Graphical tutorial on creating servlet using Java myeclipse
This article mainly introduces the relevant information of myeclipse to create servlets in detail, which has certain reference value. Interested friends can refer to it
Now let's create a web application, which is called [myservlet] Ok, as shown below:
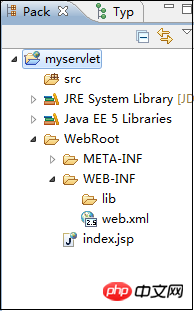
As you can see from the project window, as long as we create a web project, it will automatically create [WEB-INF] for us. directory, and create the [lib] directory and web.xml file under it. Let's take a look at the content of the web.xml file we just created:
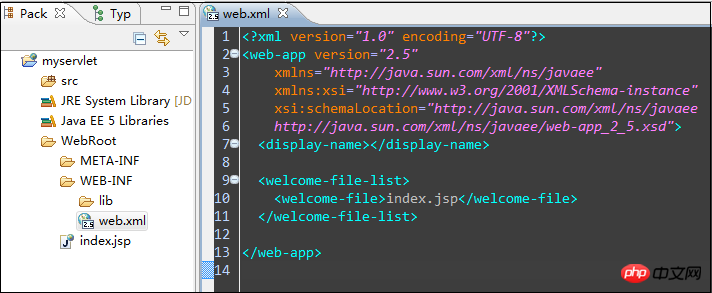
The Web.xml file only sets the homepage. Why look at this first? I will talk about it later.
Of course we can create a Servlet according to the method in "Servlet Learning (1)", that is, create a class to inherit the Servlet implementation class GenericServelet, override the service() method, and add it in the web.xml file Configure this Servlet.
but! ! ! We do not use the method of inheriting the GenericServelet class, but inherit the HttpServlet class, a subclass of the GenericServelet class. What are the benefits of doing this? HttpServlet refers to a Servlet that can handle HTTP requests. It adds some HTTP protocol processing methods to the original Servlet interface, which is more powerful than the Servlet interface, so we only need to inherit the HttpServlet class. If you create a Servlet for a web project in MyEclipse, you can also see that MyEclipse inherits the Servlet you create from HttpServlet by default, as shown in the following figure:
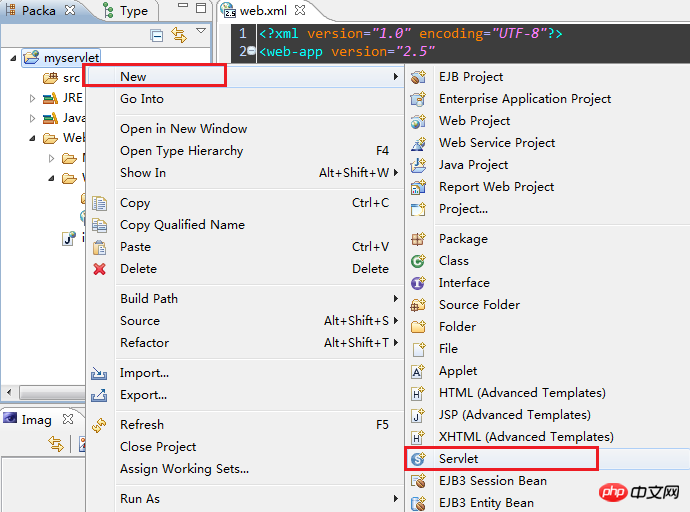
Select [Servlet] , pop up, write the package name and the name of the Servlet I want to create: SecondServlet, as shown below:
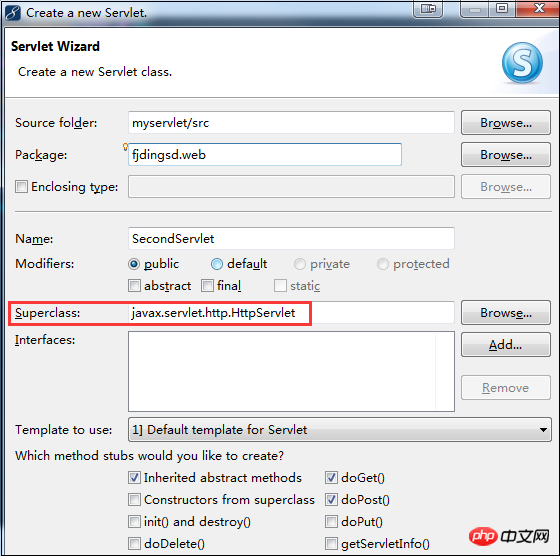
You can see that MyEclipse automatically selects the parent class of the Servlet you want to create as HttpServlet.
