Native JS implements table sorting
I have been learning JS table sorting recently, but I didn’t expect that the inconspicuous table sorting actually implies many JS knowledge points. Record this learning process here. Hope it helps everyone too.
Complete table sorting involves the following knowledge points:
call method uses
-
sort method in-depth
Data Binding
DOM Mapping
Function.prototype. Any function we define can be considered as an instance of the Function class. Then you can find the prototype of the class through the __proto__ attribute of the instance. Any function can call methods such as call and apply.
var obj = {
name : 'JS'
}
function testCall () {
console.log(this);
}
testCall.call( obj ); // {name: "JS"}testCall finds the call method to execute through the prototype chain search mechanism. The call method calls the call method during the execution process. This in the instance is changed to the first parameter of call, and then the instance function of the call method is called and executed.
function fn1() {
console.log(1);
console.log(this);
}
function fn2() {
console.log(2);
console.log(this);
}
fn1.call(fn2); //this -> fn2
fn1.call.call(fn2); //这里的call是改变function.__proto__.call的call方法中的this,相当于执行参数window.
sum.call(); //window sum.call(null); //window sum.call(undefined); //window
sum.call(); //undefined sum.call(null); //null sum.call(undefined); //undefined
function listToArray (likeAry) {
var ary = [];
try {
ary = Array.prototype.slice.call(likeAry);
} catch (e) {
for (var i = 0; i < likeAry.length; i ++) {
ary[ary.length] = likeAry[i];
}
}
return ary;
}function sum(num1, num2) {
console.log(num2 + num1);
console.log(this);
}
sum.apply(null,[100,200]);function sum(num1, num2) {
console.log(num2 + num1);
console.log(this);
}
var obj = {name : 'zx'}
var temp = sum.bind(obj); //temp已经是被改变了this的函数
temp(100,200); //当我们需要的时候才执行
//或者像这样处理
var temp = sum.bind(null, 100, 200);
temp();sort method of an array can only sort arrays within 10. If there are numbers greater than 10 in the array that needs to be sorted, we need to pass the callback function to the sort method. The common one is like this:
ary.sort(function (a,b) {
return a - b;
});a represents the current item in the found array, and b represents the item after the current item.
return a -b
: If a is greater than b, return the result, and a and b exchange positions. If a is smaller than b, then the positions of a and b remain unchanged. This is ascending orderreturn b -a
: If b is greater than a, return the result, and a and b exchange positions. If a is smaller than b, then the positions of a and b remain unchanged. This is descending order
var persons = [{
name:'dawei',
age:55
},{
name:'ahung',
age:3
},{
name:'maomi',
age:2
},{
name:'heizi',
age:78
},{
name:'afu',
age:32
}];ary.sort(function(a,b){
return a.age - b.age;
});localeCompare() method of the string is involved:
ary.sort(function(a,b){
return a.name.localeCompare(b.name);
}); name.localeCompare()This method will compare the letters of the two strings. If the first letter of the previous string appears in a position higher than the first character of the latter string among the 24 English letters, If it appears in the front position, the first string is considered small and -1 is returned. If it appears later, the first string is considered larger and 1 is returned. If the compared characters are equal. Then compare the next character.
//ary为需要添加到页面中的数据数组
var op = document.getElementById("box");//获取容器
var myUl = op.getElementsByTagName("ul")[0];//获取列表
var arrLength = ary.length;
for (var i = 0;i < arrLength ; i ++)
{ //动态创建元素
var oli = document.createElement("li");
oli.innerHTML = '<span>' + (i + 5) + '</span>' + ary[i].title;
myUl.appendChild(oli);//动态添加元素
}var str = "";
for(var i=0; i<ary.length; i++){
str += '<li>';
str += '<span>';
str += (i+5);
str += '</span>';
str += ary[i].title;
str += '</li>';
}
myUl.innerHTML += str;var frg = document.createDocumentFragment();//创建文档碎片
