The most comprehensive common techniques for CSS development
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is a computer language used to express file styles such as HTML (an application of Standard Generalized Markup Language) or XML (a subset of Standard Generalized Markup Language). CSS can not only statically modify web pages, but can also cooperate with various scripting languages to dynamically format various elements of web pages. CSS can perform pixel-level precise control over the layout of element positions in web pages, supports almost all font size styles, and has the ability to edit web page object and model styles.
Benefits of using css abbreviations
Using abbreviations can help reduce the size of your CSS file and make it easier to read.
Explicitly define units unless the value is 0, as well as px and em distinctions.
Forgetting to define the unit of size is a common mistake among CSS newbies. In HTML you can just write width="100", but in CSS you must give an exact unit, such as: width:100px width:100em. There are only two exceptions for not defining units: row height and 0 value. In addition, other values must follow the unit. Be careful not to add spaces between the value and the unit. The px unit is suitable for fixed layouts such as 960Grid. em is suitable for fluid layouts.
Use line-height for vertical centering, and experimental demonstration of the difference between line-height and height
line-height:24px; When using a fixed-width container and need a row to be vertically centered, use line-height That’s it (the height is the same as the parent layer container.
Syntax:
line-height : normal | length
Parameters:
normal: Default row height
length: Percentage number | By The length value composed of floating point numbers and unit identifiers is allowed to be negative. The percentage value is based on the height size of the font. See length unit
Description:
Retrieve or set the line height of the object. The distance between the bottom and the top of the font. If there are multiple objects in the line, the maximum line height cannot be negative.
<div style="line-height:24px; border:2px; border-style:dashed; margin:"> 使用 line-height 垂直居中<br /> 使用 line-height 垂直居中<br /> 使用 line-height 垂直居中<br /> 使用 line-height 垂直居中<br /> </div>
Clear container float, and overflow:hidden; Association of clear:both
#main {overflow:hidden; },clear:both;clear:left;clear:right; Overflow can be used to clear the overall container such as Body, and clear can be used to clear the div. And it is more flexible. It is also a very commonly used two attributes: clear: none | left | both
Parameters:
none: allowed. There can be floating objects on both sides
both: Floating objects are not allowed
left: Floating objects are not allowed on the left side
right: Floating objects are not allowed on the right side Description: The The value of the attribute indicates the edge on which floating objects are not allowed.
div { clear : left } img { float: right }
Syntax: overflow : visible | auto | hidden | scroll
Parameters:
visible: Do not cut the content or add scroll bars. If this default value is explicitly declared, the object will be cut to the size of the window or frame containing the object. ;The clip attribute setting will be invalid
auto: This is the default value for the body object and textarea. Cut the content and add scroll bars when needed
hidden: Do not display content that exceeds the object size
scroll: Always display scroll bars
Description:
Retrieve or set how to manage content when the content of the object exceeds its specified height and width. Setting the textarea object to the hidden value will hide its scroll bars. For tables, if the table-layout attribute is set to fixed, the td object supports the overflow attribute with a default value of hidden. If set to hidden, scroll or auto, content exceeding the td size will be cut. If set to visible, it will cause extra text to overflow to the cells on the right or left (depending on the direction property setting). Starting with IE5, this property is available on MAC platforms.
Do not allow links to wrap
a { white-space: nowrap; } p { white-space: nowrap; } The above settings can prevent links from wrapping.
Syntax: white-space : normal | pre | nowrap
Parameters:
normal: Default processing method
pre: Display pre in fixed-width font Formatted text. Do not merge spacing between words and perform justification. See pre object
nowrap: Force all text to be displayed on the same line until the end of the text or a br object is encountered. See the nowrap attribute (property) of td, div and other objects
Description: Set or retrieve the processing method of spaces within the object.
Always make Firefox show scroll bars
1 html {overflow:-moz-scrollbars-vertical; }
2 body, html {min-height:101%; } If it is greater than 100%, a scroll bar will inevitably appear.
