
Today I would like to share with you some knowledge about regular expressions and their application in javascript. Regular expressions are simple but not simple. For example, when my teacher used to teach us, he said that if you get started with this thing, you can master it in 20 to 30 minutes. Once you don't get started, you won't be able to catch up in a few days. So I studied and researched it very seriously at the beginning. Unexpectedly, regular expressions not only simplify the code, but also save front-end engineers a lot of trouble in actual operations. As we all know, when users browse a page, the only thing that interacts with data is the form. Regarding form verification, there are actually many methods. Next, I will share with you two methods. One is an ordinary and cumbersome method. , one is regular expression, let’s see what effect it can bring to the form.
First let’s take a look at the regular version:
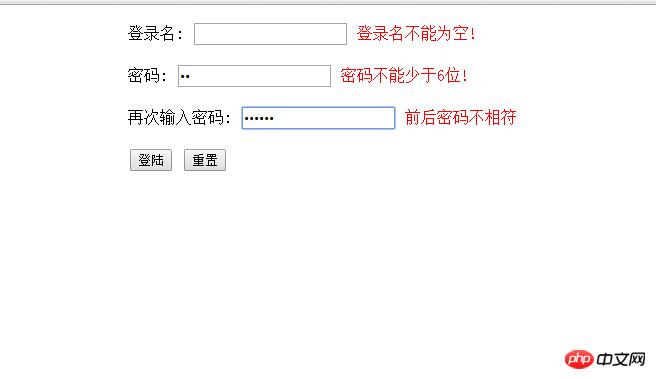
I personally feel that the method is too crude. This is a simple form I made when I first started learning. The effect is that no CSS style sheet is added.
Let’s take another look at the upgraded regular expression:
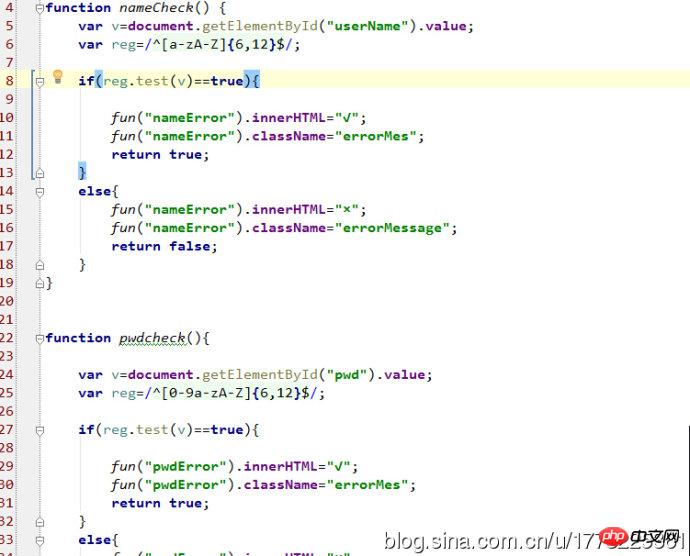
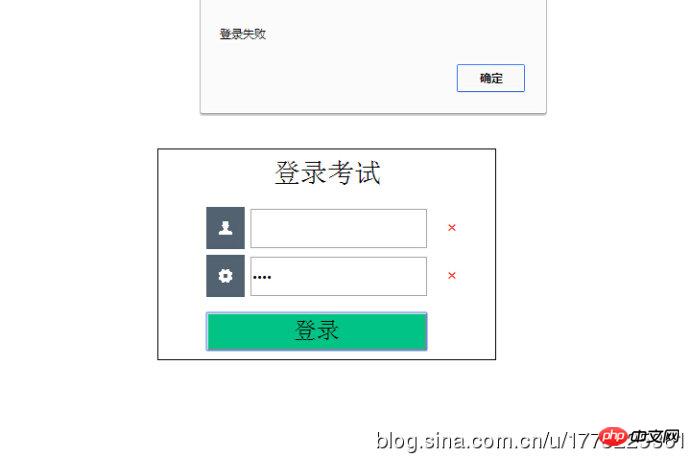
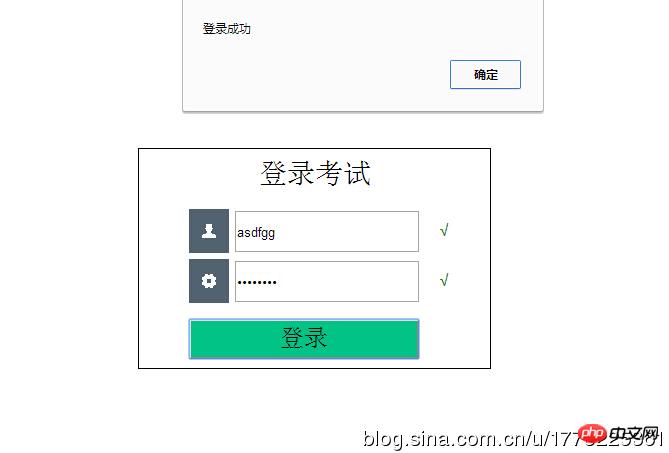
Continue Let’s learn about regular expressions together.
Regular expression is an object that describes a character pattern, also known as regular representation and conventional representation.
Regular expression uses a single string to describe and match a series of A string that conforms to a certain syntax rule. In many text editors, regular expressions are often used to retrieve and replace text that matches a certain pattern. The characteristics of regular expressions are: 1. Very flexible, logical and functional; 2. Complex control of strings can be achieved quickly and in an extremely simple way. 3. It is relatively obscure and difficult to understand for those who are new to it.
Define regular expression 1: Normal way varreg=/expression/additional parameters
reg.test(v.value)2:
methodvar reg=new RegExp("expression","additional parameters) var reg=new RegExp("china");Expression mode 1: simple mode var reg=/china/; 2: Matches the pattern var reg=/^\w+$/; var reg=/^\w+@\w+.[a-zA-Z]{2,3}(.[a-zA- Z]{2,3})?$/;
