 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Detailed explanation of graphic code for line wrapping of print function in Python3
Detailed explanation of graphic code for line wrapping of print function in Python3
Detailed explanation of graphic code for line wrapping of print function in Python3
I was learning python3 recently and found a problem that I wanted to summarize. So the following article mainly introduces you to the relevant information about the line wrapping of the print function in Python 3. The article introduces it in detail through the example code and provides the necessary information. Friends, it has certain reference and learning value. Friends who are interested, please follow the editor to learn together.
Preface
Due to work needs, I recently looked at Python applications, starting with the entry-level multiplication table, and found that There are really big differences between Python3.
#Code in Python2. . There are two issues involved here: First, at the end of the
print() function in the inner loop, in Pyhon2,
print()
Figure 1
Running in Linux is shown in Figure 2,
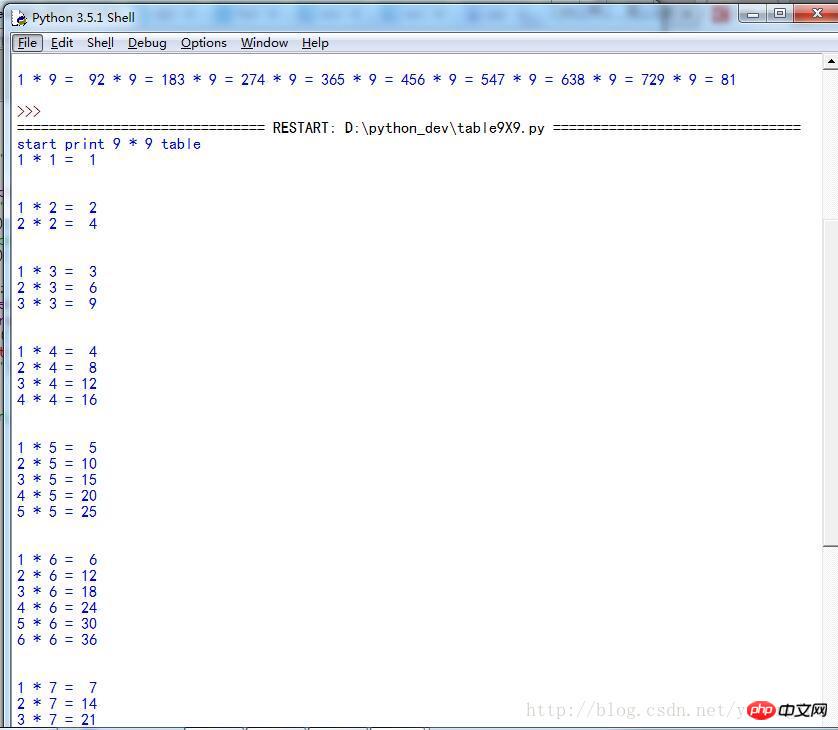
Figure 2
It can be seen that, There is no line break. The reason is that in Python3, line break adopts new syntax, which is in the form of
print('*', end=”)
print()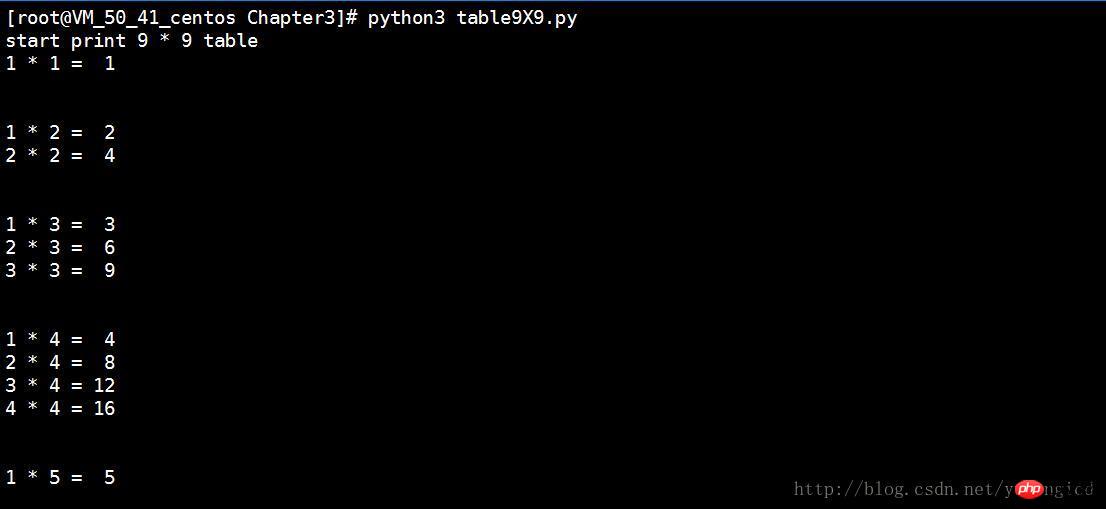 The second parameter of the function is added with end=", modified and run. The final running result is as shown in Figure 3,
The second parameter of the function is added with end=", modified and run. The final running result is as shown in Figure 3,
Figure 3Normal output.