for (var i =0; i <ary.length ;i ++ ){
var li = document.createElement("li");
li.innerHTML = '<span>' + ( i + 5 ) + '</span>' + ary[i].title;
frg.appendChild(li);//将数据动态添加至文档碎片中
}
myUl.appendChild(frg); //将数据一次性添加到页面中
frg = null; //释放内存4、DOM映射
DOM映射机制:所谓映射,就是指两个元素集之间元素相互“对应”的关系。页面中的标签集合和在JS中获取到的元素对象(元素集合)就是这样的关系。如果页面中的HTML标签结构发送变化,那么集合中对应的内容也会跟着自动改变。
<ul id="myul"> <li>1</li> <li>2</li> <li>3</li> <li>4</li> <li>5</li> </ul>
对于这样一个列表使用下列脚本:
var myul = document.getElementById("myul");
var mylis = myul.getElementsByTagName('li');
for (var i = mylis.length - 1 ; i >= 0; i --) {
myul.appendChild(mylis[i]);
}
console.log(mylis.length); // 5将获取到的列表元素反序重新插入ul中,那么ul列表会变成下面这样:
<ul id="myul"> <li>5</li> <li>4</li> <li>3</li> <li>2</li> <li>1</li> </ul>
我们看到列表的长度依然是5,只是位置颠倒了。这是因为每个li标签和JS中获取的标签对象存在一个对应关系,当某个标签被重新插入到页面中时,页面中对应的标签会移动到插入的位置。这就是DOM映射。
二、实现表格排序
1、使用ajax获取数据
之所以使用动态获取数据,是为了使用文档碎片绑定数据。
var res = ''; //声明一个全局变量,接收数据
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open('get', 'date.txt', false);
xhr.onreadystatechange = function() {
if (xhr.readyState == 4 && xhr.status == 200) {
res = JSON.parse(xhr.responseText);
}
}
xhr.send(null);此时数据就保存在了res这个全局变量之中。
2、使用文档碎片绑定数据
var frg = document.createDocumentFragment();
for (let i = 0; i < res.length; i++) {
var tr = document.createElement("tr");
for (key in res[i]) {
var td = document.createElement("td");
td.innerHTML = res[i][key];
tr.appendChild(td);
}
frg.appendChild(tr);
}
tbody.appendChild(frg);3、对表格进行排序
这里涉及的点较多
//为两列添加点击事件
for (let i = 0; i < ths.length; i++) {
let curTh = ths[i];
curTh.sortFlag = -1; //用于对列进行升降序排列
curTh.index = i; //记录当前点击列的索引,便于排序操作
if (curTh.className == 'sort') {
curTh.onclick = function() {
sort.call(this); //改变排序函数内this的指向,让其指向当前点击列
}
}
}
//排序方法
function sort() {
//对数组元素进行排序
let target = this; //这里将this取出,因为在sort方法里需要使用该this,但是sort方法里的this是调用方法的数组
this.sortFlag *= -1; //1 代表升序 -1代表降序
let ary = listToArray(bodyTrs); //获取body数据
ary = ary.sort(function(a, b) {
let one = a.cells[target.index].innerHTML;
let two = b.cells[target.index].innerHTML;
let oneNum = parseFloat(one);
let twoNum = parseFloat(two);
if (isNaN(oneNum) || isNaN(two)) {
return one.localeCompare(two) * target.sortFlag;
} else {
return (oneNum - twoNum) * target.sortFlag;
}
});
//把排好序的数组重新写入页面
let frg = document.createDocumentFragment();
for (let i = 0; i < ary.length; i++) {
rg.appendChild(ary[i]);
}
tbody.appendChild(frg);
frg = null;
//点击某列时,要将其他列的排序标志恢复为-1,让下次再点击任意一个标签时都是默认是升序排列
for (let i = 0; i < ths.length; i++) {
if (ths[i] != this) {
ths[i].sortFlag = -1;
}
}
}表格排序应用很常见,在面试中也会有这样的题目。这个小案例做下来,受益匪浅。这是我在学习的某峰学院的JS课程中的一个案例,如果对JS掌握不扎实的同学,欢迎保存:链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1jHVy8Uq 密码: v4jk。如果链接失效,加Q群领取:154658901。
I have been learning JS table sorting recently, but I didn’t expect that the inconspicuous table sorting actually implies many JS knowledge points. Record this learning process here. Hope it helps everyone too.
Complete table sorting involves the following knowledge points:
call method uses
sort method in-depth
Data Binding
DOM Mapping

Function.prototype. Any function we define can be considered as an instance of the Function class. Then you can find the prototype of the class through the __proto__ attribute of the instance. Any function can call methods such as call and apply.
var obj = {
name : 'JS'
}
function testCall () {
console.log(this);
}
testCall.call( obj ); // {name: "JS"}testCall finds the call method to execute through the prototype chain search mechanism. The call method calls the call method during the execution process. This in the instance is changed to the first parameter of call, and then the instance function of the call method is called and executed.
function fn1() {
console.log(1);
console.log(this);
}
function fn2() {
console.log(2);
console.log(this);
}
fn1.call(fn2); //this -> fn2
fn1.call.call(fn2); //这里的call是改变function.__proto__.call的call方法中的this,相当于执行参数window.
