The main feature of AJax is to use scripts to manipulate data exchange between HTTP and web servers without causing page reloading.
Using XMLHttpRequest
All modern browsers support the XMLHttpRequest object (IE5 and IE6 use ActiveXObject).
Create XMLHttpRequest object
var xmlhttp =new XMLHttpRequest()
var xmlhttp =new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
For example
function createXML(){
if(typeof XMLHttpRequest != "undefined"){//标准
return new XMLHttpRequest();
}else if(typeof ActiveXObject != "undefined"){//兼容IE5,IE6
if(typeof arguments.callee.activeXString != "string"){
var versions = ["MSXML2.XMLHttp.6.0","MSXML2.XMLHttp.3.0","MSXML2.XMLHttp"],i,len;
for (i=0,len=versions.length; i < len; i++) {
try{
new ActiveXObject(versions[i]);
arguments.callee.activeXString = versions[i];
break;
}catch(ex){ //跳过
}
}
}
return new ActiveXObject(arguments.callee.activeXString);
}else{
throw new Error("no XRL object available.");
}
}var xml = new createXML();Copy after loginSpecify request
After the object is created, the next step to initiate an http request is to call the open() method of the XMLHttpRequest object. It receives three parameters:
The type of request to send, case-insensitive
The requested URL, here relative to the document URL, if the absolute URL, protocol, host and port are specified, they must match the corresponding content of the document: cross-domain requests will usually report an error
Boolean value of whether to send asynchronously;
If there is request header, then the next step is to set it.
xml.setRequestHeader("Content-Type","text/plain");Copy after loginIf the request header is called multiple times, overwriting will not occur
If the request requires a password-protected URL, the username and The password is passed as the fourth and fifth parameters to open()
The last step in making the request is to specify the optional body and send it to the server. It should be noted that GET requests have absolutely no body, but when using POST to send a request, you must cooperate with the setRequestHeader method
xml.send(null);
Copy after loginGet a response
A complete HTTP response has a status code, response It consists of a collection of headers and a response body. These are available through the properties and methods of the XMLHttpRequest object:
- The status and statusText properties return the HTTP status code (such as 200 ok) in the form of numbers and text
- Use getResponseHeader and getAllResponseHeaders() to query response headers
- The response body can be obtained in text form from the responseText attribute and in Document form from the responseXML attribute
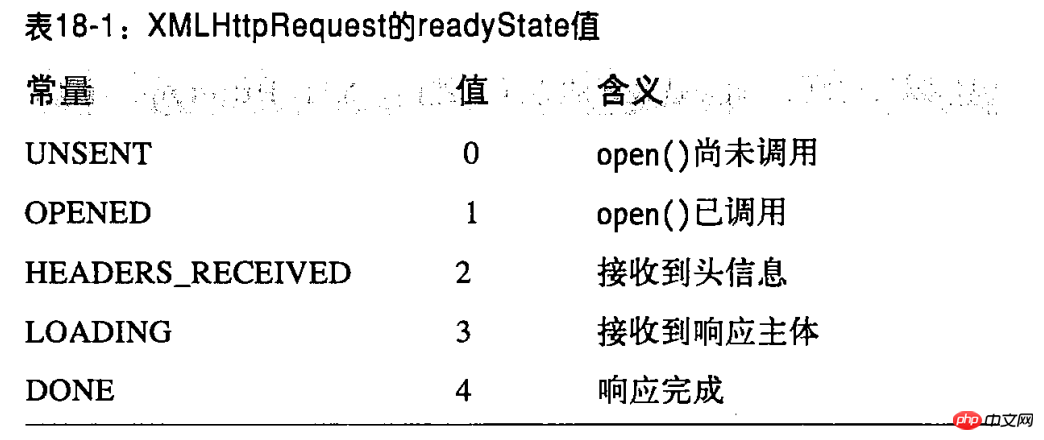