xrange()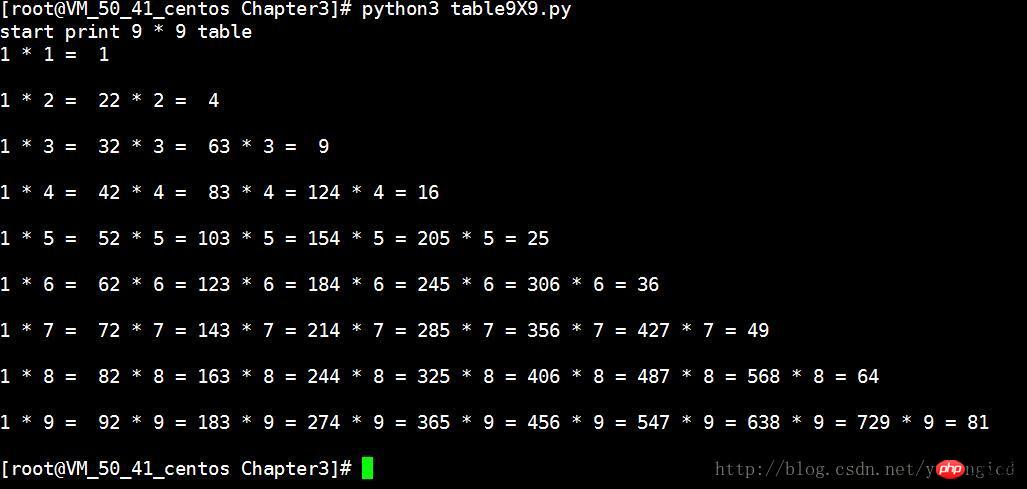 function, if you just modified the
function, if you just modified the
function syntax, if you don’t pay attention to
xrange()
##Figure 4 The prompt here says 'xrange' is not defined. In fact, in Python3, the xrange() function has been integrated into the
range()
range()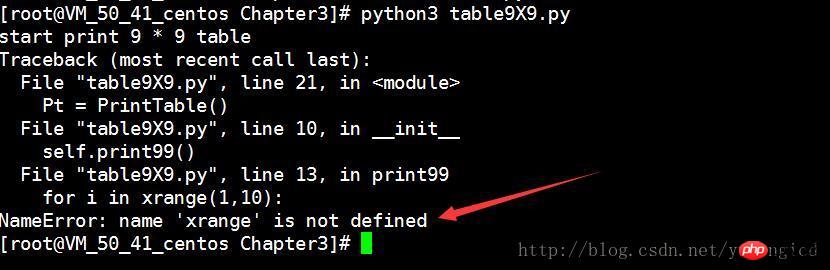 function is used uniformly.
function is used uniformly.
OK, after modification, the normal result in Figure 3 will be output.
Summarize
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of graphic code for line wrapping of print function in Python3. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What are the revenue rules for Baijiahao graphics and text? Can you make money by doing graphics?
Mar 24, 2024 am 09:41 AM
What are the revenue rules for Baijiahao graphics and text? Can you make money by doing graphics?