Center the block element horizontally
margin:0 auto; is actually margin-left: auto; margin-right: auto; (top, right, bottom, left), remember one rule. Turn clockwise.
body{text-align: center; }
Then define the inner container text-align: left;
Hide the scroll bar of the Explorer textarea
textarea { overflow:auto; }
Exploer By default textarea will have vertical scroll bars (don't ask me why).
Set printing paging (if the experiment is not successful and the effect is not seen, please communicate)
h2 {page-break-before:always; } The page-break-before attribute can set the page break when printing a web page. Pagination.
Syntax:
page-break-before : auto | always | avoid | left | right | null
Parameters:
auto : 假如需要在对象之前插入页分割符
always : 始终在对象之前插入页分割符
avoid : 避免在对象前面插入页分割符
left : 在对象前面插入页分割符直到它到达一个空白的左页边
right : 在对象前面插入页分割符直到它到达一个空白的右页边 null : 空值。IE5用来取消页分割符设置
说明:
检索或设置对象前出现的页分割符。 IE5仅支持always值和空白值(null)。 在IE4中此属性不作用于br对象,但是IE5作用。
删除链接上的虚线框
a:active, a:focus {outline:none; }
Firefox 默认会在链接获得焦点(或者点击时)加上条虚线框,使用上面的属性可以删除。
最简单的 CSS 重置
* {margin: 0; padding: 0 } 如果想“复杂详细”,参考YUI 的做法(还有这里)。
http://developer.yahoo.com/yui/2/
/*CSS reset 示例*/
body,div,dl,dt,dd,ul,ol,li,h1,h2,h3,h4,h5,h6,pre,form,fieldset,input,textarea,p,blockquote,th,td{ margin:0; padding:0;}
table{border-collapse:collapse; border-spacing:0;}
fieldset,img{border:0}
address,caption,cite,code,dfn,em,strong,th,var{ font-style:normal;font-weight:normal;}
ol,ul{list-style:none}
caption,th{text-align:left}
h1,h2,h3,h4,h5,h6{ font-size:100%; font-weight:normal}
q:before,q:after{ content:''}
abbr,acronym{border:0}CSS盒模型以及IE和Firefox盒模型的区别
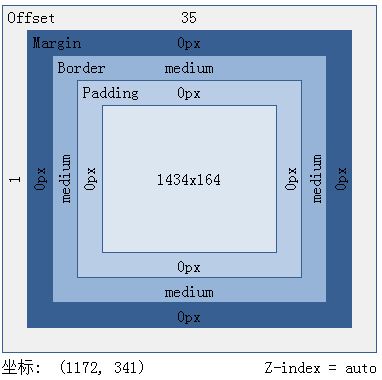
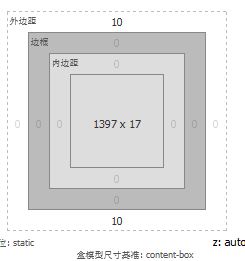
CSS盒子模型-什么是CSS盒子模型。
认识日常生活中盒子:
常常我们遇到盒子是用于可装东西长方形、正方形的盒子。如装皮鞋盒子、装电视机盒子,这个是比较具体的盒子。
CSS盒子:
根据字面我们可以理解,CSS盒子也是装东西的,比如我们要将文字内容、图片布局网页中,那就需要像盒子一样装着。这个时候我们对其对象设置高度(height)、宽度(width)、边框(border)、边距(margin)、填充(padding),即可实现像盒子一样的长方形、正方形平面盒子。
通常我们这样:
一组
日常使用CSS盒子:
我们说将什么内容放入一个盒子里,我们就要想到是放入
假如我们说设置一个宽度为100px盒子,我们就要知道如下一个概念:
Css样式代码:
.yangshi{width:100px;}对应html代码:
<div class="yangshi">内容</div>
这个时候我们可以将
<div class="yangshi">内容</div>看作为一个盒子。CSS简化了网页的格式代码,外部的样式表还会被浏览器保存在缓存里,加快了下载显示的速度,也减少了需要上传的代码数量(因为重复设置的格式将被只保存一次)。只要修改保存着网站格式的CSs样式表文件就町以改变整个站点的风格特色,在修改页面数量庞大的站点时,显得格外有用。这就避免了一个个网页的修改,大大减少了工作量。以上就是CSS开发常用的技巧总结,希望在开发上能帮助到大家。
相关推荐:
The above is the detailed content of The most comprehensive common techniques for CSS development. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What does placeholder mean in vue
May 07, 2024 am 09:57 AM
What does placeholder mean in vue
May 07, 2024 am 09:57 AM
In Vue.js, the placeholder attribute specifies the placeholder text of the input element, which is displayed when the user has not entered content, provides input tips or examples, and improves form accessibility. Its usage is to set the placeholder attribute on the input element and customize the appearance using CSS. Best practices include being relevant to the input, being short and clear, avoiding default text, and considering accessibility.
