JAVA--Example of how to install Nginx server under CentOS
1. nginx installation environment
nginx is developed in C language and is recommended to be run on Linux. This tutorial uses Centos7 as the installation environment.
1.1 gcc
To install nginx, you need to compile the source code downloaded from the official website first. The compilation depends on the gcc environment. If there is no gcc environment, you need to install gcc: yum install gcc-c++
1.2 PCRE
PCRE (Perl Compatible Regular Expressions) is a Perl library, including a perl-compatible regular expression library. The http module of nginx uses pcre to parse regular expressions, so the pcre library needs to be installed on Linux.
yum install -y pcre pcre-devel
Note: pcre-devel is a secondary development library developed using pcre. nginx also requires this library.
1.3 zlib
The zlib library provides many compression and decompression methods. nginx uses zlib to gzip the contents of the http package, so the zlib library needs to be installed on Linux.
yum install -y zlib zlib-devel
1.4 openssl
OpenSSL is a powerful Secure Sockets Layer cryptographic library, including major Cryptographic algorithms, commonly used key and certificate encapsulation management functions and SSL protocols, and provides a wealth of applications for testing or other purposes.
nginx not only supports http protocol, but also supports https (that is, transmitting http over ssl protocol), so you need to install the openssl library on Linux.
yum install -y openssl openssl-devel
2. Compile and install
2.1 Official website download
Download .tar directly. gz installation package
2.2 Unzip
tar -zxvf nginx-1.12.1.tar.gz cd nginx-1.12.1
2.3 Configuration
Actually in nginx-1.10. In version 1, you don’t need to configure related things, the default is fine. Of course, it is also possible if you want to configure the directory yourself.
1. Use the default configuration (recommended)
./configure
2. Customize the configuration (not recommended)
Note: To specify the temporary file directory as /var/temp/nginx, you first need to create the temp and nginx directories under /var (/var/temp/nginx)
./configure \--prefix=/usr/local/nginx \--conf-path=/usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf \--pid-path=/usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.pid \--lock-path=/var/lock/nginx.lock \--error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log \--http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log \--with-http_gzip_static_module \--http-client-body-temp-path=/var/temp/nginx/client \--http-proxy-temp-path=/var/temp/nginx/proxy \--http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/temp/nginx/fastcgi \--http-uwsgi-temp-path=/var/temp/nginx/uwsgi \--http-scgi-temp-path=/var/temp/nginx/scgi
3. Compile and install
make make install
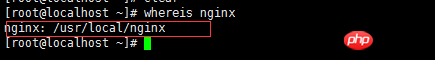
After the compilation and installation are completed, you can view the installation path of nginx:
whereis nginx
4. Start and stop nginx
cd /usr/local/nginx/sbin/./nginx ./nginx -s stop ./nginx -s quit ./nginx -s reload ./nginx -s quit:此方式停止步骤是待nginx进程处理任务完毕进行停止。 ./nginx -s stop:此方式相当于先查出nginx进程id再使用kill命令强制杀掉进程。
5. Query nginx process
ps aux|grep nginx
Restart nginx
1. Stop and then start (recommended):
Restarting nginx is equivalent to stopping and then starting, that is, executing first Stop command and then execute start command. As follows:
./nginx -s quit ./nginx
2. Reload the configuration file:
When the nginx configuration file nginx.conf is modified, a restart is required for the configuration to take effect. nginx, use -s reload to make the configuration information effective in nginx without first stopping ngin Corresponding to the IP address of the machine (such as: 192.168.1.121), you can see a page like this:
2.4 Auto-start at boot
That is, in rc.local Just add the startup code. 
