How JS uses greedy algorithm to solve the change problem
In real life, we often encounter the problem of making change. Suppose there is an unlimited number of coins with face values of 20,10,5,1. Given the amount of change needed, find the change plan. The requirement is: use the minimum number of coins.
For this kind of problem, the greedy algorithm adopts the method of always selecting the maximum value of coins available for change when changing money. For example, when the number of change required is 25, the change method is 20+5 instead of 10+10+5.
The greedy algorithm is still one of the most common algorithms. This is because it is simple and easy to implement, and it is not very difficult to construct a greedy strategy. In this article, we will share with you an example of JS using greedy algorithm to solve the change problem.
Unfortunately, it needs to be proved before it can be truly applied to the algorithm of the problem.
<script>
var money= [20,10,5,1];
/*
* m[]:存放可供找零的面值,降序排列
* n:需要找零数
*/
function greedyMoney(m,n){
for(var i=0;i<m.length;i++){
while(n>=m[i] && n>0){
document.write(m[i]+" ");
n = n-m[i];
}
}
document.write("<br>");
}
greedyMoney(money,73);
greedyMoney([25,10,1],63);
</script>The result is:
20 20 20 10 1 1 1 25 25 10 1 1 1
It should be noted that in some cases, using the greedy algorithm for the change problem cannot obtain the overall optimal solution, and the result may only be a good approximation of the optimal solution.
For example, if the face value of the change provided is 11, 5, 1, the change is 15.
The change method using the greedy algorithm is 11+1+1+1+1, which requires five coins. The optimal solution is 5+5+5, which only requires 3 coins.
Related recommendations:
JS implements the minimum number of change sheets
##code sharing of a small program for change implemented in Python
The above is the detailed content of How JS uses greedy algorithm to solve the change problem. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 Five tips to teach you how to solve the problem of Black Shark phone not turning on!
Mar 24, 2024 pm 12:27 PM
Five tips to teach you how to solve the problem of Black Shark phone not turning on!
Mar 24, 2024 pm 12:27 PM
As smartphone technology continues to develop, mobile phones play an increasingly important role in our daily lives. As a flagship phone focusing on gaming performance, the Black Shark phone is highly favored by players. However, sometimes we also face the situation that the Black Shark phone cannot be turned on. At this time, we need to take some measures to solve this problem. Next, let us share five tips to teach you how to solve the problem of Black Shark phone not turning on: Step 1: Check the battery power. First, make sure your Black Shark phone has enough power. It may be because the phone battery is exhausted
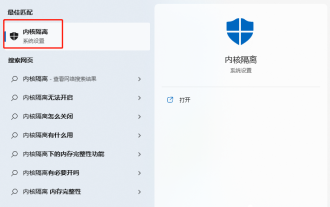 The driver cannot be loaded on this device. How to solve it? (Personally tested and valid)
Mar 14, 2024 pm 09:00 PM
The driver cannot be loaded on this device. How to solve it? (Personally tested and valid)
Mar 14, 2024 pm 09:00 PM
Everyone knows that if the computer cannot load the driver, the device may not work properly or interact with the computer correctly. So how do we solve the problem when a prompt box pops up on the computer that the driver cannot be loaded on this device? The editor below will teach you two ways to easily solve the problem. Unable to load the driver on this device Solution 1. Search for "Kernel Isolation" in the Start menu. 2. Turn off Memory Integrity, and it will prompt "Memory Integrity has been turned off. Your device may be vulnerable." Click behind to ignore it, and it will not affect the use. 3. The problem can be solved after restarting the machine.
 How to solve the problem of automatically saving pictures when publishing on Xiaohongshu? Where is the automatically saved image when posting?
Mar 22, 2024 am 08:06 AM
How to solve the problem of automatically saving pictures when publishing on Xiaohongshu? Where is the automatically saved image when posting?
