
1. Full page static caching
That is, all pages are generated into html static pages. The static pages are directly accessed when users visit, without going to the PHP server to parse them. process. This method is more common in CMS systems, such as dedecms;
A more common implementation method is to use output caching:
Ob_start() ******要运行的代码******* $content = Ob_get_contents(); ****将缓存内容写入html文件***** Ob_end_clean();
2. Page partial caching
This method is to statically cache the infrequently changing parts of a page, while frequently changing blocks are not cached, and are finally assembled together for display; it can be implemented using a method similar to ob_get_contents, or you can use Page fragment caching strategies such as ESI are used to cache relatively static fragments in dynamic pages.
The content of any Web website is constantly updated and changing, but this does not mean that The content of this website is dynamic content. In fact, dynamic content refers to the content that users get every time they click on the same link. It is generated by a Web server application, such as common ASP, JSP, etc., corresponding to this , Static content generally refers to consisting of text, images and multimedia, which basically remains unchanged every time the user clicks the corresponding link. The latest technology to solve dynamic content caching is to design the content of the website through ESI technology.
How ESI technology works
Dynamically generated content can bring rich and exciting pages to users , Website developers can also control related content more easily and flexibly, but while enjoying these conveniences, it also increases the processing pressure on the website database and application server. When the number of visits to a website increases, the investment in hardware and databases is very huge. Even so, it may still cause serious delays in the page or even access failure.
The fundamental reason why users access dynamically generated content is slow is that dynamically generated content needs to go through a complex process. First, the user's request is assigned to the application server based on the user's request. In the corresponding software module, the software module must determine what kind of data needs to be extracted from the database to the user through calculations, and then extract the corresponding data from the database and pass it to the user in the defined format. These lengthy processes result in slower user access and increase the load on the server.
In the actual environment, a dynamically generated page may have only a small amount of content that changes frequently or is personalized. For traditional Cache servers, in order to ensure The timeliness of the page, but due to the small amount of dynamic content in the page, the entire page cannot be cached. ESI (Edge Side Include) uses a simple markup language to describe content fragments in web pages that can and cannot be accelerated. Each web page is divided into different small parts and assigned different cache control strategies, so that Cache Based on these policies, the server can dynamically combine different small parts together before sending the complete web page to the user. Through this control, the number of times to crawl the entire page from the server can be effectively reduced, and only a small number of fragments that cannot be cached are extracted from the original server. Therefore, the load of the original server can be effectively reduced and the response time of user access can be improved.
