Detailed explanation of examples of ActionMapping in Struts1
This article mainly introduces the ActionMapping of the Struts1 tutorial. The editor thinks it is quite good. Now I will share it with you and give it as a reference. Let’s follow the editor and take a look.
First of all, the breakpoint is out of the processpath method.
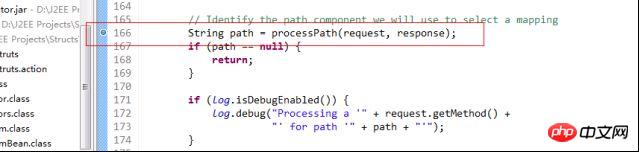
This method is used To intercept strings, today we will look at how to obtain the ActionMapping method---processMapping.
Before that, let’s briefly talk about ActionMapping. It can be seen from its source code that the most important attributes are similar to the ActionMapping in our mvc small instance. They all have path, type and forwardMap. The main ones are It comes from the corresponding struts-config configuration file. This is to save the information of this configuration file into memory.
The ActionMapping code of the specific mvc small instance is as follows:
package com.cjq.servlet;
import java.util.Map;
public class ActionMapping {
private String path;
private Object type;
private Map forwardMap;
public String getPath() {
return path;
}
public void setPath(String path) {
this.path = path;
}
public Object getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(Object type) {
this.type = type;
}
public Map getForwardMap() {
return forwardMap;
}
public void setForwardMap(Map forwardMap) {
this.forwardMap = forwardMap;
}
}And the Actionconfig in Struts (because ActionMapping inherits this ActionConfig, so let’s take a look ActionConfig is more direct) The code is as follows:


##
/**
* <p>Select the mapping used to process theselection path for this request
* If no mapping can be identified, createan error response and return
* <code>null</code>.</p>
*
* @param request The servlet request weare processing
* @param response The servlet response weare creating
* @param path The portion of the requestURI for selecting a mapping
*
* @exception IOException if an input/outputerror occurs
*/
protectedActionMapping processMapping(HttpServletRequestrequest,
HttpServletResponse response,
String path)
throws IOException {
// Is there a mapping for this path?
ActionMapping mapping = (ActionMapping)
moduleConfig.findActionConfig(path);
// If a mapping is found, put it in the request and return it
if (mapping != null) {
request.setAttribute(Globals.MAPPING_KEY, mapping);
return (mapping);
}
// Locate the mapping for unknown paths (if any)
ActionConfig configs[] = moduleConfig.findActionConfigs();
for (int i = 0; i < configs.length; i++) {
if (configs[i].getUnknown()) {
mapping = (ActionMapping)configs[i];
request.setAttribute(Globals.MAPPING_KEY, mapping);
return (mapping);
}
}
// No mapping can be found to process this request
String msg = getInternal().getMessage("processInvalid");
log.error(msg + " " + path);
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND, msg);
return null;
}First we pass in the path we intercepted in the previous step , find ActionConfig through the findAction method of moduleConfig, and return ActionMapping. The specific code is:
ActionMapping mapping =(ActionMapping) moduleConfig.findActionConfig(path);
If found, then the ActionMapping is stored in the context of the request. Code:
if (mapping != null) {
request.setAttribute(Globals.MAPPING_KEY, mapping);
return (mapping);
}If the mapping is not found through the path, traverse the Actionconfig to find the mapping for the unknown path. If it is found, it will be stored in the request. If it is not found, , the error message is returned. The specific code is as follows:
// Locate the mapping for unknownpaths (if any)
ActionConfig configs[] = moduleConfigfindActionConfigs();
for (int i = 0; i < configslength; i++) {
if (configs[i].getUnknown()) {
mapping = (ActionMapping)configs[i];
request.setAttribute(Globals.MAPPING_KEY, mapping);
return (mapping);
}
}
// No mapping can be found to process this request
String msg = getInternal().getMessage("processInvalid");
log.error(msg + " " + path);
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND, msg);
return null;Let’s take a look at processActionForm, a method in ActionServlet. When we intercept the string, then according to the string After obtaining ActionMapping (which was introduced in the first two articles), we will use ActionMapping to create ActionForm, and put ActionForm in request or session for management.
