How does MySQL database allow remote connections?
This article mainly introduces how to configure mysql under Linux to allow remote connections. Generally, we cannot connect remotely after installing mysql.
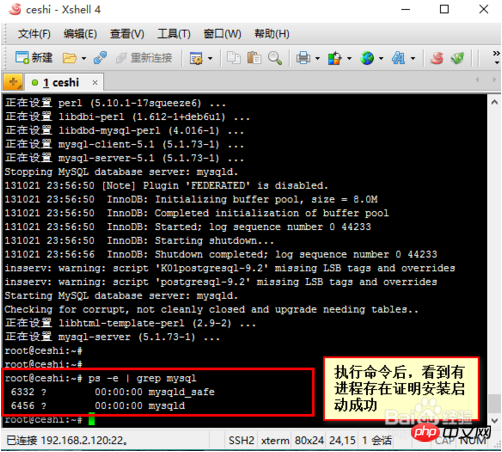
1. First, we install mysql on the linux system. By default in this article, the linux system can be connected to the Internet or the CD iso has been mounted. We use the command apt-get install mysql-server to install it. , after the installation is completed, check whether mysql is started and execute the command ps -e |grep mysql.
2. Verify whether remote connections are allowed initially. Since the virtual machine IP this time is 192.168.2.120, we execute mysql -h 192.168.20.120 -P 3306 -u root -proot (Note: -proot, root refers to the password of the root account), you can get the result that the connection cannot be made.
If we do not use remote connection, we can connect, the command is:
mysql -u root -proot。
# #3. Next, we connect to the database and execute the command use mysql; to use the mysql database.
And check the user table information, the execution command is:
select Host,User from user。
#4. Through the above steps, we can get the value in the data table user. Next, we update the record in the table to allow remote access,
The execution command is:update user set Host='%' where User ='root' limit 1;
5. Execute the forced refresh command flush privileges;
After execution, close Database Connectivity.
## 6. Change my.cnf in the mysql installation directory document.
Generally, the default path is under /etc/mysql/. Find the line bind-address = 127.0.0.1. You can delete it, comment it or change 127.0.0.1 to 0.0.0.0 and modify it. Save when finished.
#Notes
Make sure“update user set Host='%' where User ='root' limit 1”
The above is the detailed content of How does MySQL database allow remote connections?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to use MySQL backup and restore in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 12:19 PM
How to use MySQL backup and restore in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 12:19 PM
Backing up and restoring a MySQL database in PHP can be achieved by following these steps: Back up the database: Use the mysqldump command to dump the database into a SQL file. Restore database: Use the mysql command to restore the database from SQL files.
 How to optimize MySQL query performance in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 08:11 PM
How to optimize MySQL query performance in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 08:11 PM
MySQL query performance can be optimized by building indexes that reduce lookup time from linear complexity to logarithmic complexity. Use PreparedStatements to prevent SQL injection and improve query performance. Limit query results and reduce the amount of data processed by the server. Optimize join queries, including using appropriate join types, creating indexes, and considering using subqueries. Analyze queries to identify bottlenecks; use caching to reduce database load; optimize PHP code to minimize overhead.
 How to insert data into a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:26 PM
How to insert data into a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:26 PM
How to insert data into MySQL table? Connect to the database: Use mysqli to establish a connection to the database. Prepare the SQL query: Write an INSERT statement to specify the columns and values to be inserted. Execute query: Use the query() method to execute the insertion query. If successful, a confirmation message will be output.
 How to create a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 01:57 PM
How to create a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 01:57 PM
Creating a MySQL table using PHP requires the following steps: Connect to the database. Create the database if it does not exist. Select a database. Create table. Execute the query. Close the connection.
 How to use MySQL stored procedures in PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:13 PM
How to use MySQL stored procedures in PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:13 PM
To use MySQL stored procedures in PHP: Use PDO or the MySQLi extension to connect to a MySQL database. Prepare the statement to call the stored procedure. Execute the stored procedure. Process the result set (if the stored procedure returns results). Close the database connection.
 How to fix mysql_native_password not loaded errors on MySQL 8.4
Dec 09, 2024 am 11:42 AM
How to fix mysql_native_password not loaded errors on MySQL 8.4
Dec 09, 2024 am 11:42 AM
One of the major changes introduced in MySQL 8.4 (the latest LTS release as of 2024) is that the "MySQL Native Password" plugin is no longer enabled by default. Further, MySQL 9.0 removes this plugin completely. This change affects PHP and other app
 iOS 18 adds a new 'Recovered' album function to retrieve lost or damaged photos
Jul 18, 2024 am 05:48 AM
iOS 18 adds a new 'Recovered' album function to retrieve lost or damaged photos
Jul 18, 2024 am 05:48 AM
Apple's latest releases of iOS18, iPadOS18 and macOS Sequoia systems have added an important feature to the Photos application, designed to help users easily recover photos and videos lost or damaged due to various reasons. The new feature introduces an album called "Recovered" in the Tools section of the Photos app that will automatically appear when a user has pictures or videos on their device that are not part of their photo library. The emergence of the "Recovered" album provides a solution for photos and videos lost due to database corruption, the camera application not saving to the photo library correctly, or a third-party application managing the photo library. Users only need a few simple steps
 Detailed tutorial on establishing a database connection using MySQLi in PHP
Jun 04, 2024 pm 01:42 PM
Detailed tutorial on establishing a database connection using MySQLi in PHP
Jun 04, 2024 pm 01:42 PM
How to use MySQLi to establish a database connection in PHP: Include MySQLi extension (require_once) Create connection function (functionconnect_to_db) Call connection function ($conn=connect_to_db()) Execute query ($result=$conn->query()) Close connection ( $conn->close())