./nginx -s reload
Add a line to /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
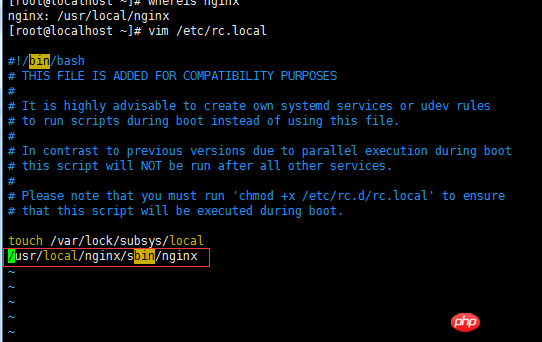
vim /etc/rc.local
The above is the detailed content of JAVA--Example of how to install Nginx server under CentOS. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to optimize CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
How to optimize CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
Improve HDFS performance on CentOS: A comprehensive optimization guide to optimize HDFS (Hadoop distributed file system) on CentOS requires comprehensive consideration of hardware, system configuration and network settings. This article provides a series of optimization strategies to help you improve HDFS performance. 1. Hardware upgrade and selection resource expansion: Increase the CPU, memory and storage capacity of the server as much as possible. High-performance hardware: adopts high-performance network cards and switches to improve network throughput. 2. System configuration fine-tuning kernel parameter adjustment: Modify /etc/sysctl.conf file to optimize kernel parameters such as TCP connection number, file handle number and memory management. For example, adjust TCP connection status and buffer size
 Centos stops maintenance 2024
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Centos stops maintenance 2024
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
CentOS will be shut down in 2024 because its upstream distribution, RHEL 8, has been shut down. This shutdown will affect the CentOS 8 system, preventing it from continuing to receive updates. Users should plan for migration, and recommended options include CentOS Stream, AlmaLinux, and Rocky Linux to keep the system safe and stable.
 How to check CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
How to check CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
Complete Guide to Checking HDFS Configuration in CentOS Systems This article will guide you how to effectively check the configuration and running status of HDFS on CentOS systems. The following steps will help you fully understand the setup and operation of HDFS. Verify Hadoop environment variable: First, make sure the Hadoop environment variable is set correctly. In the terminal, execute the following command to verify that Hadoop is installed and configured correctly: hadoopversion Check HDFS configuration file: The core configuration file of HDFS is located in the /etc/hadoop/conf/ directory, where core-site.xml and hdfs-site.xml are crucial. use
 Centos shutdown command line
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
Centos shutdown command line
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
The CentOS shutdown command is shutdown, and the syntax is shutdown [Options] Time [Information]. Options include: -h Stop the system immediately; -P Turn off the power after shutdown; -r restart; -t Waiting time. Times can be specified as immediate (now), minutes ( minutes), or a specific time (hh:mm). Added information can be displayed in system messages.
 How to create a mirror in docker
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:27 AM
How to create a mirror in docker
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:27 AM
Steps to create a Docker image: Write a Dockerfile that contains the build instructions. Build the image in the terminal, using the docker build command. Tag the image and assign names and tags using the docker tag command.
 Tips for using HDFS file system on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:30 PM
Tips for using HDFS file system on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:30 PM
The Installation, Configuration and Optimization Guide for HDFS File System under CentOS System This article will guide you how to install, configure and optimize Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) on CentOS System. HDFS installation and configuration Java environment installation: First, make sure that the appropriate Java environment is installed. Edit /etc/profile file, add the following, and replace /usr/lib/java-1.8.0/jdk1.8.0_144 with your actual Java installation path: exportJAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/java-1.8.0/jdk1.8.0_144exportPATH=$J
 What files do you need to modify in HDFS configuration CentOS?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:27 PM
What files do you need to modify in HDFS configuration CentOS?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:27 PM
When configuring Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) on CentOS, the following key configuration files need to be modified: core-site.xml: fs.defaultFS: Specifies the default file system address of HDFS, such as hdfs://localhost:9000. hadoop.tmp.dir: Specifies the storage directory for Hadoop temporary files. hadoop.proxyuser.root.hosts and hadoop.proxyuser.ro
 Difference between centos and ubuntu
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
Difference between centos and ubuntu
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
The key differences between CentOS and Ubuntu are: origin (CentOS originates from Red Hat, for enterprises; Ubuntu originates from Debian, for individuals), package management (CentOS uses yum, focusing on stability; Ubuntu uses apt, for high update frequency), support cycle (CentOS provides 10 years of support, Ubuntu provides 5 years of LTS support), community support (CentOS focuses on stability, Ubuntu provides a wide range of tutorials and documents), uses (CentOS is biased towards servers, Ubuntu is suitable for servers and desktops), other differences include installation simplicity (CentOS is thin)