Let’s first look at the specific implementation of the processActionForm method in struts:
/**
* <p>Retrieve and return the <code>ActionForm</code> associatedwith
* this mapping, creating and retaining oneif necessary. If there is no
* <code>ActionForm</code> associated with this mapping,return
* <code>null</code>.</p>
*
* @param request The servlet request weare processing
* @param response The servlet response weare creating
* @param mapping The mapping we are using
*/
protectedActionForm processActionForm(HttpServletRequestrequest,
HttpServletResponse response,
ActionMapping mapping) {
// Create (if necessary) a form bean to use
ActionForm instance = RequestUtilscreateActionForm
(request, mapping, moduleConfig, servlet);
if (instance == null) {
return (null);
}
// Store the new instance in the appropriate scope
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(" Storing ActionForm bean instance in scope '" +
mapping.getScope() + "' under attribute key '" +
mapping.getAttribute() + "'");
}
if ("request".equals(mapping.getScope())) {
request.setAttribute(mapping.getAttribute(), instance);
} else {
HttpSession session =requestgetSession();
session.setAttribute(mapping.getAttribute(), instance);
}
return (instance);
}The general process of this method is: According to ActionMapping Search the ActionForm by its name. If ActionForm is configured, search it in the request or session. If there is an ActionForm that has been created in the request or session, it will be returned. If it does not exist, it will be created using reflection according to the completion path of the ActionForm, and then the created ActionForm will be placed in the request or session, and then the ActionForm will be returned.
Specifically, we can follow breakpoint debugging to see how this method runs.
Set a breakpoint first, and then enter the processActionForm method.
The first step is to create an ActionForm:
// Create (if necessary) a formbean to use
ActionForm instance = RequestUtils.createActionForm
(request, mapping, moduleConfig, servlet);
if (instance == null) {
return (null);
}Generate an object from the ActionForm string in ActionMapping by calling the RequestUtils.createActionForm method. and return. Enter this code:
publicstaticActionForm createActionForm(
HttpServletRequest request,
ActionMapping mapping,
ModuleConfig moduleConfig,
ActionServlet servlet) {
// Is there a form bean associated with this mapping?
String attribute = mappinggetAttribute();
if (attribute == null) {
return (null);
}
// Look up the form bean configuration information to use
String name = mapping.getName();
FormBeanConfig config =moduleConfigfindFormBeanConfig(name);
if (config == null) {
log.warn("No FormBeanConfig found under '"+ name + "'");
return (null);
}
ActionForm instance = lookupActionForm(request,attribute, mappinggetScope());
// Can we recycle the existing form bean instance (if there is one)?
try {
if (instance != null && canReuseActionForm(instance,config)) {
return (instance);
}
} catch(ClassNotFoundException e) {
log.error(servlet.getInternal().getMessage("formBean",config.getType()), e);
return (null);
}
return createActionForm(config,servlet);
}The method first defines the variable name and gets the value from mapping, String name = mapping.getName(); that is, we LoginForm string in the instance. Afterwards, the corresponding LoginForm string is generated into the corresponding object by calling FormBeanConfig config =moduleConfig.findFormBeanConfig(name);.
What I want to explain here is that we have configured such a label information in the struts-config configuration file:
<form-beans>
<form-bean name="loginForm" type=".struts.LoginActionForm"/>
</form-beans>这个标签在服务器一启动的时候就会利用digester读取这里的配置信息,并且放在FormBeanConfig类中,这样我们可以通过上面那一句话就可以把LoginForm字符串生成相应的对象。
之后调用了ActionForm instance = lookupActionForm(request,attribute, mapping.getScope());这个方法,这个方法主要是查找scope属性中有没有存在ActionForm。具体实现:
if ("request".equals(scope)){
instance = (ActionForm)request.getAttribute(attribute);
} else {
session = request.getSession();
instance = (ActionForm)session.getAttribute(attribute);
}这里判断scope属性值是否为request,如果是则从request中读出ActionForm,如果不是则从session中读出。程序如果是第一次执行,那么ActionForm会是为空的。因为这里的ActionForm为空,所以就进入了if判断语句中,最后通过调用return createActionForm(config, servlet);创建ActionForm并且返回。
之后processActionForm就会把返回来的ActionForm放入request或者session中。具体实现就是:
if ("request".equals(mapping.getScope())){
request.setAttribute(mapping.getAttribute(), instance);
} else {
HttpSession session =request.getSession();
session.setAttribute(mapping.getAttribute(), instance);
}到此为止,ActionForm就创建完成,当ActionForm创建完成之后,就要用其他的方法来往ActionForm中赋值了
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of examples of ActionMapping in Struts1. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Detailed explanation of the mode function in C++
Nov 18, 2023 pm 03:08 PM
Detailed explanation of the mode function in C++
Nov 18, 2023 pm 03:08 PM
Detailed explanation of the mode function in C++ In statistics, the mode refers to the value that appears most frequently in a set of data. In C++ language, we can find the mode in any set of data by writing a mode function. The mode function can be implemented in many different ways, two of the commonly used methods will be introduced in detail below. The first method is to use a hash table to count the number of occurrences of each number. First, we need to define a hash table with each number as the key and the number of occurrences as the value. Then, for a given data set, we run