sum.call(); //window sum.call(null); //window sum.call(undefined); //window
sum.call(); //undefined sum.call(null); //null sum.call(undefined); //undefined
function listToArray (likeAry) {
var ary = [];
try {
ary = Array.prototype.slice.call(likeAry);
} catch (e) {
for (var i = 0; i < likeAry.length; i ++) {
ary[ary.length] = likeAry[i];
}
}
return ary;
}function sum(num1, num2) {
console.log(num2 + num1);
console.log(this);
}
sum.apply(null,[100,200]);function sum(num1, num2) {
console.log(num2 + num1);
console.log(this);
}
var obj = {name : 'zx'}
var temp = sum.bind(obj); //temp已经是被改变了this的函数
temp(100,200); //当我们需要的时候才执行
//或者像这样处理
var temp = sum.bind(null, 100, 200);
temp();sort method of an array can only sort arrays within 10. If there are numbers greater than 10 in the array that needs to be sorted, we need to pass the callback function to the sort method. The common one is like this:
ary.sort(function (a,b) {
return a - b;
});a represents the current item in the found array, and b represents the item after the current item.
return a -b
: If a is greater than b, return the result, and a and b exchange positions. If a is smaller than b, then the positions of a and b remain unchanged. This is ascending orderreturn b -a
: If b is greater than a, return the result, and a and b exchange positions. If a is smaller than b, then the positions of a and b remain unchanged. This is descending order
var persons = [{
name:'dawei',
age:55
},{
name:'ahung',
age:3
},{
name:'maomi',
age:2
},{
name:'heizi',
age:78
},{
name:'afu',
age:32
}];ary.sort(function(a,b){
return a.age - b.age;
});localeCompare() method of the string is involved:
ary.sort(function(a,b){
return a.name.localeCompare(b.name);
}); name.localeCompare()This method will compare the letters of the two strings. If the first letter of the previous string appears in a position higher than the first character of the latter string among the 24 English letters, If it appears in the front position, the first string is considered small and -1 is returned. If it appears later, the first string is considered larger and 1 is returned. If the compared characters are equal. Then compare the next character.
//ary为需要添加到页面中的数据数组
var op = document.getElementById("box");//获取容器
var myUl = op.getElementsByTagName("ul")[0];//获取列表
var arrLength = ary.length;
for (var i = 0;i < arrLength ; i ++)
{ //动态创建元素
var oli = document.createElement("li");
oli.innerHTML = '<span>' + (i + 5) + '</span>' + ary[i].title;
myUl.appendChild(oli);//动态添加元素
}var str = "";
for(var i=0; i<ary.length; i++){
str += '<li>';
str += '<span>';
str += (i+5);
str += '</span>';
str += ary[i].title;
str += '</li>';
}
myUl.innerHTML += str;var frg = document.createDocumentFragment();//创建文档碎片
for (var i =0; i <ary.length ;i ++ ){
var li = document.createElement("li");
li.innerHTML = '<span>' + ( i + 5 ) + '</span>' + ary[i].title;
frg.appendChild(li);//将数据动态添加至文档碎片中
}
myUl.appendChild(frg); //将数据一次性添加到页面中
frg = null; //释放内存4、DOM映射
DOM映射机制:所谓映射,就是指两个元素集之间元素相互“对应”的关系。页面中的标签集合和在JS中获取到的元素对象(元素集合)就是这样的关系。如果页面中的HTML标签结构发送变化,那么集合中对应的内容也会跟着自动改变。
<ul id="myul"> <li>1</li> <li>2</li> <li>3</li> <li>4</li> <li>5</li> </ul>
对于这样一个列表使用下列脚本:
var myul = document.getElementById("myul");
var mylis = myul.getElementsByTagName('li');
for (var i = mylis.length - 1 ; i >= 0; i --) {
myul.appendChild(mylis[i]);
}
console.log(mylis.length); // 5将获取到的列表元素反序重新插入ul中,那么ul列表会变成下面这样:
<ul id="myul"> <li>5</li> <li>4</li> <li>3</li> <li>2</li> <li>1</li> </ul>
我们看到列表的长度依然是5,只是位置颠倒了。这是因为每个li标签和JS中获取的标签对象存在一个对应关系,当某个标签被重新插入到页面中时,页面中对应的标签会移动到插入的位置。这就是DOM映射。
二、实现表格排序
1、使用ajax获取数据
之所以使用动态获取数据,是为了使用文档碎片绑定数据。
var res = ''; //声明一个全局变量,接收数据
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open('get', 'date.txt', false);
xhr.onreadystatechange = function() {
if (xhr.readyState == 4 && xhr.status == 200) {
res = JSON.parse(xhr.responseText);
}
}
xhr.send(null);此时数据就保存在了res这个全局变量之中。
2、使用文档碎片绑定数据
var frg = document.createDocumentFragment();
for (let i = 0; i < res.length; i++) {
var tr = document.createElement("tr");
for (key in res[i]) {
var td = document.createElement("td");
td.innerHTML = res[i][key];
tr.appendChild(td);
}
frg.appendChild(tr);
}
tbody.appendChild(frg);3、对表格进行排序
这里涉及的点较多
//为两列添加点击事件
for (let i = 0; i < ths.length; i++) {
let curTh = ths[i];
curTh.sortFlag = -1; //用于对列进行升降序排列
curTh.index = i; //记录当前点击列的索引,便于排序操作
