Node.js learning tutorial HTTP/2 server push example sharing
This article mainly introduces you to the relevant information about HTTP/2 server push in the Node.js learning tutorial. The article introduces it in great detail through sample code. It has certain reference learning value for everyone's study or work. Friends who need it Let’s learn together with the editor below. Hope it helps everyone.
Preface
The recent release of Node.js v8.4+ brings an experimental version of HTTP/2, which you can start by setting the parameter --expose-http2.
In this article, I will introduce the most important aspect of HTTP/2, server push, and create a small Node.js program example to use it. Not much to say below, let’s take a look at the detailed introduction.
About HTTP/2
The purpose of HTTP/2 is to reduce latency by supporting complete request and response multiplexing, minimizing protocol overhead by effectively compressing HTTP header fields, and Added support for request prioritization and server push.
Server Push
HTTP/2 Server Push allows the server to send resources to the browser before the browser requests it.
Before we move to HTTP/2, let’s see how it works with HTTP/1:
In HTTP/1, the client sends a request to the server , the server returns an HTML file containing many links to external resources (.js, .css, etc. files). When the browser processes this initial HTML file, it starts parsing these links and loading them individually.
View the image of the demo loading process below. Note the independent requests on the timeline and the initiation of these requests:
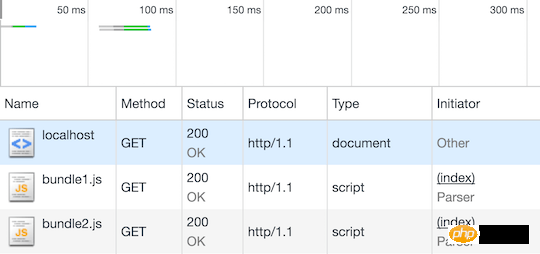
HTTP/1 Resource Loading
This is how HTTP/1 works, this That's how we developed the app over the years. Why change it?
The problem with the current approach is that the user must wait for the browser to parse the response, discover the link and obtain the resource. This delays rendering and increases load times. There are some solutions like inlining some resources but that also makes the initial response bigger and bigger.
This is where the HTTP/2 server push feature comes into view, as the server can send resources to the browser before the browser requests it.
Take a look at the image below, a website that provides the same service over HTTP/2. View the timeline and launcher. You can see that HTTP/2 multiplexing reduces the number of requests and the resource is sent immediately with the initial request.
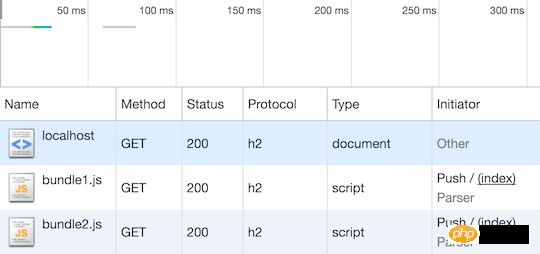
HTTP/2 Server Push
Let’s see how to use HTTP/2 Server Push in Node.js today to speed up client loading times .
A Node.js HTTP/2 server push case
By loading the built-in http2 module, we can create our server just like we use the https module.
The interesting part is pushing the other resources when index.html is requested:
const http2 = require('http2')
const server = http2.createSecureServer(
{ cert, key },
onRequest
)
function push (stream, filePath) {
const { file, headers } = getFile(filePath)
const pushHeaders = { [HTTP2_HEADER_PATH]: filePath }
stream.pushStream(pushHeaders, (pushStream) => {
pushStream.respondWithFD(file, headers)
})
}
function onRequest (req, res) {
// Push files with index.html
if (reqPath === '/index.html') {
push(res.stream, 'bundle1.js')
push(res.stream, 'bundle2.js')
}
// Serve file
res.stream.respondWithFD(file.fileDescriptor, file.headers)
}This way the bundle1.js and bundle2.js resources are sent to the browser even before it asks for them.
You can view the complete case: https://github.com/RisingStack/http2-push-example
HTTP/2 & Node
HTTP/2 can help We optimize communication between our clients and servers in many ways.
With server push, we can send resources to the browser, reducing the user's initial load time.
