 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Detailed example of how python3 uses the requests module to crawl page content
Detailed example of how python3 uses the requests module to crawl page content
Detailed example of how python3 uses the requests module to crawl page content
This article mainly introduces the actual practice of using python3 to crawl page content using the requests module. It has certain reference value. If you are interested, you can learn more
1. Install pip
My personal desktop system uses linuxmint. The system does not have pip installed by default. Considering that pip will be used to install the requests module later, I will install pip as the first step here.
$ sudo apt install python-pip
The installation is successful, check the PIP version:
$ pip -V
2. Install the requests module
Here I installed it through pip:
$ pip install requests
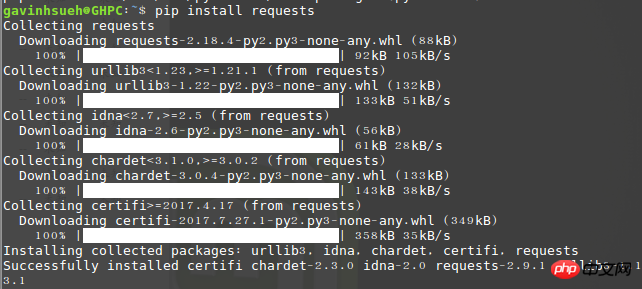
Run import requests, if no error is prompted, then It means the installation has been successful!
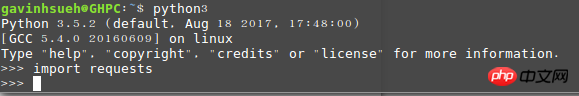
Verify whether the installation is successful
3. Install beautifulsoup4
Beautiful Soup is a tool that can be downloaded from HTML or XML Python library for extracting data from files. It enables customary document navigation, ways to find and modify documents through your favorite converter. Beautiful Soup will save you hours or even days of work.
$ sudo apt-get install python3-bs4
Note: I am using the python3 installation method here. If you are using python2, you can use the following command to install it.
$ sudo pip install beautifulsoup4
4.A brief analysis of the requests module
1) Send a request
First of all, of course, you must import Requests Module:
>>> import requests
Then, get the target crawled web page. Here I take the following as an example:
>>> r = requests.get('http://www.jb51.net/article/124421.htm')
Here returns a response object named r. We can get all the information we want from this object. The get here is the response method of http, so you can also replace it with put, delete, post, and head by analogy.
2) Pass URL parameters
Sometimes we want to pass some kind of data for the query string of the URL. If you build the URL by hand, the data is placed in the URL as key/value pairs, followed by a question mark. For example, cnblogs.com/get?key=val. Requests allow you to use the params keyword argument to provide these parameters as a dictionary of strings.
For example, when we google search for the keyword "python crawler", parameters such as newwindow (new window opens), q and oq (search keywords) can be manually formed into the URL, then you can use the following code :
>>> payload = {'newwindow': '1', 'q': 'python爬虫', 'oq': 'python爬虫'}
>>> r = requests.get("https://www.google.com/search", params=payload)3) Response content
Get the page response content through r.text or r.content.
>>> import requests
>>> r = requests.get('https://github.com/timeline.json')
>>> r.textRequests automatically decode content from the server. Most unicode character sets can be decoded seamlessly. Here is a little addition about the difference between r.text and r.content. To put it simply:
resp.text returns Unicode data;
resp.content returns data of bytes type. It is binary data;
So if you want to get text, you can pass r.text. If you want to get pictures or files, you can pass r.content.
4) Get the web page encoding
>>> r = requests.get('http://www.cnblogs.com/') >>> r.encoding 'utf-8'
5) Get the response status code
We can detect the response status code:
>>> r = requests.get('http://www.cnblogs.com/') >>> r.status_code 200
5. Case Demonstration
The company has just introduced an OA system recently. Here I take its official documentation page as an example, and Only capture useful information such as article titles and content on the page.
Demo environment
Operating system: linuxmint
Python version: python 3.5.2
Using modules: requests, beautifulsoup4
Code As follows:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
_author_ = 'GavinHsueh'
import requests
import bs4
#要抓取的目标页码地址
url = 'http://www.ranzhi.org/book/ranzhi/about-ranzhi-4.html'
#抓取页码内容,返回响应对象
response = requests.get(url)
#查看响应状态码
status_code = response.status_code
#使用BeautifulSoup解析代码,并锁定页码指定标签内容
content = bs4.BeautifulSoup(response.content.decode("utf-8"), "lxml")
element = content.find_all(id='book')
print(status_code)
print(element)The program runs and returns the crawling result:
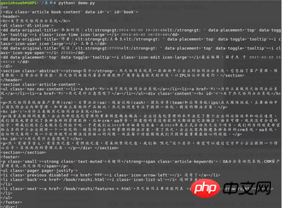
The crawl is successful
About the problem of garbled crawling results
In fact, at first I directly used the python2 that comes with the system by default, but I struggled for a long time with the problem of garbled encoding of the content returned by crawling, google Various solutions have failed. After being "made crazy" by python2, I had no choice but to use python3 honestly. Regarding the problem of garbled content in crawled pages in python2, seniors are welcome to share their experiences to help future generations like me avoid detours.