if (curTh.className == 'sort') {
curTh.onclick = function() {
sort.call(this); //改变排序函数内this的指向,让其指向当前点击列
}
}
}
//排序方法
function sort() {
//对数组元素进行排序
let target = this; //这里将this取出,因为在sort方法里需要使用该this,但是sort方法里的this是调用方法的数组
this.sortFlag *= -1; //1 代表升序 -1代表降序
let ary = listToArray(bodyTrs); //获取body数据
ary = ary.sort(function(a, b) {
let one = a.cells[target.index].innerHTML;
let two = b.cells[target.index].innerHTML;
let oneNum = parseFloat(one);
let twoNum = parseFloat(two);
if (isNaN(oneNum) || isNaN(two)) {
return one.localeCompare(two) * target.sortFlag;
} else {
return (oneNum - twoNum) * target.sortFlag;
}
});
//把排好序的数组重新写入页面
let frg = document.createDocumentFragment();
for (let i = 0; i < ary.length; i++) {
rg.appendChild(ary[i]);
}
tbody.appendChild(frg);
frg = null;
//点击某列时,要将其他列的排序标志恢复为-1,让下次再点击任意一个标签时都是默认是升序排列
for (let i = 0; i < ths.length; i++) {
if (ths[i] != this) {
ths[i].sortFlag = -1;
}
}
}以上内容就是原生JS实现表格排序,希望能帮助到大家。
jquery中tablesorter表格排序组件是如何使用的?
js表格排序实例详解(支持int,float,date,string四种数据类型)
The above is the detailed content of Native JS implements table sorting. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
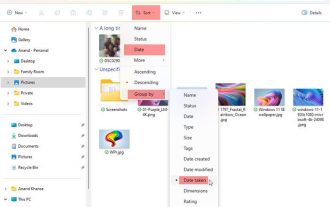 How to sort photos by date taken in Windows 11/10
Feb 19, 2024 pm 08:45 PM
How to sort photos by date taken in Windows 11/10
Feb 19, 2024 pm 08:45 PM
This article will introduce how to sort pictures according to shooting date in Windows 11/10, and also discuss what to do if Windows does not sort pictures by date. In Windows systems, organizing photos properly is crucial to making it easy to find image files. Users can manage folders containing photos based on different sorting methods such as date, size, and name. In addition, you can set ascending or descending order as needed to organize files more flexibly. How to Sort Photos by Date Taken in Windows 11/10 To sort photos by date taken in Windows, follow these steps: Open Pictures, Desktop, or any folder where you place photos In the Ribbon menu, click
 Steps to adjust the format of pictures inserted in PPT tables
Mar 26, 2024 pm 04:16 PM
Steps to adjust the format of pictures inserted in PPT tables
Mar 26, 2024 pm 04:16 PM
1. Create a new PPT file and name it [PPT Tips] as an example. 2. Double-click [PPT Tips] to open the PPT file. 3. Insert a table with two rows and two columns as an example. 4. Double-click on the border of the table, and the [Design] option will appear on the upper toolbar. 5. Click the [Shading] option and click [Picture]. 6. Click [Picture] to pop up the fill options dialog box with the picture as the background. 7. Find the tray you want to insert in the directory and click OK to insert the picture. 8. Right-click on the table box to bring up the settings dialog box. 9. Click [Format Cells] and check [Tile images as shading]. 10. Set [Center], [Mirror] and other functions you need, and click OK. Note: The default is for pictures to be filled in the table
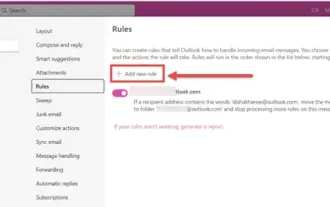 How to sort emails by sender, subject, date, category, size in Outlook
Feb 19, 2024 am 10:48 AM
How to sort emails by sender, subject, date, category, size in Outlook
Feb 19, 2024 am 10:48 AM
Outlook offers many settings and features to help you manage your work more efficiently. One of them is the sorting option that allows you to categorize your emails according to your needs. In this tutorial, we will learn how to use Outlook's sorting feature to organize emails based on criteria such as sender, subject, date, category, or size. This will make it easier for you to process and find important information, making you more productive. Microsoft Outlook is a powerful application that makes it easy to centrally manage your email and calendar schedules. You can easily send, receive, and organize email, while built-in calendar functionality makes it easy to keep track of your upcoming events and appointments. How to be in Outloo
 How to make a table for sales forecast
Mar 20, 2024 pm 03:06 PM
How to make a table for sales forecast
Mar 20, 2024 pm 03:06 PM
