As a PHP developer, sometimes we cannot complete a project or a function alone, just like when a warehouse developer has more than 1 or 20 people, each person may develop different modules and functions, using code versions Control tools such as git open different branches. The process is probably to first set up a complete environment locally, develop it and deploy it in the test environment. After self-test or tester testing, deploy it in the pre-release environment. The release is basically the same as the online environment, and then the product is inspected. After the acceptance is completed, the product is released online. Since it is developed in parallel, there must be situations where several functions are accepted or tested at the same time. At this time, whose code is deployed in the pre-release environment? If you switch to A's branch, B will not be able to accept it. Therefore, we hope that there will be a multi-person development environment where everyone's development process does not affect each other. In this article, we will share with you an analysis of the principles of the PHP multiplayer development environment.
First of all, let’s analyze the operating principle of PHP and take a look at the language characteristics of PHP. When we initiate a request from the browser, our web server (Nginx, Apache, etc.) listens to port 80 or 443. Let’s look at the simplest Nginx's vhost Configuration:
server {
listen 80;
server_name test.com;
root /data/gateway/html;
index index.php;
location ~ \.php$ {
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9001; #unix:/Users/run/php-fcgi.sock;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
}Nginx Listens to port 80, and uses the corresponding domain name when the domain name visited by the user is test.com The vhost configuration. PHP-FPM starts a service in the server and listens to a port (such as 9001) or a unix socket. Nginx is configured through fastcgi_pass and passes the request to PHP-FPM To parse the PHP code, the PHP parser starts parsing from index.php each time, processes it all the way, performs a series of logical processing, queries the database or cache, etc., and returns a HTML Or other results are given to Nginx, and Nginx is returned to the browser. The process is as follows:
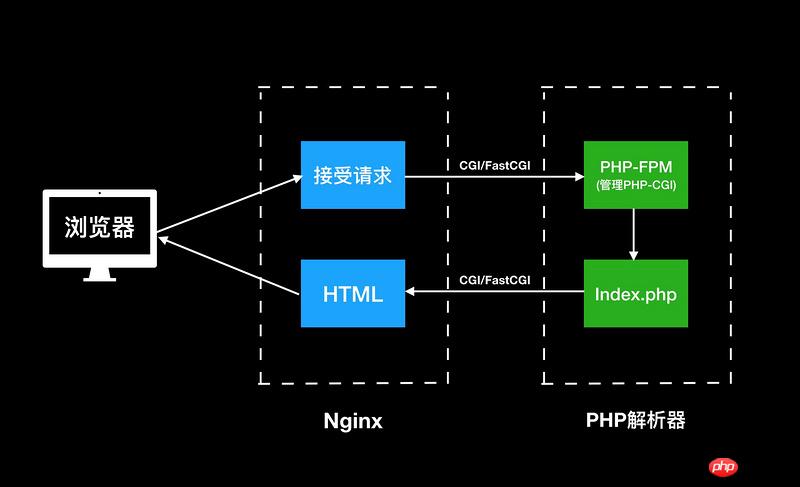
##CGI: It is Nginx and ## A protocol for data exchange between #PHP_FPM.
: Same as CGI, it is a communication protocol, but it is more efficient than CGI optimization.
: It is the interface of PHP to the CGI protocol provided by Nginx program.
: It is the interface of PHP to the FastCGI protocol provided by Nginx The program also provides some relatively intelligent task management.
principle that PHP is actually just an interpreted scripting language. Every request To parse it once from index.php, can we name many folders on the server according to the names of different developers, and in each folder, clone Good Code Warehouse , switch to your own branch. Then let Nginx handle the index in each person's directory. For example, visit http://wulv.test.com/ directly, get wulv in Nginx, and set root to wulv This directory, in this way, you can access the code in the wulv directory. You can set Nginx like this: <div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">set $who www;
if ($http_who != "") {
set $who $http_who;
}
root /data/gateway/$who/html;</pre><div class="contentsignin">Copy after login</div></div><div class="contentsignin">Copy after login</div></div> We can let
carry the user's directory, and intercept it in Nginx. You can add the following Places to carry:
: http://wulv.test.com
: http://www.test.com/wulv
http ://www.test.com?http_who=wulv
OAuth need to verify the domain name, and your domain name is inconsistent with the online domain name. Can't log in at all. So other ways are needed to achieve it, such as:
http_who to wulv, then get it in Nginx. Expand
PHP As the "best" language in the world, it occupies about 80% of the web. Small and medium-sized companies basically use the lnmp architecture. When there are more than 1 or 20 developers in a warehouse, each person may develop different modules and functions, and use code version control tools such as git to open different branches. The process is probably to set up a set locally first. The complete environment is developed and deployed in the test environment. After self-test or tester testing, it is deployed in the pre-release environment. The pre-release is basically the same as the online environment, and then the product is accepted. After the acceptance is completed, it is released and launched online.
Because it is developed in parallel, there must be situations where several functions are accepted or tested at the same time. At this time, whose code is deployed in the pre-release environment? If you switch to A's branch, B will not be able to accept it. Therefore, we hope that there will be a multi-person development environment where everyone's development process does not affect each other.
First of all, let’s analyze the operating principle of PHP and take a look at the language characteristics of PHP. When we initiate a request from the browser, our web server (Nginx, Apache, etc.) listens to port 80 or 443. Let’s look at the simplest Nginx's vhost Configuration:
server {
listen 80;
server_name test.com;
root /data/gateway/html;
index index.php;
location ~ \.php$ {
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9001; #unix:/Users/run/php-fcgi.sock;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
}Nginx Listens to port 80, and uses the corresponding domain name when the domain name visited by the user is test.com The vhost configuration. PHP-FPM starts a service in the server and listens to a port (such as 9001) or a unix socket. Nginx is configured through fastcgi_pass and passes the request to PHP-FPM To parse the PHP code, the PHP parser starts parsing from index.php each time, processes it all the way, performs a series of logical processing, queries the database or cache, etc., and returns a HTML Or other results are given to Nginx, and Nginx is returned to the browser. The process is as follows:

##CGI: It is Nginx and ## A protocol for data exchange between #PHP_FPM.
: Same as CGI, it is a communication protocol, but it is more efficient than CGI optimization.
: It is the interface of PHP to the CGI protocol provided by Nginx program.
: It is the interface of PHP to the FastCGI protocol provided by Nginx The program also provides some relatively intelligent task management.
principle that PHP is actually just an interpreted scripting language. Every request To parse it once from index.php, can we name many folders on the server according to the names of different developers, and in each folder, clone Good Code Warehouse , switch to your own branch. Then let Nginx handle the index in each person's directory. For example, visit http://wulv.test.com/ directly, get wulv in Nginx, and set root to wulv This directory, in this way, you can access the code in the wulv directory. You can set Nginx like this: <div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">set $who www;
if ($http_who != "") {
set $who $http_who;
}
root /data/gateway/$who/html;</pre><div class="contentsignin">Copy after login</div></div><div class="contentsignin">Copy after login</div></div> We can let
carry the user's directory, and intercept it in Nginx. You can add the following Places to carry:
: http://wulv.test.com
: http://www.test.com/wulv
http ://www.test.com?http_who=wulv
OAuth need to verify the domain name, and your domain name is inconsistent with the online domain name. Can't log in at all. So other ways are needed to achieve it, such as:
http_who to wulv, then get it in Nginx. Expand
Related recommendations:
php Chinese website acquires the secret of phpstudy integrated development environment with the largest number of users in the country
php Integrated Development Environment Encyclopedia
How to build a JSP development environment