retrieves the characters that match the regular expression, returns the found value, and determines its position test Retrieve the specified value in the string, return true or false exec method: if no match is found, the return value is null; if a match is found, a result array is returned, /.../ represents the beginning and end of a pattern ^ matching characters The beginning of the string $ matches the end of the string \s Any whitespace character \S Any non-whitespace character \d Matches a numeric character, equivalent to [0-9] \D Any character except digits, equivalent to [^ 0-9] \wmatches a number, underscore, or alphabetical character, equivalent to [A-Za-z0-9_] \Wany non-single-word character, equivalent to [^a-zA-z0-9_]. Except for newlines Any character other than {n} matches the previous item n times {n,} matches the previous item n times, or multiple times {n,m} matches the previous item at least n times, but cannot More than m times * matches the previous item 0 or more times, equivalent to {0,} + matches the previous item 1 or more times, equivalent to {1,}? Matches the previous item 0 or 1 times, That is to say, the previous item is optional and is equivalent to {0,1}
x|y matches x or y. For example, "z|food" can match "z." " or "food". "(z|f)ood" matches "zood" or "food". [xyz] character set. Matches any character contained in it. For example, "[abc]" can match "plain" "a" in. [a-z]
Character range. Matches any character in the specified range. For example, "[a-z]" can match any lowercase alphabetic character in the range "a" to "z". Note: Only when the hyphen is inside the character group and appears between two characters, it can represent the range of characters; if it appears at the beginning of the character group, it can only represent the hyphen itself. (pattern) Match pattern and get this A match. The obtained matches can be obtained from the generated Matches collection, using the SubMatches collection in VBScript and using the $0...$9 attributes in JScript. To match parentheses characters, use "\(" or "\)".
The above is the detailed content of Illustrations on the concepts and applications of regular expressions in JavaScript. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