- XMLHttpRequest objects are typically used asynchronously: the send method returns immediately after sending the request, and the response methods and properties listed previously are not valid until the response returns. In order to be notified when the response is ready, you must listen to the readystatechange event on the XMLHttp object
readyState is an integer that specifies the status of the HTTP request

For example
var xml = new createXML();xml.open("get","hello-world.html",false);xml.onreadystatechange = function(url,callback){ if(xml.readyState === 4){ if((xml.status >= 200 && xml.status < 300) || xml.status === 304){
console.log(xml.responseText);
}else{
console.log("request is not ok" + xml.status);
}
}
}xml.send(null);Copy after loginConsole output

##HTTP header information##NameMeaning Content type that the browser can handle Character set that can be displayed Compression encoding that can be processed Between browser and server The connection type The domain where the page is located The cookie set by the page The page URL from which the request was made Browser User Agent String
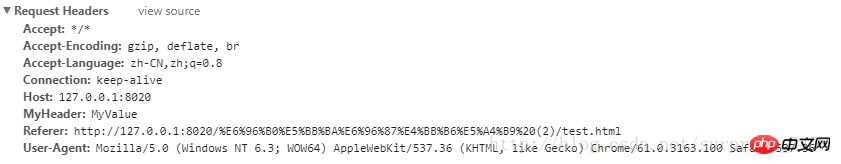
可以自定义请求头部
xml.setRequestHeader("MyHeader","MyValue");Copy after login控制台输出

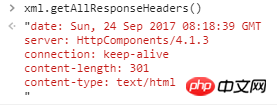
相应,可以使用getAllResponseHeaders进行查询

GET请求
可以将查询字符串参数添加到URL末尾。
function addURLParam(url,name,value){
url += (url.indexOf(?) == -1 ? "?" : "&");
url += encodeURIComponent(name) + "=" +encodeURIComponent(value);
return url;
}Copy after loginPOST请求
用来向服务器发送应该被保存的数据,将数据作为请求的主体提交,主体可以包含非常多的数据,并且数据格式不限
function submitData(){
var xml = createXML();
xml.onreadystatechange = function(){
if(xml.readyState === 4){
if((xml.status >= 200 && xml.status < 300) || xml.status === 304){
console.log(xml.responseText);
}else{
console.log("request is not ok" + xml.status);
}
}
}
xml.open("POST","postexample.php",true);
xml.setRequestHeader("Content-Type","application/x-www-form-urlencoded");//原因见表单编码的请求一节
var form = document.getElementById("user-info");
xml.send(serialize(form));//serialize函数用来将页面中的表单数据格式化}Copy after login编码请求主体
表单编码的请求
当用户提交表单时,表单中的数据编码到一个字符串中并随请求发送。默认情况下,HTML表单通过POST方法发送给服务器,编码后的表单数据则用作请求主体。对表单数据使用的编码方案:对每个单元素的键值对进行普通的URL编码,使用等号把编码后的名字和值连接起来,并使用&链接键值对,如:name1=value1&name2=value2;
表单数据编码格式有一个正式的MIME类型:application/x-www-form-urlencoded,当使用POST方法提交表单数据时,必须设置Content-Type请求头为这个值。
举个栗子
function encodeFormData(data){
if(!data) return "";//无数据就返回空串
var pairs = [];//用来保存键值对
for(var name in data){ if(!data.hasOwnProperty(name)) continue;//跳过继承属性
if(typeof data[name] === "function") continue;//跳过方法
var value = data[name].toString();
name = encodeURIComponent(name.replace(/%20/g,"+"))//因为由于历史原因,表单提交的 x-www-form-urlencoded 格式要求空格编码为 + 。但 encodeURIComponent 是遵照后来的标准编码为 %20 的。
value = encodeURIComponent(value.replace(/%20/g,"+"))
pairs.push(name + "=" + value);
} return paris.join('&')//连接键值对}function getData(url,data,callback){
var request = new XMLHttpRequest()
