 Backend Development
Backend Development
 C#.Net Tutorial
C#.Net Tutorial
 Detailed explanation of the principle of foreach implementation in C#
Detailed explanation of the principle of foreach implementation in C#
Detailed explanation of the principle of foreach implementation in C#
This article mainly introduces the foreach implementation principle in C# in detail, which has certain reference value. Interested friends can refer to it
This article mainly records my learning of the foreach traversal principle in C# experience.
Traversing elements in a collection is an operation often involved in all coding, so most programming languages have written this process into the grammar, such as foreach in C#. It is common to see the following traversal code:
var lstStr = new List<string> { "a", "b" };
foreach (var str in lstStr)
{
Console.WriteLine(str);
}The actual execution process of this code:
var lstStr = new List<string> {"a", "b"};
IEnumerator<string> enumeratorLst = lstStr.GetEnumerator();
while (enumeratorLst.MoveNext())
{
Console.WriteLine(enumeratorLst.Current);
} will find that there is the GetEnumerator() method and the IEnumerator
In order to facilitate understanding, the following is a non-generic example:
// 摘要:
// 公开枚举器,该枚举器支持在非泛型集合上进行简单迭代。
public interface IEnumerable
{
// 摘要:
// 返回一个循环访问集合的枚举器。
//
// 返回结果:
// 可用于循环访问集合的 System.Collections.IEnumerator 对象。
IEnumerator GetEnumerator();
}The class that implements this interface is called an enumerable type, which is A flag that can be traversed using foreach.
The return value of the method GetEnumerator() is an enumerator, which can be understood as a cursor.
// 摘要:
// 支持对非泛型集合的简单迭代。
public interface IEnumerator
{
// 摘要:
// 获取集合中的当前元素。
//
// 返回结果:
// 集合中的当前元素。
//
// 异常:
// System.InvalidOperationException:
// 枚举数定位在该集合的第一个元素之前或最后一个元素之后。
object Current { get; }
// 摘要:
// 将枚举数推进到集合的下一个元素。
//
// 返回结果:
// 如果枚举数成功地推进到下一个元素,则为 true;如果枚举数越过集合的结尾,则为 false。
//
// 异常:
// System.InvalidOperationException:
// 在创建了枚举数后集合被修改了。
bool MoveNext();
//
// 摘要:
// 将枚举数设置为其初始位置,该位置位于集合中第一个元素之前。
//
// 异常:
// System.InvalidOperationException:
// 在创建了枚举数后集合被修改了。
void Reset();
}The following is an example of customizing an iterator (https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.collections.ienumerator .aspx):
using System;
using System.Collections;
// Simple business object.
public class Person
{
public Person(string fName, string lName)
{
this.firstName = fName;
this.lastName = lName;
}
public string firstName;
public string lastName;
}
// Collection of Person objects. This class
// implements IEnumerable so that it can be used
// with ForEach syntax.
public class People : IEnumerable
{
private Person[] _people;
public People(Person[] pArray)
{
_people = new Person[pArray.Length];
for (int i = 0; i < pArray.Length; i++)
{
_people[i] = pArray[i];
}
}
// Implementation for the GetEnumerator method.
IEnumerator IEnumerable.GetEnumerator()
{
return (IEnumerator) GetEnumerator();
}
public PeopleEnum GetEnumerator()
{
return new PeopleEnum(_people);
}
}
// When you implement IEnumerable, you must also implement IEnumerator.
public class PeopleEnum : IEnumerator
{
public Person[] _people;
// Enumerators are positioned before the first element
// until the first MoveNext() call.
int position = -1;
public PeopleEnum(Person[] list)
{
_people = list;
}
public bool MoveNext()
{
position++;
return (position < _people.Length);
}
public void Reset()
{
position = -1;
}
object IEnumerator.Current
{
get
{
return Current;
}
}
public Person Current
{
get
{
try
{
return _people[position];
}
catch (IndexOutOfRangeException)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException();
}
}
}
}
class App
{
static void Main()
{
Person[] peopleArray = new Person[3]
{
new Person("John", "Smith"),
new Person("Jim", "Johnson"),
new Person("Sue", "Rabon"),
};
People peopleList = new People(peopleArray);
foreach (Person p in peopleList)
Console.WriteLine(p.firstName + " " + p.lastName);
}
}
/* This code produces output similar to the following:
*
* John Smith
* Jim Johnson
* Sue Rabon
*
*/After having the yield keyword, we can create an enumerator in this way:
using System;
using System.Collections;
// Simple business object.
public class Person
{
public Person(string fName, string lName)
{
this.firstName = fName;
this.lastName = lName;
}
public string firstName;
public string lastName;
}
// Collection of Person objects. This class
// implements IEnumerable so that it can be used
// with ForEach syntax.
public class People : IEnumerable
{
private Person[] _people;
public People(Person[] pArray)
{
_people = new Person[pArray.Length];
for (int i = 0; i < pArray.Length; i++)
{
_people[i] = pArray[i];
}
}
// Implementation for the GetEnumerator method.