The above is the detailed content of Detailed example of how python3 uses the requests module to crawl page content. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
![WLAN expansion module has stopped [fix]](https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/465/014/170832352052603.gif?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_207,w_330) WLAN expansion module has stopped [fix]
Feb 19, 2024 pm 02:18 PM
WLAN expansion module has stopped [fix]
Feb 19, 2024 pm 02:18 PM
If there is a problem with the WLAN expansion module on your Windows computer, it may cause you to be disconnected from the Internet. This situation is often frustrating, but fortunately, this article provides some simple suggestions that can help you solve this problem and get your wireless connection working properly again. Fix WLAN Extensibility Module Has Stopped If the WLAN Extensibility Module has stopped working on your Windows computer, follow these suggestions to fix it: Run the Network and Internet Troubleshooter to disable and re-enable wireless network connections Restart the WLAN Autoconfiguration Service Modify Power Options Modify Advanced Power Settings Reinstall Network Adapter Driver Run Some Network Commands Now, let’s look at it in detail
 WLAN extensibility module cannot start
Feb 19, 2024 pm 05:09 PM
WLAN extensibility module cannot start
Feb 19, 2024 pm 05:09 PM
This article details methods to resolve event ID10000, which indicates that the Wireless LAN expansion module cannot start. This error may appear in the event log of Windows 11/10 PC. The WLAN extensibility module is a component of Windows that allows independent hardware vendors (IHVs) and independent software vendors (ISVs) to provide users with customized wireless network features and functionality. It extends the capabilities of native Windows network components by adding Windows default functionality. The WLAN extensibility module is started as part of initialization when the operating system loads network components. If the Wireless LAN Expansion Module encounters a problem and cannot start, you may see an error message in the event viewer log.
 How to realize the mutual conversion between CURL and python requests in python
May 03, 2023 pm 12:49 PM
How to realize the mutual conversion between CURL and python requests in python
May 03, 2023 pm 12:49 PM
Both curl and Pythonrequests are powerful tools for sending HTTP requests. While curl is a command-line tool that allows you to send requests directly from the terminal, Python's requests library provides a more programmatic way to send requests from Python code. The basic syntax for converting curl to Pythonrequestscurl command is as follows: curl[OPTIONS]URL When converting curl command to Python request, we need to convert the options and URL into Python code. Here is an example curlPOST command: curl-XPOST https://example.com/api
 How to use the Python crawler Requests library
May 16, 2023 am 11:46 AM
How to use the Python crawler Requests library
May 16, 2023 am 11:46 AM
1. Install the requests library. Because the learning process uses the Python language, Python needs to be installed in advance. I installed Python 3.8. You can check the Python version you installed by running the command python --version. It is recommended to install Python 3.X or above. After installing Python, you can directly install the requests library through the following command. pipinstallrequestsPs: You can switch to domestic pip sources, such as Alibaba and Douban, which are fast. In order to demonstrate the function, I used nginx to simulate a simple website. After downloading, just run the nginx.exe program in the root directory.
 Python commonly used standard libraries and third-party libraries 2-sys module
Apr 10, 2023 pm 02:56 PM
Python commonly used standard libraries and third-party libraries 2-sys module
Apr 10, 2023 pm 02:56 PM
1. Introduction to the sys module The os module introduced earlier is mainly for the operating system, while the sys module in this article is mainly for the Python interpreter. The sys module is a module that comes with Python. It is an interface for interacting with the Python interpreter. The sys module provides many functions and variables to deal with different parts of the Python runtime environment. 2. Commonly used methods of the sys module. You can check which methods are included in the sys module through the dir() method: import sys print(dir(sys))1.sys.argv-Get the command line parameters sys.argv is used to implement the command from outside the program. The program is passed parameters and it is able to obtain the command line parameter column
 Python programming: Detailed explanation of the key points of using named tuples
Apr 11, 2023 pm 09:22 PM
Python programming: Detailed explanation of the key points of using named tuples
Apr 11, 2023 pm 09:22 PM
Preface This article continues to introduce the Python collection module. This time it mainly introduces the named tuples in it, that is, the use of namedtuple. Without further ado, let’s get started – remember to like, follow and forward~ ^_^Creating named tuples The named tuple class namedTuples in the Python collection gives meaning to each position in the tuple and enhances the readability of the code Sexual and descriptive. They can be used anywhere regular tuples are used, and add the ability to access fields by name rather than positional index. It comes from the Python built-in module collections. The general syntax used is: import collections XxNamedT
 How Python uses Requests to request web pages
Apr 25, 2023 am 09:29 AM
How Python uses Requests to request web pages
Apr 25, 2023 am 09:29 AM
Requests inherits all features of urllib2. Requests supports HTTP connection persistence and connection pooling, the use of cookies to maintain sessions, file uploading, automatic determination of the encoding of response content, and automatic encoding of internationalized URLs and POST data. Installation method uses pip to install $pipinstallrequestsGET request basic GET request (headers parameters and parmas parameters) 1. The most basic GET request can directly use the get method 'response=requests.get("http://www.baidu.com/"
 How does Python's import work?
May 15, 2023 pm 08:13 PM
How does Python's import work?
May 15, 2023 pm 08:13 PM
Hello, my name is somenzz, you can call me Brother Zheng. Python's import is very intuitive, but even so, sometimes you will find that even though the package is there, we will still encounter ModuleNotFoundError. Obviously the relative path is very correct, but the error ImportError:attemptedrelativeimportwithnoknownparentpackage imports a module in the same directory and a different one. The modules of the directory are completely different. This article helps you easily handle the import by analyzing some problems often encountered when using import. Based on this, you can easily create attributes.