When we select the HttpServlet class as the Servlet parent class to inherit, then we should know that the HttpServlet class has overridden the service() method. The code in this method will automatically determine the user's request method. If it is GET For requests, the doGet() method of HttpServlet is called; if it is a POST request, the doPost() method is called. Therefore, when we develop, we only need to override the doGet() method or doPost() method, and there is no need to override the service. ()method. For details, please see the Servlet API documentation for details about HttpServlet.
We check the doGet method and doPost method, and add other methods according to the actual situation. Then click [Next] and you will see another setting window:
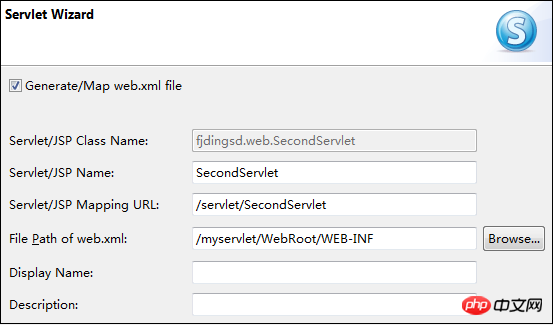
【Generate/Map web.xml file】: Map the created Servlet to the web.xml file , this can save us a lot of things. When we choose to map the Servlet into the web.xml file, we can set what content is mapped to the web.xml file according to the following specifications.
【Servlet/JSP Class Name】: This is the content in the
[Servlet/JSP Name]: Set the content in the
[Servlet/JSP Mapping URL]: Set the content of the
[File Path of web.xml]: The path of the web.xml, generally does not need to be set.
After clicking Finish, let’s take a look at the web.xml file again. Yes, the mapping from the Servlet to the web.xml file that we just set has been added by MyEclipse in the web.xml file, which saves us trouble. A lot. As shown in the figure below:
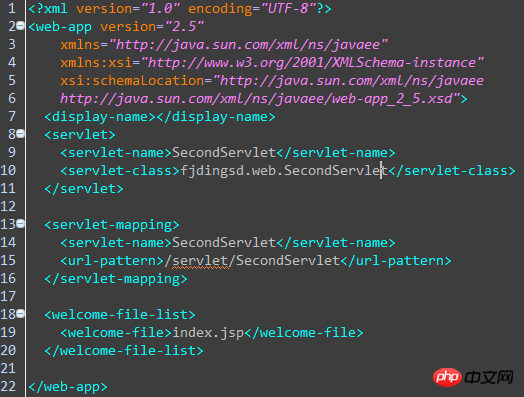
Let’s take a look at the content in the Servlet:
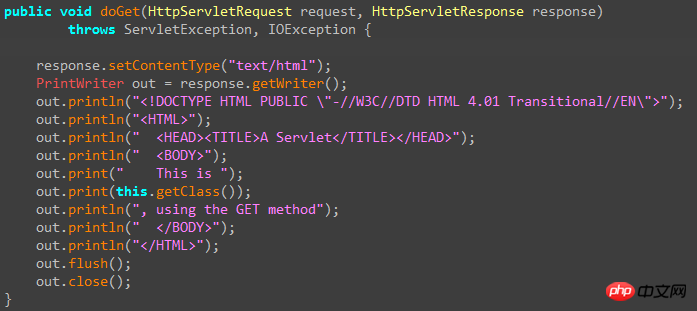
Yes, it’s a bit messy, This is because MyEclipse generates Servlets based on templates when creating them. Here we can remove these unnecessary codes first. In the last part, we will explain how to modify the Servlet template in MyEclipse.