request.open("GET",url+"?"+encodeFormData(data))
request.onreadystatechange = function(){
if(request.readyState === 4 && callback) callback(request)
}
request.send(null);
}function postData(url,data,callback){
var request = new XMLHttpRequest();
request.open("POST",url);
request.onreadystatechange = function(){
if(request.readyState === 4 && callback){
callback(request);
}
}
request.setRequestHeader("Content-Type","application/x-www-form-urlencoded");
request.send(encodeURIComponent(data));
}Copy after loginJSON编码的请求
举个栗子
function postJson(url,data,callback){
var request = new XMLHttpRequest();
request.open("POST",url);
request.onreadystatechange = function(){
if(request.readyState === 4 && callback){
callback(request);
}
} request.setRequestHeader("Content-Type","application/json");
request.send(JSON.stringify(data));
}Copy after login上传文件
举个栗子
input.addEventListener("change",function(){//添加事件监听
var file = this.file[0];
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open("POST",URL);
xhr.send(file);
},false)Copy after loginmultipart/form-data 请求
当表单同时包含上传文件和其他元素的时候,浏览器必须使用“multipart/form-data”的特殊Content-Type来用POST方法提交表单。XHR2定义了新的FormData API,。
举个栗子
function postData(url,data,callback){
var request = new XMLHttpRequest();
request.open("POST",url);
request.onreadystatechange = function(){
if(request.readyState === 4 && callback){
callback(request);
}
} var form = document.getElementById("user-info");
request.send(new FormData(form));
}Copy after loginHTTP进度事件
六个基本事件
loadstart:在接收到响应数据的第一个字节时触发
progress:在接收响应期间持续不断地触
error:在请求发生错误时触发
abort:在因为调用abort()方法而终止连接时触发
load:在接收到完整的响应数据时触发
loadend:在通信完成或者触发error、abort或load事件后触发
load事件
使用load事件代替onreadystatechange事件,响应完毕后就触发load事件,没有必要再去检查readystate属性。
只要浏览器接收到服务器的响应,无论状态如何,都会触发load事件,所以需要确定status属性值从而确定数据是否可用。
举个栗子
var xml = new createXML();xml.onload = function(event){
if((xml.status >= 200 && xml.status < 300) || xml.status === 304){
var request = document.getElementById("request");
request.innerHTML = xml.responseText;
}else{
console.log("request is not ok" + xml.status);
}
}xml.open("get","hello-world.html",false);xml.send(null);Copy after loginprogress事件
这个时间会在浏览器接受新数据期间周期性的触发。而progress事件处理程序会接收到一个event对象,其中target属性就是XHR对象,还有其他三种属性:lengthConputable表示进度信息是否可用的布尔值,loaded表示已经接收到的字节数,total表示根据Content-Length响应头部确定的预期字节数。
举个栗子
var xml = new createXML();xml.onload = function(event){
if((xml.status >= 200 && xml.status < 300) || xml.status === 304){
var request = document.getElementById("request");
request.innerHTML = xml.responseText;
}else{
console.log("request is not ok" + xml.status);
}
}xml.onprogress = function(event){
var p = document.getElementById("data");
if(event.lengthComputable){
console.log(event.position);
p.innerHTML = "Received " + event.loaded + " of " + event.total + " bytes";
}
