What are the layout methods of HTML web pages?
Summary of three HTML layout methods
1 Ordinary flow
Also known as regular flow , the default formatting method of the browser. Normal flow is how elements are rendered on a web page in most cases. All HTML is inside block boxes (block-level elements) or inline boxes (inline elements). When a browser begins rendering an HTML document, it allocates the space required by elements starting at the top of the window and working its way through the document's content. Unless the document's dimensions are specifically limited by CSS, the browser expands the document vertically to accommodate the entire content. Each new block-level element is rendered as a new line. Inline elements (inline element/inline block level) are rendered horizontally in order until the current line encounters a boundary, and then switch to the next line for vertical rendering.
2 Positioning flow
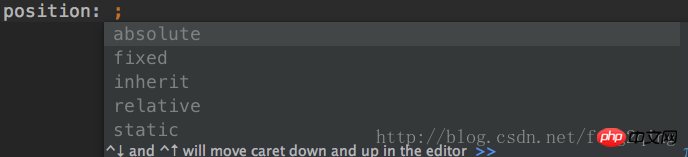
absolute, absolute positioning: absolutely positioned elements The position is determined relative to the nearest positioned (positioning flow) ancestor (relative/absolute/fixed) element. If the element has no positioned ancestors, its position is relative to the initial containing block (body).
The position of the element is specified through the "left", "top", "right" and "bottom" attributes. Absolutely positioned elements are out of standard flow. Does not take up space in the standard stream. Absolutely positioned elements do not distinguish between block-level elements/inline elements/inline block-level elements. If an absolutely positioned element uses the body as the reference point, then it actually uses the width and height of the first screen of the web page as the reference point, rather than the width and height of the entire web page. The positioned element will scroll as the page scrolls. When a box is absolutely positioned, you cannot use margin: 0 auto; to center the box itself, you can use left: 50%; margin-left: - set the element width to half px to center;2>
fixed, fixed positioning: Fixed positioning can be understood as a type of absolute positioning. Fixed positioning elements are positioned relative to the browser window. This enables the creation of elements that always appear at a fixed position in the window.
The position of the element is specified through the "left", "top", "right" and "bottom" attributes. Fixed-positioned elements are separated from the standard flow and will not occupy space in the standard flow. That can be understood as being deleted from the standard stream. Fixed positioned elements do not distinguish between block-level elements/inline elements/inline block-level elements. E6 and lower versions do not support fixed positioning and can be solved using javascript.3>
inherit, inheritance: inherit the value of the position attribute of the parent element.
4>relative, Relative positioning: Relative positioning means moving relative to its previous position in the ordinary flow. That is, positioned relative to its normal position.
When using relative positioning, no matter whether the element is moved or not, the element still occupies the original space, so moving the element will cause it to cover other boxes. In relative positioning, only one positioning attribute can be used in the same direction. Relative positioning does not deviate from the standard flow, so distinguish block-level elements/inline elements/inline block-level elements in relative positioning. And because relatively positioned elements will occupy positions in the standard flow, setting attributes such as margin/padding for relatively positioned elements will affect the layout of the standard flow.5>
static, static positioning: default value, no positioning, the element appears in the normal flow, that is, the normal flow above, ignoring top, bottom, left, right Or z-index declaration.
3 Floating flow
Floating flow has only one typesetting method, which is horizontal typesetting. It can only set an element to left or right alignment. The elements floated first will be displayed in the front, and the elements floated later will be displayed in the back.There is no center alignment in the floating stream, and there is no center value. Margin: 0 auto cannot be used in floating streams. In the floating stream, block-level elements/inline elements/inline block-level elements are not distinguished. Whether it is block-level elements/inline elements/inline block-level elements, they can be typeset horizontally. Both width and height can be set. When an element is set to float, it will be separated from the standard stream (off-standard) and will not occupy space in the standard stream. If the following element is not floating at this time, then this element will cover the following element at this time.
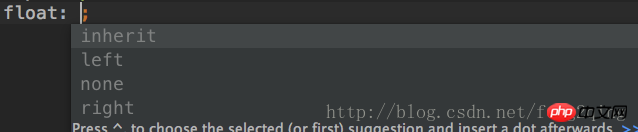
inherit, inheritance: inherit the value of the float attribute of the parent element.
2>left, left floating: the element floats to the left. The one that floats first is on the left, and the one that floats later is on the right.
3>none, not floating: default value.
4>right, right float: the element floats to the right. The one that floats first is on the right, and the one that floats later is on the left.
The above is the detailed content of What are the layout methods of HTML web pages?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Table Border in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Table Border in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Guide to Table Border in HTML. Here we discuss multiple ways for defining table-border with examples of the Table Border in HTML.
 HTML margin-left
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:48 PM
HTML margin-left
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:48 PM
Guide to HTML margin-left. Here we discuss a brief overview on HTML margin-left and its Examples along with its Code Implementation.
 Nested Table in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Nested Table in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
This is a guide to Nested Table in HTML. Here we discuss how to create a table within the table along with the respective examples.
 HTML Table Layout
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
HTML Table Layout
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
Guide to HTML Table Layout. Here we discuss the Values of HTML Table Layout along with the examples and outputs n detail.
 HTML Input Placeholder
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
HTML Input Placeholder
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
Guide to HTML Input Placeholder. Here we discuss the Examples of HTML Input Placeholder along with the codes and outputs.
 Moving Text in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:45 PM
Moving Text in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:45 PM
Guide to Moving Text in HTML. Here we discuss an introduction, how marquee tag work with syntax and examples to implement.
 HTML Ordered List
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:43 PM
HTML Ordered List
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:43 PM
Guide to the HTML Ordered List. Here we also discuss introduction of HTML Ordered list and types along with their example respectively
 HTML onclick Button
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
HTML onclick Button
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Guide to HTML onclick Button. Here we discuss their introduction, working, examples and onclick Event in various events respectively.