In this Servlet development that inherits HttpServlet, we only care about the doGet method and the doPost method. If you don’t know when the http request is GET and when it is POST, you can use the following "clever" method To handle GET requests or POST requests at the same time in one method:
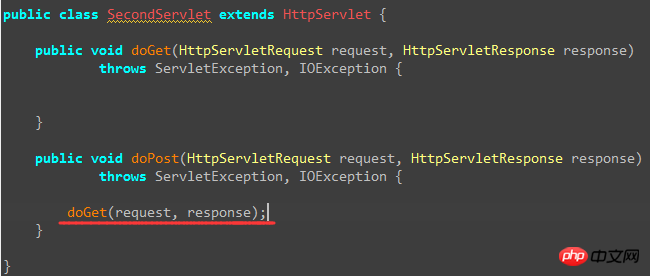
Just mentioned that the service() method in HttpServlet has overridden the service() method of its parent class GenericServlet, then let’s take a look at the service() method in HttpServlet, click the cursor on HttpServlet, and then press the keyboard "F3" key, you will find:
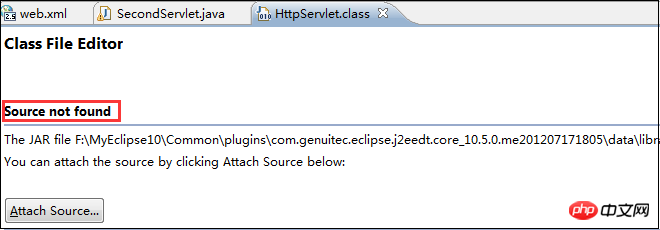
The Servlet jar package source code is missing. Here we have two solutions:
1. Go to the sun official website or Download the Servlet source code from the oracle official website;
2. Go to the Apache-Tomcat official website to download the Tomcat source code. Here I choose this method:
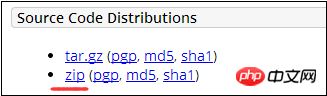 Just choose the zip format (looks like tar.gz is for Linux).
Just choose the zip format (looks like tar.gz is for Linux).
After downloading and decompressing, the directory is followed by the word "src":

Then we can click "Attach Source" in MyEclipse, because it is Import the entire directory, so select "External Folder". After importing, we can see the source code of HttpServlet and its service() method. The code is long and will not be attached here, but the idea is to get the request object first. HttpServletRequest request method, and then use if judgment to call different methods for each request, such as doGet method or doPost method.
Next we can safely return to the Servlet we just created and write code in the doGet method. We will simply write a simple return to the client with some data:
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
OutputStream out = response.getOutputStream();
out.write("Hello servlet again !".getBytes());
} Then start the server and publish the written Servlet
Finally, we can view it in the browser:
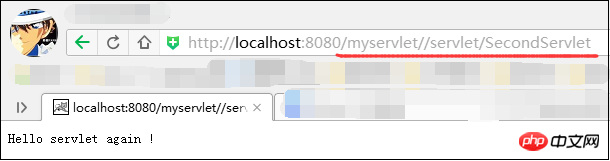
Note After entering the host address and port (if any) in the address bar, if the web.xml is not set otherwise, it will be followed by the web project name and the external access path you set for the Servlet in the web.xml file.
The above is the detailed content of Graphical tutorial on creating servlet using Java myeclipse. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to Square Root in Java. Here we discuss how Square Root works in Java with example and its code implementation respectively.
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in Java. Here we discuss Functions in Java with examples and two different Generators with ther examples.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to the Armstrong Number in Java. Here we discuss an introduction to Armstrong's number in java along with some of the code.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is