}/*需要注意的是,必须保证调用open之前定义onprogress事件处理程序*/xml.open("get","hello-world.html",true);xml.send(null);Copy after login终止请求和请求超时abort()
举个栗子
function timeGetText(url,timeout,callback){
var request = new XMLHttpRequest();
var timedout = false; //判断是否超时
var timer = setTimeout(function(){
timedout = true;//超时
request.abort();//触发终止事件
},timeout);//如果超时,触发一个启动器
request.open("GET",url);//发起请求
request.onreadystatechange = function(){
if(request.readyState !== 4) return;//忽略未完成程序
if(timedout) return;//忽略超时程序
clearTimeout(timer);//取消等待的超时
if(request.status === 200){
callback(request.responseText);//成功
}
}
request.send(null);
}Copy after login图像ping
图像Ping最常用于跟踪用户点击页面或动态广告曝光次数。图像Ping有两个主要的缺点,一是只能发送GET请求,二是无法访问服务器的响应文本。
var img = new Image();
img.onload = img.onerror = function(){
console.log("Done!");
};
img.src = "hello-world.html";Copy after login借助<script>发送HTTP请求:JSONP
设置script元素也可以作为一种AJAX传输机制,只需要设置其src属性,浏览器就会发送一个HTTP请求以下载src属性指定的URL。
使用这种方法进行传输的主要原因是它不受同源策略的影响,因此可以使用他们从其他服务器请求数据,还有一个原因是包含JSON数据的响应体会自动解码。
JSONP是JSON with padding的缩写。和JSON差不多,只不过是被包含在函数调用中的JSON。
JSONP由两部分组成,回调函数和数据。
举个栗子
var bd = document.body;function callbackFunction(result, methodName)
{
bd.innerText = result;
}
var script = document.createElement("script");
script.src = "***/jsonp.php?jsoncallback=callbackFunction";
bd.insertBefore(script,bd.firstChild);Copy after login但是,不会强制指定客户端必须实现的回调函数,它们使用查询参数的值,允许客户端指定一个函数名,然后使用函数名去响应
举个栗子
function getJSONP(url,callback){
var cbnum = "cb" + getJSONP.counter++;
var cbname = "getJSONP." + cbnum;
if(url.indexOf("?") === -1){
url += "?jsonp=" + cbname;
}else{
url += "&jsonp=" + cbname;
} var script = document.createElement("script");
getJSONP[cbname] = function(response){
try{
callback(response);
} finally{ delete getJSONP[cbname];
script.parentNode.removeChild(script);
}
}
script.src = url;
document.body.appendChild(script);
}
getJSONP.counter = 0;Copy after loginConmet技术(服务器推送)
有两种实现Comet的方式:长轮询和流。
长轮询把传统轮询颠倒了一下,页面发送一个到服务器的请求,然后服务器一直保持连接打开,知道有数据可发送。发送完数据后,浏览器关闭连接,随即又发起一个到服务器的新请求。这个过程在页面打开期间一直不断持续。
第二种流行的Comet方式是HTTP流。流在页面的整个生命周期中只使用一个HTTP连接。具体来说就是浏览器向服务器发送一个请求,然后服务器保持连接打开,然后周期性的向浏览器发送数据。
举个栗子
function createStreamingClient(url, progress/*接收到数据时调用的函数*/, finished/*关闭连接时调用的函数*/) {
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest(),
received = 0;
xhr.open("get", url, true);
xhr.onreadystatechange = function() {
var result; if (xhr.readyState == 3) {
result = xhr.responseText.substring(received);
received += result.length;
progress(result);
} else if (xhr.readyState == 4) {
finished(xhr.responseText);
}
};
xhr.send(null); return xhr;
}var client = createStreamingCilent("streaming.php", function(data) {
alert("Received:" + data);
}, function(data) {
alert("Done!");
});Copy after login服务器发送事件
SSE( Server - Sent Events, 服务器发送事件) 是围绕只读Comet交互推出的API或者模式。 SSE API用于创建到服务器的单向连接, 服务器通过这个连接可以发送任意数量的数据。 服务器响应的MIME类型必须是text / event - stream, 而且是浏览器中的Javascript API能解析的格式输出。 SSE支持短轮询, 长轮询和HTTP流, 而且能够在断开连接时自动确定何时重新连接。