Mar 22, 2024 am 08:06 AM
With the continuous development of social media, Xiaohongshu has become a platform for more and more young people to share their lives and discover beautiful things. Many users are troubled by auto-save issues when posting images. So, how to solve this problem? 1. How to solve the problem of automatically saving pictures when publishing on Xiaohongshu? 1. Clear the cache First, we can try to clear the cache data of Xiaohongshu. The steps are as follows: (1) Open Xiaohongshu and click the "My" button in the lower right corner; (2) On the personal center page, find "Settings" and click it; (3) Scroll down and find the "Clear Cache" option. Click OK. After clearing the cache, re-enter Xiaohongshu and try to post pictures to see if the automatic saving problem is solved. 2. Update the Xiaohongshu version to ensure that your Xiaohongshu
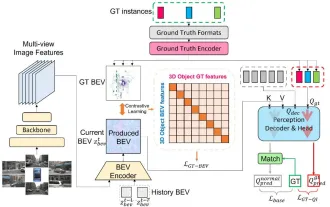 CLIP-BEVFormer: Explicitly supervise the BEVFormer structure to improve long-tail detection performance
Mar 26, 2024 pm 12:41 PM
CLIP-BEVFormer: Explicitly supervise the BEVFormer structure to improve long-tail detection performance
Mar 26, 2024 pm 12:41 PM
Written above & the author’s personal understanding: At present, in the entire autonomous driving system, the perception module plays a vital role. The autonomous vehicle driving on the road can only obtain accurate perception results through the perception module. The downstream regulation and control module in the autonomous driving system makes timely and correct judgments and behavioral decisions. Currently, cars with autonomous driving functions are usually equipped with a variety of data information sensors including surround-view camera sensors, lidar sensors, and millimeter-wave radar sensors to collect information in different modalities to achieve accurate perception tasks. The BEV perception algorithm based on pure vision is favored by the industry because of its low hardware cost and easy deployment, and its output results can be easily applied to various downstream tasks.
 Implementing Machine Learning Algorithms in C++: Common Challenges and Solutions
Jun 03, 2024 pm 01:25 PM
Implementing Machine Learning Algorithms in C++: Common Challenges and Solutions
Jun 03, 2024 pm 01:25 PM
Common challenges faced by machine learning algorithms in C++ include memory management, multi-threading, performance optimization, and maintainability. Solutions include using smart pointers, modern threading libraries, SIMD instructions and third-party libraries, as well as following coding style guidelines and using automation tools. Practical cases show how to use the Eigen library to implement linear regression algorithms, effectively manage memory and use high-performance matrix operations.
 Explore the underlying principles and algorithm selection of the C++sort function
Apr 02, 2024 pm 05:36 PM
Explore the underlying principles and algorithm selection of the C++sort function
Apr 02, 2024 pm 05:36 PM
The bottom layer of the C++sort function uses merge sort, its complexity is O(nlogn), and provides different sorting algorithm choices, including quick sort, heap sort and stable sort.
 Can artificial intelligence predict crime? Explore CrimeGPT's capabilities
Mar 22, 2024 pm 10:10 PM
Can artificial intelligence predict crime? Explore CrimeGPT's capabilities
Mar 22, 2024 pm 10:10 PM
The convergence of artificial intelligence (AI) and law enforcement opens up new possibilities for crime prevention and detection. The predictive capabilities of artificial intelligence are widely used in systems such as CrimeGPT (Crime Prediction Technology) to predict criminal activities. This article explores the potential of artificial intelligence in crime prediction, its current applications, the challenges it faces, and the possible ethical implications of the technology. Artificial Intelligence and Crime Prediction: The Basics CrimeGPT uses machine learning algorithms to analyze large data sets, identifying patterns that can predict where and when crimes are likely to occur. These data sets include historical crime statistics, demographic information, economic indicators, weather patterns, and more. By identifying trends that human analysts might miss, artificial intelligence can empower law enforcement agencies
 How to solve the problem of garbled characters when importing Chinese data into Oracle?
Mar 10, 2024 am 09:54 AM
How to solve the problem of garbled characters when importing Chinese data into Oracle?
Mar 10, 2024 am 09:54 AM
Title: Methods and code examples to solve the problem of garbled characters when importing Chinese data into Oracle. When importing Chinese data into Oracle database, garbled characters often appear. This may be due to incorrect database character set settings or encoding conversion problems during the import process. . In order to solve this problem, we can take some methods to ensure that the imported Chinese data can be displayed correctly. The following are some solutions and specific code examples: 1. Check the database character set settings In the Oracle database, the character set settings are