Mar 24, 2024 am 09:41 AM
As a self-media platform under Baidu, Baijiahao provides a platform for many creators to showcase their talents and share knowledge. For these self-media creators, the revenue rules for images and texts are undoubtedly a topic of great concern. 1. What are the revenue rules for Baijiahao graphics and text? Baijiahao graphics and text revenue rules are mainly divided into three parts: traffic reward mechanism, advertising revenue sharing and paid subscription revenue. The traffic reward mechanism refers to the evaluation based on the quality, reading volume and communication effect of original content, and corresponding rewards are given based on the evaluation results. This means that if your articles are of high quality, read a lot, and spread widely, you will have the opportunity to receive more rewards. Advertising revenue sharing means inserting advertising links into your own content or conducting cooperative promotions, and you will receive a certain amount after users click on the ads.
 Where is print on the keyboard?
Jun 19, 2023 am 09:37 AM
Where is print on the keyboard?
Jun 19, 2023 am 09:37 AM
The printscreen key is on the arrow keys of the keyboard device, with the words "prtsc sysrq" on it, and is located to the right of f12. If there is no button with the word "prtsc sysrq", you can find "fn" and "insert(prt sc)", click "fn" first, and then click "insert(PRT sc)" to realize the printscreen screenshot function.
 How to install pip in python3
Dec 20, 2023 pm 05:42 PM
How to install pip in python3
Dec 20, 2023 pm 05:42 PM
Installation steps: 1. Make sure that Python3 has been installed and can be accessed through the command line; 2. Open the terminal and enter the "python3 -m ensurepip --upgrade" command to install pip; 3. Download the pip installation package from the official Python website; 4. Extract the downloaded pip installation package into a directory; 5. Open the terminal and navigate to the decompressed pip directory; 6. Run the "python3 setup.py install" command to install pip.
 Introduction to Python functions: functions and usage examples of the print function
Nov 03, 2023 pm 04:33 PM
Introduction to Python functions: functions and usage examples of the print function
Nov 03, 2023 pm 04:33 PM
Python is a popular programming language designed to make computer programming simpler and easier to understand. In Python, using the print function to output text to the console is a basic task. In this article, we'll introduce Python's print function, explore its capabilities and usage examples, and provide code examples to help you better understand how to use the function. Python's print function is a built-in function used to output text and the value of a variable. Its syntax is very simple. You just need to
 Using the print function in Python
Feb 18, 2024 pm 02:48 PM
Using the print function in Python
Feb 18, 2024 pm 02:48 PM
Python is a simple and easy-to-learn high-level programming language that is widely used in data analysis, artificial intelligence, web development and other fields. In Python, print is a commonly used function used to output results or debugging information on the screen. This article will introduce the usage of the print function in detail and provide specific code examples to help readers better master it. First, the print function can accept multiple parameters and print them to the screen. These parameters can be strings, integers, floating point numbers, etc., or even variables,
 What does print mean in vb
Jan 18, 2021 am 10:47 AM
What does print mean in vb
Jan 18, 2021 am 10:47 AM
Print in VB is an output statement. Under the WINDOWS graphical interface, this statement is not necessary; and in the VB.NET version, Print as a print output no longer exists.
 Write a C macro PRINT(x) which prints x
Sep 19, 2023 pm 01:25 PM
Write a C macro PRINT(x) which prints x
Sep 19, 2023 pm 01:25 PM
Here we will see how to define a macro called PRINT(x), which will print any value of x passed as argument. To solve this problem we will use stringize operator. Use this operator to convert x to a string and then by calling the printf() function internally, the value of x will be printed. Let's look at an example to get a better idea. Example #include<stdio.h>#definePRINT(x)printf(#x)intmain(){ PRINT(Hello); printf(&q
 String formatting in Python: How to use the format() function
Apr 22, 2023 pm 07:01 PM
String formatting in Python: How to use the format() function
Apr 22, 2023 pm 07:01 PM
Method of inserting variables into a string The format() function in Python is a method of inserting variables into a string, which can make the string easier to read and understand. It supports many different usages. The following are specific usages and instructions: Use positional parameters to pass variables name='John'age=25print('Mynameis{},andIam{}yearsold.'.format(name,age))#output :MynameisJohn,andIam25yearsold. Use the index to pass the variable name='