Being able to skillfully make forms is not only a necessary skill for accounting, human resources, and finance. For many sales staff, learning to make forms is also very important. Because the data related to sales is very large and complex, and it cannot be simply recorded in a document to explain the problem. In order to enable more sales staff to be proficient in using Excel to make tables, the editor will introduce the table making issues about sales forecasting. Friends in need should not miss it! 1. Open [Sales Forecast and Target Setting], xlsm, to analyze the data stored in each table. 2. Create a new [Blank Worksheet], select [Cell], and enter [Label Information]. [Drag] downward and [Fill] the month. Enter [Other] data and click [
 How to set WPS value to automatically change color according to conditions_Steps to set WPS table value to automatically change color according to condition
Mar 27, 2024 pm 07:30 PM
How to set WPS value to automatically change color according to conditions_Steps to set WPS table value to automatically change color according to condition
Mar 27, 2024 pm 07:30 PM
1. Open the worksheet and find the [Start]-[Conditional Formatting] button. 2. Click Column Selection and select the column to which conditional formatting will be added. 3. Click the [Conditional Formatting] button to bring up the option menu. 4. Select [Highlight conditional rules]-[Between]. 5. Fill in the rules: 20, 24, dark green text with dark fill color. 6. After confirmation, the data in the selected column will be colored with corresponding numbers, text, and cell boxes according to the settings. 7. Conditional rules without conflicts can be added repeatedly, but for conflicting rules WPS will replace the previously established conditional rules with the last added rule. 8. Repeatedly add the cell columns after [Between] rules 20-24 and [Less than] 20. 9. If you need to change the rules, you can just clear the rules and then reset the rules.
 Do you know how to sum a Word table?
Mar 21, 2024 pm 01:10 PM
Do you know how to sum a Word table?
Mar 21, 2024 pm 01:10 PM
Sometimes, we often encounter counting problems in Word tables. Generally, when encountering such problems, most students will copy the Word table to Excel for calculation; some students will silently pick up the calculator. Calculate. Is there a quick way to calculate it? Of course there is, in fact the sum can also be calculated in Word. So, do you know how to do it? Today, let’s take a look together! Without further ado, friends in need should quickly collect it! Step details: 1. First, we open the Word software on the computer and open the document that needs to be processed. (As shown in the picture) 2. Next, we position the cursor on the cell where the summed value is located (as shown in the picture); then, we click [Menu Bar
 How to switch tables horizontally and vertically in word
Mar 20, 2024 am 09:31 AM
How to switch tables horizontally and vertically in word
Mar 20, 2024 am 09:31 AM
Word software is indispensable to us and needs to be used frequently. I have learned how to edit tables using Word software before. However, if I accidentally edit the table in the horizontal and vertical directions, and I don’t want to waste time re-creating it, is it possible to change the horizontal and vertical directions of the table? Woolen cloth? The answer is of course yes. Next, the editor will introduce to you in detail how to swap tables horizontally and vertically in Word. Let us learn together. First, we need to swap the rows and columns of the Word table below. To do this, we need to first select the table entirely, then right-click and select the copy function. Step 2: After selecting copy, we minimize word, then open an Excel table, right-click, select paste, and paste it into Exc
 What are the tips for novices to create forms?
Mar 21, 2024 am 09:11 AM
What are the tips for novices to create forms?
Mar 21, 2024 am 09:11 AM
We often create and edit tables in excel, but as a novice who has just come into contact with the software, how to use excel to create tables is not as easy as it is for us. Below, we will conduct some drills on some steps of table creation that novices, that is, beginners, need to master. We hope it will be helpful to those in need. A sample form for beginners is shown below: Let’s see how to complete it! 1. There are two methods to create a new excel document. You can right-click the mouse on a blank location on the [Desktop] - [New] - [xls] file. You can also [Start]-[All Programs]-[Microsoft Office]-[Microsoft Excel 20**] 2. Double-click our new ex