IEnumerator IEnumerable.GetEnumerator()
{
for (int i = 0; i < _people.Length; i++)
{
yield return _people[i];
}
}
}
class App
{
static void Main()
{
Person[] peopleArray = new Person[3]
{
new Person("John", "Smith"),
new Person("Jim", "Johnson"),
new Person("Sue", "Rabon"),
};
People peopleList = new People(peopleArray);
foreach (Person p in peopleList)
Console.WriteLine(p.firstName + " " + p.lastName);
}
}The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of the principle of foreach implementation in C#. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 What is the difference between using foreach and iterator to delete elements when traversing Java ArrayList?
Apr 27, 2023 pm 03:40 PM
What is the difference between using foreach and iterator to delete elements when traversing Java ArrayList?
Apr 27, 2023 pm 03:40 PM
1. The difference between Iterator and foreach is the polymorphic difference (the bottom layer of foreach is Iterator) Iterator is an interface type, it does not care about the type of collection or array; both for and foreach need to know the type of collection first, even the type of elements in the collection; 1. Why is it said that the bottom layer of foreach is the code written by Iterator: Decompiled code: 2. The difference between remove in foreach and iterator. First, look at the Alibaba Java Development Manual, but no error will be reported in case 1, and an error will be reported in case 2 (java. util.ConcurrentModificationException) first
 How to determine the number of foreach loop in php
Jul 10, 2023 pm 02:18 PM
How to determine the number of foreach loop in php
Jul 10, 2023 pm 02:18 PM
The steps for PHP to determine the number of the foreach loop: 1. Create an array of "$fruits"; 2. Create a counter variable "$counter" with an initial value of 0; 3. Use "foreach" to loop through the array, and Increase the value of the counter variable in the loop body, and then output each element and their index; 4. Output the value of the counter variable outside the "foreach" loop to confirm which element the loop reaches.
 What are the employment prospects of C#?
Oct 19, 2023 am 11:02 AM
What are the employment prospects of C#?
Oct 19, 2023 am 11:02 AM
Whether you are a beginner or an experienced professional, mastering C# will pave the way for your career.
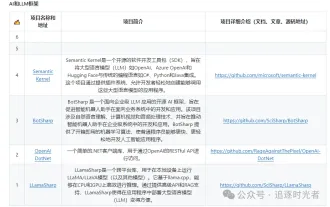 Share several .NET open source AI and LLM related project frameworks
May 06, 2024 pm 04:43 PM
Share several .NET open source AI and LLM related project frameworks
May 06, 2024 pm 04:43 PM
The development of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies is in full swing today, and they have shown great potential and influence in various fields. Today Dayao will share with you 4 .NET open source AI model LLM related project frameworks, hoping to provide you with some reference. https://github.com/YSGStudyHards/DotNetGuide/blob/main/docs/DotNet/DotNetProjectPicks.mdSemanticKernelSemanticKernel is an open source software development kit (SDK) designed to integrate large language models (LLM) such as OpenAI, Azure
 PHP returns an array with key values flipped
Mar 21, 2024 pm 02:10 PM
PHP returns an array with key values flipped
Mar 21, 2024 pm 02:10 PM
This article will explain in detail how PHP returns an array after key value flipping. The editor thinks it is quite practical, so I share it with you as a reference. I hope you can gain something after reading this article. PHP Key Value Flip Array Key value flip is an operation on an array that swaps the keys and values in the array to generate a new array with the original key as the value and the original value as the key. Implementation method In PHP, you can perform key-value flipping of an array through the following methods: array_flip() function: The array_flip() function is specially used for key-value flipping operations. It receives an array as argument and returns a new array with the keys and values swapped. $original_array=[
 PHP returns the current element in an array
Mar 21, 2024 pm 12:36 PM
PHP returns the current element in an array
Mar 21, 2024 pm 12:36 PM
This article will explain in detail about the current element in the array returned by PHP. The editor thinks it is very practical, so I share it with you as a reference. I hope you can gain something after reading this article. Get the current element in a PHP array PHP provides a variety of methods for accessing and manipulating arrays, including getting the current element in an array. The following introduces several commonly used techniques: 1. current() function The current() function returns the element currently pointed to by the internal pointer of the array. The pointer initially points to the first element of the array. Use the following syntax: $currentElement=current($array);2.key() function key() function returns the array internal pointer currently pointing to the element
 What is the difference between foreach and for loop
Jan 05, 2023 pm 04:26 PM
What is the difference between foreach and for loop
Jan 05, 2023 pm 04:26 PM
Difference: 1. for loops through each data element through the index, while forEach loops through the data elements of the array through the JS underlying program; 2. for can terminate the execution of the loop through the break keyword, but forEach cannot; 3. for can control the execution of the loop by controlling the value of the loop variable, but forEach cannot; 4. for can call loop variables outside the loop, but forEach cannot call loop variables outside the loop; 5. The execution efficiency of for is higher than forEach.
 .NET performance optimization technology for developers
Sep 12, 2023 am 10:43 AM
.NET performance optimization technology for developers
Sep 12, 2023 am 10:43 AM
If you are a .NET developer, you must be aware of the importance of optimizing functionality and performance in delivering high-quality software. By making expert use of the provided resources and reducing website load times, you not only create a pleasant experience for your users but also reduce infrastructure costs.



