
It’s National Day and Mid-Autumn Festival in a few days, and the holiday is about to begin. I wish you all a happy holiday! I have written about js writing suggestions and techniques before, so let’s talk about css today! Speaking of CSS, every web page is inseparable from CSS. However, many developers think that as long as CSS can be used for layout and renderings, other details or optimizations do not need to be considered. . But I think CSS is not just about completing the layout of the page, but also needs to consider many details and optimization, and it is not as simple as everyone thinks. During the study, if I find any skills or optimization points, I will also learn them. Use it! So today, I will share some of the CSS writing suggestions and performance optimization issues I have summarized! I hope it can help give everyone a new understanding of the magical CSS. Of course, if you think you have any other suggestions. Welcome to give advice!
First choice, regarding the rules of css rendering, everyone may know that it is rendering from right to left! The following chestnut
.nav h3 a{font-size: 14px;}The rendering process is probably: first find all a, find h3 along the parent element of a, and then follow h3, search for .nav. If a node that meets the matching rules is found midway, it is added to the result set. If there is no match for the root element html, the path will no longer be traversed and the search will be repeated starting from the next a (as long as there are multiple rightmost nodes on the page that are a).
Reference: CSS selector matching rules from right to left
Generally, the nesting level of elements cannot exceed 3 levels. Excessive nesting can cause code to become bloated, redundant, and complex. As a result, the size of the CSS file becomes larger, resulting in a waste of performance and affecting the rendering speed! And it relies too much on HTML document structure. Such a CSS style is extremely troublesome to maintain. If you want to modify the style in the future, you may need to use !important to overwrite it.
I currently maintain a neutral opinion on this, because looking at articles on the Internet, some people support the use of style reset, and some people do not support its use. No one can convince anyone. . In my own case, I used style reset, but it is a relatively simple summary, the code is as follows!
body,dl,dd,h1,h2,h3,h4,h5,h6,p,form,ol,ul {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
h1, h2, h3, h4, h5, h6 {
font-weight: normal;
}
ol, ul {
list-style: none;
}
h1{
font-size: 24px;
}
h2{
font-size: 20px;
}
h3{
font-size: 18px;
}
h4 {
font-size: 16px;
}
h5{
font-size: 14px;
}
h6{
font-size: 12px;