 What does span mean in js
May 06, 2024 am 11:42 AM
What does span mean in js
May 06, 2024 am 11:42 AM
The span tag can add styles, attributes, or behaviors to text. It is used to: add styles, such as color and font size. Set attributes such as id, class, etc. Associated behaviors such as clicks, hovers, etc. Mark text for further processing or citation.
 What does rem mean in js
May 06, 2024 am 11:30 AM
What does rem mean in js
May 06, 2024 am 11:30 AM
REM in CSS is a relative unit relative to the font size of the root element (html). It has the following characteristics: relative to the root element font size, not affected by the parent element. When the root element's font size changes, elements using REM will adjust accordingly. Can be used with any CSS property. Advantages of using REM include: Responsiveness: Keep text readable on different devices and screen sizes. Consistency: Make sure font sizes are consistent throughout your website. Scalability: Easily change the global font size by adjusting the root element font size.
 How to introduce images into vue
May 02, 2024 pm 10:48 PM
How to introduce images into vue
May 02, 2024 pm 10:48 PM
There are five ways to introduce images in Vue: through URL, require function, static file, v-bind directive and CSS background image. Dynamic images can be handled in Vue's computed properties or listeners, and bundled tools can be used to optimize image loading. Make sure the path is correct otherwise a loading error will appear.
 What language is the browser plug-in written in?
May 08, 2024 pm 09:36 PM
What language is the browser plug-in written in?
May 08, 2024 pm 09:36 PM
Browser plug-ins are usually written in the following languages: Front-end languages: JavaScript, HTML, CSS Back-end languages: C++, Rust, WebAssembly Other languages: Python, Java
 What is node in js
May 07, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
What is node in js
May 07, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
Nodes are entities in the JavaScript DOM that represent HTML elements. They represent a specific element in the page and can be used to access and manipulate that element. Common node types include element nodes, text nodes, comment nodes, and document nodes. Through DOM methods such as getElementById(), you can access nodes and operate on them, including modifying properties, adding/removing child nodes, inserting/replacing nodes, and cloning nodes. Node traversal helps navigate within the DOM structure. Nodes are useful for dynamically creating page content, event handling, animation, and data binding.
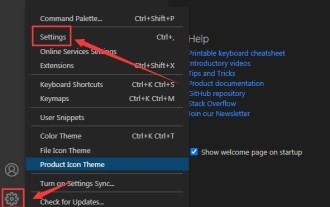 How to set unknown attributes in vscode vscode method to set unknown attributes
May 09, 2024 pm 02:43 PM
How to set unknown attributes in vscode vscode method to set unknown attributes
May 09, 2024 pm 02:43 PM
1. First, open the settings icon in the lower left corner and click the settings option. 2. Then, find the CSS column in the jumped window. 3. Finally, change the drop-down option in the unknownproperties menu to the error button.
 Can less files in vue introduce data?
May 07, 2024 pm 12:06 PM
Can less files in vue introduce data?
May 07, 2024 pm 12:06 PM
Yes, Less files in Vue can introduce data through CSS variables and Less mixins: create a JSON file containing data. Import JSON files using the @import rule. Access JSON data using CSS variables or Less mixins.