 Detailed explanation of obtaining administrator rights in Win11
Mar 08, 2024 pm 03:06 PM
Detailed explanation of obtaining administrator rights in Win11
Mar 08, 2024 pm 03:06 PM
Windows operating system is one of the most popular operating systems in the world, and its new version Win11 has attracted much attention. In the Win11 system, obtaining administrator rights is an important operation. Administrator rights allow users to perform more operations and settings on the system. This article will introduce in detail how to obtain administrator permissions in Win11 system and how to effectively manage permissions. In the Win11 system, administrator rights are divided into two types: local administrator and domain administrator. A local administrator has full administrative rights to the local computer
 Detailed explanation of division operation in Oracle SQL
Mar 10, 2024 am 09:51 AM
Detailed explanation of division operation in Oracle SQL
Mar 10, 2024 am 09:51 AM
Detailed explanation of division operation in OracleSQL In OracleSQL, division operation is a common and important mathematical operation, used to calculate the result of dividing two numbers. Division is often used in database queries, so understanding the division operation and its usage in OracleSQL is one of the essential skills for database developers. This article will discuss the relevant knowledge of division operations in OracleSQL in detail and provide specific code examples for readers' reference. 1. Division operation in OracleSQL
 Detailed explanation of remainder function in C++
Nov 18, 2023 pm 02:41 PM
Detailed explanation of remainder function in C++
Nov 18, 2023 pm 02:41 PM
Detailed explanation of the remainder function in C++ In C++, the remainder operator (%) is used to calculate the remainder of the division of two numbers. It is a binary operator whose operands can be any integer type (including char, short, int, long, etc.) or a floating-point number type (such as float, double). The remainder operator returns a result with the same sign as the dividend. For example, for the remainder operation of integers, we can use the following code to implement: inta=10;intb=3;
 Detailed explanation of the usage of Vue.nextTick function and its application in asynchronous updates
Jul 26, 2023 am 08:57 AM
Detailed explanation of the usage of Vue.nextTick function and its application in asynchronous updates
Jul 26, 2023 am 08:57 AM
Detailed explanation of the usage of Vue.nextTick function and its application in asynchronous updates. In Vue development, we often encounter situations where data needs to be updated asynchronously. For example, data needs to be updated immediately after modifying the DOM or related operations need to be performed immediately after the data is updated. The .nextTick function provided by Vue emerged to solve this type of problem. This article will introduce the usage of the Vue.nextTick function in detail, and combine it with code examples to illustrate its application in asynchronous updates. 1. Vue.nex
 Detailed explanation of php-fpm tuning method
Jul 08, 2023 pm 04:31 PM
Detailed explanation of php-fpm tuning method
Jul 08, 2023 pm 04:31 PM
PHP-FPM is a commonly used PHP process manager used to provide better PHP performance and stability. However, in a high-load environment, the default configuration of PHP-FPM may not meet the needs, so we need to tune it. This article will introduce the tuning method of PHP-FPM in detail and give some code examples. 1. Increase the number of processes. By default, PHP-FPM only starts a small number of processes to handle requests. In a high-load environment, we can improve the concurrency of PHP-FPM by increasing the number of processes
 Detailed explanation of the role and usage of PHP modulo operator
Mar 19, 2024 pm 04:33 PM
Detailed explanation of the role and usage of PHP modulo operator
Mar 19, 2024 pm 04:33 PM
The modulo operator (%) in PHP is used to obtain the remainder of the division of two numbers. In this article, we will discuss the role and usage of the modulo operator in detail, and provide specific code examples to help readers better understand. 1. The role of the modulo operator In mathematics, when we divide an integer by another integer, we get a quotient and a remainder. For example, when we divide 10 by 3, the quotient is 3 and the remainder is 1. The modulo operator is used to obtain this remainder. 2. Usage of the modulo operator In PHP, use the % symbol to represent the modulus
 Detailed explanation of the linux system call system() function
Feb 22, 2024 pm 08:21 PM
Detailed explanation of the linux system call system() function
Feb 22, 2024 pm 08:21 PM
Detailed explanation of Linux system call system() function System call is a very important part of the Linux operating system. It provides a way to interact with the system kernel. Among them, the system() function is one of the commonly used system call functions. This article will introduce the use of the system() function in detail and provide corresponding code examples. Basic Concepts of System Calls System calls are a way for user programs to interact with the operating system kernel. User programs request the operating system by calling system call functions