ESI is a simple markup language that developers can use to mark content fragments to speed up caching through the corresponding Cache server. At the same time, ESI also defines a set of content validation standards, which can realize the management of cached content in the Cache server by the original server and improve the website's ability to control content. The CDN network can also provide CDN services for the dynamic content of the website by installing Cache servers that support ESI in nodes distributed across the country.
This method can be used for product pages in shopping malls;
3. Data caching
As the name suggests, it caches data One way; for example, when a certain product information in the mall is requested using the product ID, data including store information, product information, etc. can be cached in a php file. The name contains the product id to create a unique identifier; the next time someone wants to view this product, they will first directly adjust the information in this file without querying the database; in fact, what is cached in the cache file is a php array;
This method is used in the Ecmall mall system;
4. Query cache
其实这跟数据缓存是一个思路,就是根据查询语句来缓存;将查询得到的数据缓存在一个文件中,下次遇到相同的查询时,就直接先从这个文件里面调数据,不会再去查数据库;但此处的缓存文件名可能就需要以查询语句为基点来建立唯一标示;
按时间变更进行缓存
其实,这一条不是真正的缓存方式;上面的2、3、4的缓存技术一般都用到了时间变更判断;就是对于缓存文件您需要设一个有效时间,在这个有效时间 内,相同的访问才会先取缓存文件的内容,但是超过设定的缓存时间,就需要重新从数据库中获取数据,并生产最新的缓存文件;比如,我将我们商城的首页就是设 置2个小时更新一次;
5、按内容变更进行缓存
这个也并非独立的缓存技术,需结合着用;就是当数据库内容被修改时,即刻更新缓存文件;
比如,一个人流量很大的商城,商品很多,商品表必然比较大,这表的压力也比较重;我们就可以对商品显示页进行页面缓存;
当商家在后台修改这个商品的信息时,点击保存,我们同时就更新缓存文件;那么,买家访问这个商品信息时,实际上访问的是一个静态页面,而不需要再去访问数据库;
试想,如果对商品页不缓存,那么每次访问一个商品就要去数据库查一次,如果有10万人在线浏览商品,那服务器压力就大了;
6、内存式缓存
提到这个,可能大家想到的首先就是Memcached;memcached是高性能的分布式内存缓存服务器。 一般的使用目的是,通过缓存数据库查询结果,减少数据库访问次数,以提高动态Web应用的速度、 提高可扩展性。
它就是将需要缓存的信息,缓存到系统内存中,需要获取信息时,直接到内存中取;比较常用的方式就是 key–>value方式;
<?php
$memcachehost = '192.168.6.191';
$memcacheport = 11211;
$memcachelife = 60;
$memcache = new Memcache;
$memcache->connect($memcachehost,$memcacheport) or die ("Could not connect");
$memcache->set('key','缓存的内容');
$get = $memcache->get($key); //获取信息
?>7、apache缓存模块
apache安装完以后,是不允许被cache的。如果外接了cache或squid服务器要求进行web加速的话,就需要在htttpd.conf里进行设置,当然前提是在安装apache的时候要激活mod_cache的模块。
安装apache时:./configure –enable-cache –enable-disk-cache –enable-mem-cache
8、php APC缓存扩展
Php有一个APC缓存扩展,windows下面为php_apc.dll,需要先加载这个模块,然后是在php.ini里面进行配置:
[apc]
extension=php_apc.dll
apc.rfc1867 = on
upload_max_filesize = 100M
post_max_size = 100M
apc.max_file_size = 200M
upload_max_filesize = 1000M
post_max_size = 1000M
max_execution_time = 600 ; 每个PHP页面运行的最大时间值(秒),默认30秒
max_input_time = 600 ; 每个PHP页面接收数据所需的最大时间,默认60
memory_limit = 128M ; 每个PHP页面所吃掉的最大内存,默认8M9、Opcode缓存
我们知道,php的执行流程可以用下图来展示:
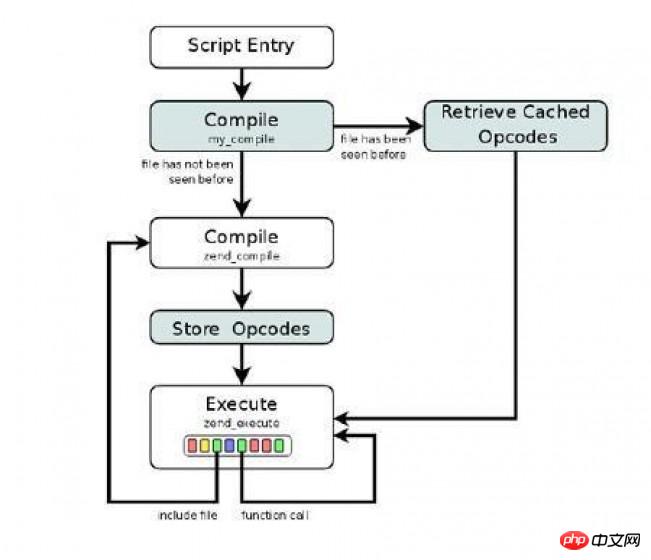
首先php代码被解析为Tokens,然后再编译为Opcode码,最后执行Opcode码,返回结果;所以,对于相同的php文件,第一次运行时 可以缓存其Opcode码,下次再执行这个页面时,直接会去找到缓存下的opcode码,直接执行最后一步,而不再需要中间的步骤了。
比较知名的是XCache、Turck MM Cache、PHP Accelerator等。
The above is the detailed content of An explanation of the summary of 9 major caching technologies in PHP. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




