are usually written in the following languages: Front-end languages: JavaScript, HTML, CSS Back-end languages: C++, Rust, WebAssembly Other languages: Python, Java
 How to set unknown attributes in vscode vscode method to set unknown attributes
May 09, 2024 pm 02:43 PM
How to set unknown attributes in vscode vscode method to set unknown attributes
May 09, 2024 pm 02:43 PM
1. First, open the settings icon in the lower left corner and click the settings option. 2. Then, find the CSS column in the jumped window. 3. Finally, change the drop-down option in the unknownproperties menu to the error button.
 Can less files in vue introduce data?
May 07, 2024 pm 12:06 PM
Can less files in vue introduce data?
May 07, 2024 pm 12:06 PM
Yes, Less files in Vue can introduce data through CSS variables and Less mixins: create a JSON file containing data. Import JSON files using the @import rule. Access JSON data using CSS variables or Less mixins.
 Graphical steps for setting the default properties of CSS in Visual Studio 2019
May 09, 2024 pm 02:01 PM
Graphical steps for setting the default properties of CSS in Visual Studio 2019
May 09, 2024 pm 02:01 PM
1. Open Visual Studio 2019, find its option settings, and click CSS. 2. Here you can see the technical settings of the following attributes. 3. Now you can set text and fill borders here. 4. At this time, you can also set the floating positioning here. 5. At this moment, you can also set the border and background here to complete the operation. 6. Finally, click the OK button here to set the CSS default properties.