}First, the css style level is organized as follows
!important>Inline style>id style>class style>Tag name style.
Then one thing to mention is that the weights used by the combined selectors will be superimposed. For example, the weight of id is 100, the class is 10, and the tag name is 1 (others are unclear)! Then the p.test-class weight is 11, p#test is 101
For example, if there is a p
<p id="test" class="test-class" style="color:green;"></p>
, then the style weight It’s
p {color: red !improtant;}
(大于下面的一切)
<p id="test" class="test-class" style="color:black;"></p>
(大于111)
p#test.test-class
(111)
#id.test-class
(110)
p#test
(101)
#test
(100)
p.test-class
(11)
.test-class
(10)
p
(1)
*
(小于1)I won’t explain it, just look at the picture
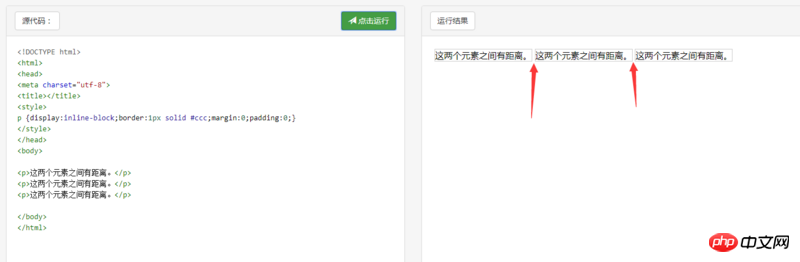
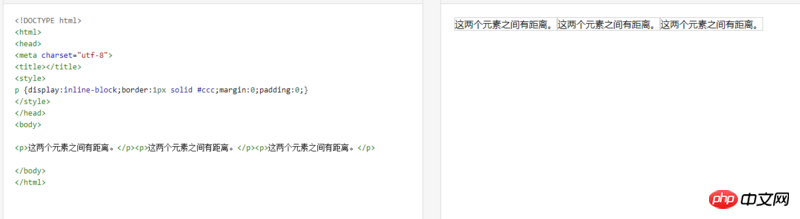
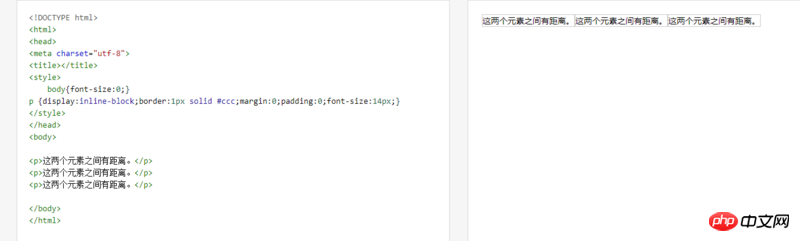
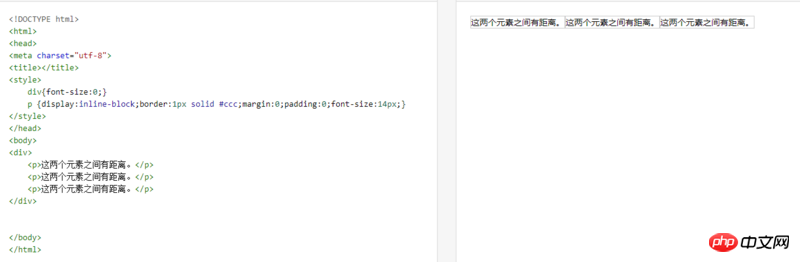
The p elements margin and padding are both 0, but there are still margins. There are two solutions to this
1. Delete the blank lines before the code.
Delete the blank lines before the elements with display:inline-block. It is written as follows
The following is a chestnut, a very common layout. 



关于设置width和height,我顺便说几点
1.PC站,建议在img标签的属性设置width和height。这样避免加载不出css而错位
2.手机站,建议用css设置img的width和height,因为手机站要做适配,在属性设置width和height不灵活,比如使用rem布局,在属性那里设置不了width和height。
3.如果图片不固定,但是有一个max-width和max-height,那么建议在img的父元素设置width和height。img根据父元素的width和height设置max-width和max-height。
这里只放图,不解释




这个方式不推荐使用,因为这个写法,.p2的宽高必须要设置,否则就是100%;比如设置了top:0;bottom:0;效果和设置height:100%;是一样的。如果想要避免,就必须要设置height。
这里说的预加载,不是懒加载。首先根据我个人理解科普下,懒加载和预加载的区别。
懒加载:页面加载的时候,先加载一部分内容(一般是先加载首屏内容),其它内容等到需要加载的时候再进行加载!
预加载:页面加载的时候,先加载一部分内容(一般是先加载首屏内容),其它内容等到先加载的一部分内容(一般是首屏内容)加载完了,再进行加载。
两种方式,都是为了减少用户进入网站的时候,更快的看到首屏的内容!
下面栗子,将这#preloader这个元素加入到到html中,就可以实现通过CSS的background属性将图片预加载到屏幕外的背景上。只要这些图片的路径保持不变,当它们在web页面的其他地方被调用时,浏览器就会在渲染过程中使用预加载(缓存)的图片。简单、高效,不需要任何JavaScript。
#preloader {
/*需要预加载的图片*/
background: url(image1.jpg) no-repeat,url(image2.jpg) no-repeat,url(image3.jpg) no-repeat;
width: 0px;
height: 0px;
display: inline;
}但是这样会有一个问题,因为#preloader预加载的图片,会和页面上的其他内容一起加载,增加了页面的整体加载时间。所以需要用js控制
function preloader(urlArr,obj) {
var bgText='';
for(var i=0,len=urlArr.length;i<len;i++){
bgText+='url('+urlArr[i]+') no-repeat,';
}
obj.style.background=bgText.substr(0,bgText.length-1);
}
window.onload = function() {
preloader(['image1.jpg','image2.jpg','image3.jpg'],document.getElementById('preloader'));
}原理也很简单,就是先让首屏的图片加载完,然后再加载其它的图片。通过给#preloader设置背景图片,加载所需要的图片,然后页面上需要加载这些图片的时候,就直接从缓存里面拿图片,不需要通过http请求获取图片,这样加载就很快。
在做网页的时候经常会使用下面两种方式重置样式,以此来消除标签的默认布局和不同浏览器对于同一个标签的渲染。
*{margin:0;padding:0;}上面这种方式,代码少,但是性能差,因为渲染的时候,要匹配页面上所有的元素!很多基础样式没有margin和padding的元素,比如p,li等。都被匹配,完全没必要!