Related recommendations:
Explanation of HTML5 server push events
Detailed introduction to server push events
PHP Web real-time message background server push technology GoEasy
The above is the detailed content of Node.js learning tutorial HTTP/2 server push example sharing. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Understand common application scenarios of web page redirection and understand the HTTP 301 status code
Feb 18, 2024 pm 08:41 PM
Understand common application scenarios of web page redirection and understand the HTTP 301 status code
Feb 18, 2024 pm 08:41 PM
Understand the meaning of HTTP 301 status code: common application scenarios of web page redirection. With the rapid development of the Internet, people's requirements for web page interaction are becoming higher and higher. In the field of web design, web page redirection is a common and important technology, implemented through the HTTP 301 status code. This article will explore the meaning of HTTP 301 status code and common application scenarios in web page redirection. HTTP301 status code refers to permanent redirect (PermanentRedirect). When the server receives the client's
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
 HTTP 200 OK: Understand the meaning and purpose of a successful response
Dec 26, 2023 am 10:25 AM
HTTP 200 OK: Understand the meaning and purpose of a successful response
Dec 26, 2023 am 10:25 AM
HTTP Status Code 200: Explore the Meaning and Purpose of Successful Responses HTTP status codes are numeric codes used to indicate the status of a server's response. Among them, status code 200 indicates that the request has been successfully processed by the server. This article will explore the specific meaning and use of HTTP status code 200. First, let us understand the classification of HTTP status codes. Status codes are divided into five categories, namely 1xx, 2xx, 3xx, 4xx and 5xx. Among them, 2xx indicates a successful response. And 200 is the most common status code in 2xx
 How to implement HTTP streaming using C++?
May 31, 2024 am 11:06 AM
How to implement HTTP streaming using C++?
May 31, 2024 am 11:06 AM
How to implement HTTP streaming in C++? Create an SSL stream socket using Boost.Asio and the asiohttps client library. Connect to the server and send an HTTP request. Receive HTTP response headers and print them. Receives the HTTP response body and prints it.
 What status code is returned for an HTTP request timeout?
Feb 18, 2024 pm 01:58 PM
What status code is returned for an HTTP request timeout?
Feb 18, 2024 pm 01:58 PM
The HTTP request times out, and the server often returns the 504GatewayTimeout status code. This status code indicates that when the server executes a request, it still fails to obtain the resources required for the request or complete the processing of the request after a period of time. It is a status code of the 5xx series, which indicates that the server has encountered a temporary problem or overload, resulting in the inability to correctly handle the client's request. In the HTTP protocol, various status codes have specific meanings and uses, and the 504 status code is used to indicate request timeout issues. in customer
 How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
Introduction to the method of obtaining HTTP status code in JavaScript: In front-end development, we often need to deal with the interaction with the back-end interface, and HTTP status code is a very important part of it. Understanding and obtaining HTTP status codes helps us better handle the data returned by the interface. This article will introduce how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide specific code examples. 1. What is HTTP status code? HTTP status code means that when the browser initiates a request to the server, the service
 How to solve HTTP 503 error
Mar 12, 2024 pm 03:25 PM
How to solve HTTP 503 error
Mar 12, 2024 pm 03:25 PM
Solution: 1. Retry: You can wait for a period of time and try again, or refresh the page; 2. Check the server load: Check the server's CPU, memory and disk usage. If the capacity limit is exceeded, you can try to optimize the server configuration or increase the capacity. Server resources; 3. Check server maintenance and upgrades: You can only wait until the server returns to normal; 4. Check network connection: Make sure the network connection is stable, check whether the network device, firewall or proxy settings are correct; 5. Ensure cache or CDN configuration Correct; 6. Contact the server administrator, etc.
 The AI era of JS is here!
Apr 08, 2024 am 09:10 AM
The AI era of JS is here!
Apr 08, 2024 am 09:10 AM
Introduction to JS-Torch JS-Torch is a deep learning JavaScript library whose syntax is very similar to PyTorch. It contains a fully functional tensor object (can be used with tracked gradients), deep learning layers and functions, and an automatic differentiation engine. JS-Torch is suitable for deep learning research in JavaScript and provides many convenient tools and functions to accelerate deep learning development. Image PyTorch is an open source deep learning framework developed and maintained by Meta's research team. It provides a rich set of tools and libraries for building and training neural network models. PyTorch is designed to be simple, flexible and easy to use, and its dynamic computation graph features make