SSE API
SSE是为javascript api与其他传递消息的javascript api很相似。 要预定新的事件流, 要创建新的EventSource对象, 并传入一个入口点:
var source = new EventSource("myevents.php");/*必须同源*/Copy after loginEventSource的实例有一个readyState属性, 值为0表示正连接到服务器, 值为1表示打开了连接, 值为2表示关闭连接。还有三个事件:
open: 在建立连接时触发
message: 在从服务器接收到新事件时触发
error: 在无法建立连接时触发
- 服务器返回的数据以字符串的格式保存在event.data中。 如果想强制立即断开并且不再重新连接, 可以调用close() 方法。
事件流
响应格式为纯文本。
对于多个连续数据,需要使用换行符分割。
在设置了ID之后, EventSource对象会跟踪上一次触发的事件。 如果连接断开, 会向服务器发送一个包含名为Last - Event - ID的特殊HTTP头部请求, 以便服务器知道下次触发那个事件。 在多次连接的事件流中, 这种机制保证了浏览器能够以正确的顺序接收到连接的数据段。
Web Sockets
WebSocket是HTML5开始提供的一种在单个 TCP 连接上进行全双工通讯的协议。
当创建web Sockets之后,会有一个http请求发送到浏览器以发起连接。在取得服务器响应后,建立的连接会从http协议交换为Web Socket协议
由于使用了自定义的协议,未加密的URL是ws://,加密后的URLwss://
好处是能够在客户端和服务器之间发送非常少的数据,而不必担心http那样字节级的开销。
var Socket = new WebSocket(url, [protocol]/*可接受的子协议*/ );//创建对象
Copy after login
事件
事件处理程序
描述
open
Socket.onopen
连接建立时触发
message
Socket.onmessage
客户端接收服务端数据时触发
error
Socket.onerror
通信发生错误时触发
close
Socket.onclose
连接关闭时触发
参考文档——websocket
AJax的主要特点是使用脚本操纵HTTP和web服务器之间的数据交换,不会导致页面重载。
The above is the detailed content of Scripting HTTP with Ajax. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Statement of this Website
The content of this article is voluntarily contributed by netizens, and the copyright belongs to the original author. This site does not assume corresponding legal responsibility. If you find any content suspected of plagiarism or infringement, please contact admin@php.cn

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article
R.E.P.O. Energy Crystals Explained and What They Do (Yellow Crystal)
4 weeks ago
By 尊渡假赌尊渡假赌尊渡假赌
R.E.P.O. Best Graphic Settings
4 weeks ago
By 尊渡假赌尊渡假赌尊渡假赌
Assassin's Creed Shadows: Seashell Riddle Solution
2 weeks ago
By DDD
R.E.P.O. How to Fix Audio if You Can't Hear Anyone
4 weeks ago
By 尊渡假赌尊渡假赌尊渡假赌
R.E.P.O. Chat Commands and How to Use Them
4 weeks ago
By 尊渡假赌尊渡假赌尊渡假赌

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
CakePHP Tutorial
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to solve the 403 error encountered by jQuery AJAX request
Feb 20, 2024 am 10:07 AM
How to solve the 403 error encountered by jQuery AJAX request
Feb 20, 2024 am 10:07 AM
Title: Methods and code examples to resolve 403 errors in jQuery AJAX requests. The 403 error refers to a request that the server prohibits access to a resource. This error usually occurs because the request lacks permissions or is rejected by the server. When making jQueryAJAX requests, you sometimes encounter this situation. This article will introduce how to solve this problem and provide code examples. Solution: Check permissions: First ensure that the requested URL address is correct and verify that you have sufficient permissions to access the resource.