下面看另一种方式。
body,dl,dd,h1,h2,h3,h4,h5,h6,p,form,ol,ul{margin:0;padding:0;}这种方式,代码稍微多,但是性能比上面的方式好,在渲染的时候,只匹配body,dl,dd,h1,h2,h3,h4,h5,h6,p,form,ol,ul这里面的元素,这些元素带有margin和padding,需要重置!
再看例子:
.test * {color: red;}匹配文档中所有的元素,然后分别向上逐级匹配class为test的元素,直到文档的根节点
.test a {color: red;}匹配文档中所有a的元素,然后分别向上逐级匹配class为test的元素,直到文档的根节点
两种方式,哪种更好不言而喻,所以在开发的时候,建议避免使用通配选择器。
这个没什么好解释的,就是压缩和合并css。
首先压缩css,除了使用工具,比如gulp,webpack等把代码压缩,把空格和换行都去掉。还有一个建议就是属性简写。
比如
margin-top:0; margin-right:10px; margin-bottom:10px; margin-left:10px; background-image: url('test.jpg'); background-position: top center; background-repeat: no-repeat; border-width:1px; border-style:solid; border-color:#000; color:#0099FF;
可以换成下面的
margin:0 10px 10px 10px; background: url('test.jpg') no-repeat top center; border:1px solid #000; color:#09F;
至于合并的时候,我按照自己的开发习惯给几个建议:
1.合并公用的样式,比如项目的头部,底部,侧边栏这些,一般都是公用的,这些可以写在一个公用样式表上,比如main.css。
2.上面所说的main.css是每一个页面都需要引入,而样式重置表reset.css也是每一个页面都需要用到的,那么建议main.css和reset.css合并成一个文件,给页面引入!减少请求!
3.每个页面对应的样式为独立的文件,比如首页对应的是index.css。产品列表页对应的样式是product-list.css。那么index.css就只在首页引入,其它页面不引入,因为引入纯属浪费请求资源!其他页面对应的样式也是这个处理方式!index.css,product-list.css等其它页面的样式就保留单独的文件,不作合并处理!
浏览器在所有的 stylesheets 加载完成之后,才会开始渲染整个页面,在此之前,浏览器不会渲染页面里的任何内容,页面会一直呈现空白。这也是为什么要把 stylesheet 放在头部的原因。如果放在 HTML 页面底部,页面渲染就不仅仅是在等待 stylesheet 的加载,还要等待 html 内容加载完成,这样一来,用户看到页面的时间会更晚。
css样式文件有两种引入方式,一种是link元素,另一种是@import。在这里,我建议就是避免使用@import。因为@import会影响浏览器的并行下载,使得页面在加载时增加额外的延迟,增添了额外的往返耗时。而且多个@import可能会导致下载顺序紊乱。比如一个css文件index.css包含了以下内容:@import url("reset.css")。那么浏览器就必须先把index.css下载、解析和执行后,才下载、解析和执行第二个文件reset.css。简单的解决方法是使用<link>替代@import。
接到效果图,先不用着急切图,先看下psd文件。思考下怎么排版,那些模块可以做成公用的模块,模块应该怎么命名,写样式等!
当我们拿到设计师给的PSD时,首先不要急于写CSS代码,首先对整个页面进行分析,先思考下面几点:
(1)分析页面有哪些模块是公用的,常见公用模块有头部,底部,菜单栏,悬浮按钮等等
(2)分析模块有什么样式,把公用的样式提取出来,公用样式包括公用的状态样式,比如按钮,输入框,下拉框等公用的选中状态,禁用状态的样式等等。
一个网站,肯定会有很多个小图标,对于这些小图标,目前的解决方案有两个,cssSprite(雪碧图),字体图标,把图片转成base64。下面对比一下这两种方式!
cssSprite:把所有icon图片合成一张png图片,使用的是在,对节点设置宽高,加上bacgroud-position。以背景图方式显展示需要的icon,如果一个网站有20图标,那么就要请求20次,使用cssSprite,只需要请求一次,大大的减少了http请求。缺点就是管理不灵活,如果需要新增一个图标,都需要改合并图片的源文件,图标定位也要规范,不然容易干扰图片之间的定位!