 How to solve jQuery AJAX request 403 error
Feb 19, 2024 pm 05:55 PM
How to solve jQuery AJAX request 403 error
Feb 19, 2024 pm 05:55 PM
jQuery is a popular JavaScript library used to simplify client-side development. AJAX is a technology that sends asynchronous requests and interacts with the server without reloading the entire web page. However, when using jQuery to make AJAX requests, you sometimes encounter 403 errors. 403 errors are usually server-denied access errors, possibly due to security policy or permission issues. In this article, we will discuss how to resolve jQueryAJAX request encountering 403 error
 Understand common application scenarios of web page redirection and understand the HTTP 301 status code
Feb 18, 2024 pm 08:41 PM
Understand common application scenarios of web page redirection and understand the HTTP 301 status code
Feb 18, 2024 pm 08:41 PM
Understand the meaning of HTTP 301 status code: common application scenarios of web page redirection. With the rapid development of the Internet, people's requirements for web page interaction are becoming higher and higher. In the field of web design, web page redirection is a common and important technology, implemented through the HTTP 301 status code. This article will explore the meaning of HTTP 301 status code and common application scenarios in web page redirection. HTTP301 status code refers to permanent redirect (PermanentRedirect). When the server receives the client's
 How to get variables from PHP method using Ajax?
Mar 09, 2024 pm 05:36 PM
How to get variables from PHP method using Ajax?
Mar 09, 2024 pm 05:36 PM
Using Ajax to obtain variables from PHP methods is a common scenario in web development. Through Ajax, the page can be dynamically obtained without refreshing the data. In this article, we will introduce how to use Ajax to get variables from PHP methods, and provide specific code examples. First, we need to write a PHP file to handle the Ajax request and return the required variables. Here is sample code for a simple PHP file getData.php:
 How to solve the problem of jQuery AJAX error 403?
Feb 23, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
How to solve the problem of jQuery AJAX error 403?
Feb 23, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
How to solve the problem of jQueryAJAX error 403? When developing web applications, jQuery is often used to send asynchronous requests. However, sometimes you may encounter error code 403 when using jQueryAJAX, indicating that access is forbidden by the server. This is usually caused by server-side security settings, but there are ways to work around it. This article will introduce how to solve the problem of jQueryAJAX error 403 and provide specific code examples. 1. to make
 PHP and Ajax: Building an autocomplete suggestion engine
Jun 02, 2024 pm 08:39 PM
PHP and Ajax: Building an autocomplete suggestion engine
Jun 02, 2024 pm 08:39 PM
Build an autocomplete suggestion engine using PHP and Ajax: Server-side script: handles Ajax requests and returns suggestions (autocomplete.php). Client script: Send Ajax request and display suggestions (autocomplete.js). Practical case: Include script in HTML page and specify search-input element identifier.
 What status code is returned for an HTTP request timeout?
Feb 18, 2024 pm 01:58 PM
What status code is returned for an HTTP request timeout?
Feb 18, 2024 pm 01:58 PM
The HTTP request times out, and the server often returns the 504GatewayTimeout status code. This status code indicates that when the server executes a request, it still fails to obtain the resources required for the request or complete the processing of the request after a period of time. It is a status code of the 5xx series, which indicates that the server has encountered a temporary problem or overload, resulting in the inability to correctly handle the client's request. In the HTTP protocol, various status codes have specific meanings and uses, and the 504 status code is used to indicate request timeout issues. in customer
 What does TikTok recommended video mean? How to use Douyin to recommend videos?
Mar 27, 2024 pm 03:01 PM
What does TikTok recommended video mean? How to use Douyin to recommend videos?
Mar 27, 2024 pm 03:01 PM
As a world-renowned short video social platform, Douyin has won the favor of a large number of users with its unique personalized recommendation algorithm. This article will delve into the value and principles of Douyin video recommendation to help readers better understand and make full use of this feature. 1. What is Douyin recommended video? Douyin recommended video uses intelligent recommendation algorithms to filter and push personalized video content to users based on their interests and behavioral habits. The Douyin platform analyzes users' viewing history, like and comment behavior, sharing records and other data to select and recommend videos that best suit users' tastes from a huge video library. This personalized recommendation system not only improves user experience, but also helps users discover more video content that matches their preferences, thereby enhancing user stickiness and retention rate. at this
See all articles