字体图标:简单粗暴的理解就是把所有的图标当成一个字体处理!这样不用去请求图片。一般是使用class来定义图标,要替换图标时,只需更换样式名,管理方便,语意明确,灵活放大缩小,并且不会造成失真。但是只支持单色的图片。
base64:另一种方案就是把小的icon图片转成base64编码,这样可以不用去请求图片,把base64编码直接整合到js或者css里面,可以防止因为一些相对路径,或者图片被不小删除了等问题导致图片404错误。但是找个方式会生成一大串的base64编码。一般来说,8K以下的图片才转换成base64编码。如果把一张50K的图片转成base64编码,那么会生成超过65000个字符的base64编码,字符的大小就已经是将近70K了!建议就是:8K以下的图片才转换成base64编码。
1.ID在页面上本来就是唯一的而且人家权值那么大,前方嵌套(.content #test)完全是浪费性能。以及多写一些没有意义的代码!这个虽然是一句话,但是还是有人犯这样的错!
2.除了嵌套,在id的前面也不需要加标签或者其它选择器。比如 p#test或者.test#test。这两种方式完全是多余的,理由就是ID在页面就是唯一的。前面加任何东西都是多余的!
把长段相同样式提取出来作为公用样式使用,比如常用的清除浮动,单行超出显示省略号,多行超出省略号等等。
如下栗子
/*超出省略号*/
/*<p class='text-ellipsis'></p>*/
.text-ellipsis{
overflow: hidden;
white-space: nowrap;
text-overflow: ellipsis;
}
/*清除浮动*/
/*<p class='clearfix'></p>*/
.clearfix:after {
display: block;
content: '';
clear: both;
height:0;
}在我之前一篇文章(移动web开发问题和优化小结),也有写过关于这个的优化建议,之前说的两个建议是:
1.CSS3动画或者过渡尽量使用transform和opacity来实现动画,不要使用left和top。
2.动画和过渡能用css3解决的,就不要使用js。如果是复杂的动画可以使用css3+js(或者html5+css3+js)配合开发,效果只有想不到,没有做不到。
下面补充一个:动画不宜过多,尤其是手机网站,否则会出现性能的问题,比如cpu一下子就被占用满了,掉帧等。而且,不建议给每一个元素都使用硬件加速。
参考链接:
CSS Animation性能优化
css3动画性能优化
CSS动画之硬件加速
Web动画
这个是在PC站会出现的问题,应该大家都知道。下面简单说一下!
比如下面的栗子,一个网站,页面内容宽度是1200px。看着很正常,没什么特别

如果这个时候,把页面窗口缩小。小于1200px,页面出现滚动条,然后把滚动条拖到最右边
这样是不是就发现,顶部的图片和背景有一部分是断层了!解决这个问题也很简单,就是给body加上min-width。值就是页面宽度的值。body{min-width:1200px;}
重复上一步操作,无论怎么改变浏览器窗口大小,都是正常的

之所以会出现这样的问题,是因为,比如窗口缩小到900px的时候,小于内容宽度的1200px。就是出现横向的滚动条,但是body的宽度是900px。这个时候,如果有元素(比如图片的灰色区域和粉红色的图片)是相对body的width设置100%,那么实际上这些元素的宽度也就是900px。所以会出现断层那些的视觉!解决方式就是给body加上min-width。让body的宽度最小不会小于内容的宽度!
关于我对css写作建议和性能优化的一个总结,就到这里了。css,绝对不是那种只要能用就行,或者只要能用css把布局弄好就行的一门语言。css给我的感觉,就是上手很简单,但是如果想用好css,还是得花时间去研究。css或者css3,能够优化的东西还有很多,用好css或者css3能够少写很多js代码,做出来的东西也是很神奇,大家还是得继续学习当中的知识!
如果大家觉得我文章有哪个地方写得不好,写错了,欢迎指正。如果有什么其它的建议,欢迎指点,让大家互相交流,互相学习,一起进步!最后,祝大家节日快乐!
![]()
The above is the detailed content of Suggestions and performance optimization summary about css. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




