vuejs implements the filtering and paging function of local data
To do a project, you need a filtering and paging function based on local data. Below, the editor will share the implementation ideas of vuejs to implement the filtering and paging function of local data to the Script Home platform. Friends who need it can refer to it. I hope it can help everyone. .
Rendering:
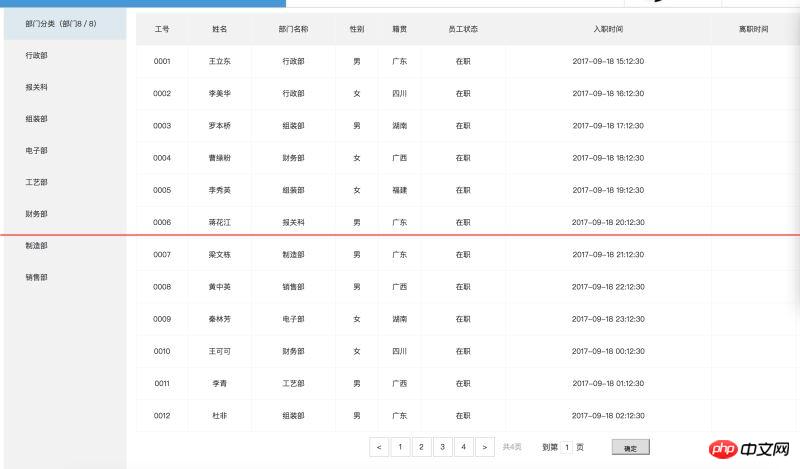
Project requirements: Click on the left to filter data, realize automatic paging, automatically generate the number of pages, click to automatically jump
Project code: js code
var subList=new Vue({
el:'#main',
data:{
// subcontentData为本地数据
subContents:subcontentData,
// 页面需要展现的数据
yemiandata:[],
// 页面展现条数
datanum:12,
// 开始椰树
startnum:0,
// 结束椰树
endnum:1,
// 一共多少页
btnnum:0,
// 生成切换页面的按钮用
listnum:[],
// input跳转
jemp:1,
},
methods:{
filters(num){
this.subContents=subcontentData;
// 需要重置防止翻页导致startnum和endnum不一致
this.startnum=0;
this.endnum=1;
// 这里是判断筛选按钮
switch(num){
case 0: $('#sublist li').css({
background:'#f2f2f2'
}).eq(0).css({
background:'#dbe9f0'
});
this.fenye();
break;
case 1:
$('#sublist li').css({
background:'#f2f2f2'
}).eq(1).css({
background:'#dbe9f0'
});
this.subContents=this.subContents.filter(num=>{
return String(num['department']).includes('行政');
});
this.fenye();
break;
case 2:
$('#sublist li').css({
background:'#f2f2f2'
}).eq(2).css({
background:'#dbe9f0'
});
this.subContents=this.subContents.filter(num=>{
return String(num['department']).includes('报关');
});
this.fenye();
break;
case 3:
$('#sublist li').css({
background:'#f2f2f2'
}).eq(3).css({
background:'#dbe9f0'
});
this.subContents=this.subContents.filter(num=>{
return String(num['department']).includes('组装');
});
this.fenye();
break;
case 4:
$('#sublist li').css({
background:'#f2f2f2'
}).eq(4).css({
background:'#dbe9f0'
});
this.subContents=this.subContents.filter(num=>{
return String(num['department']).includes('电子');
});
this.fenye();
break;
case 5:
$('#sublist li').css({
background:'#f2f2f2'
}).eq(5).css({
background:'#dbe9f0'
});
this.subContents=this.subContents.filter(num=>{
return String(num['department']).includes('工艺');
});
this.fenye();
break;
case 6:
$('#sublist li').css({
background:'#f2f2f2'
}).eq(6).css({
background:'#dbe9f0'
});
this.subContents=this.subContents.filter(num=>{
return String(num['department']).includes('财务');
});
this.fenye();
break;
case 7:
$('#sublist li').css({
background:'#f2f2f2'
}).eq(7).css({
background:'#dbe9f0'
});
this.subContents=this.subContents.filter(num=>{
return String(num['department']).includes('制造');
});
this.fenye();
break;
case 8:
$('#sublist li').css({
background:'#f2f2f2'
}).eq(8).css({
background:'#dbe9f0'
});
this.subContents=this.subContents.filter(num=>{
return String(num['department']).includes('销售');
});
this.fenye();
break;
}
},
// 分野函数
fenye(){
this.yemiandata=this.subContents.slice(this.startnum*this.datanum,this.endnum*this.datanum);
this.btnnum=Math.ceil(this.subContents.length/this.datanum);
this.listnum=[];
for(i=0;i<this.btnnum;i++){
this.listnum[i]=i+1;
}
btnwidth();
},
// 下一页函数
nextlist(){
if(this.endnum>= this.btnnum){
alert('最后一页了');
return false;
}
this.endnum++;
this.startnum++;
},
// 上一页函数
prevlist(){
if(this.startnum<= 0){
alert('第一页了');
return false;
}
this.endnum--;
this.startnum--;
},
// 按钮跳转到制定的页面
jemppage(list){
this.startnum=list-1;
this.endnum=list;
},
// input跳抓
goindex(){
console.log(parseInt(this.jemp));
if(parseInt(this.jemp)>this.btnnum){alert('请输入合法参数');return}
this.endnum=this.jemp;
this.startnum=this.jemp-1;
}
},
// 使用一个监听。可以减少很多代码
watch:{
startnum(n,o){
this.yemiandata=this.subContents.slice(n*this.datanum,(parseInt(n)+1)*this.datanum);
}
}
});
subList.filters(0);
subList.fenye();
// 封装一下底部btn方法 底部自动大小
function btnwidth(){
$('#fbtn').css({
width:(subList.listnum.length+2)*40+293+'px',
marginLeft:-((subList.listnum.length+2)*40+293)/2+'px'
})
}
btnwidth();The following is the html node code:
<p class="main_content">
<p class="table2_nav">
<ul id="sublist">
<li @click="filters(0)"><p class="blockcenter">部门分类(部门8/8)</p></li>
<li @click="filters(1)"><p class="blockcenter">行政部</p></li>
<li @click="filters(2)"><p class="blockcenter">报关科</p></li>
<li @click="filters(3)"><p class="blockcenter">组装部</p></li>
<li @click="filters(4)"><p class="blockcenter">电子部</p></li>
<li @click="filters(5)"><p class="blockcenter">工艺部</p></li>
<li @click="filters(6)"><p class="blockcenter">财务部</p></li>
<li @click="filters(7)"><p class="blockcenter">制造部</p></li>
<li @click="filters(8)"><p class="blockcenter">销售部</p></li>
</ul>
</p>
<p class="table2_content">
<p class="col-title bg-fff clearfix">
<h5 class="fl">告警策略报表统计</h5>
<p class="btn fl">
主机名称 <span class="caret"></span>
<p class="btn_down">
<ul>
<li>下啦</li>
<li>下啦2</li>
</ul>
</p>
</p>
<p class="fl btn2">
添加
</p>
</p>
<table width="1410px" class="table" id="tablelist tab">
<tr>
<th>工号</th>
<th>姓名</th>
<th>部门名称</th>
<th>性别</th>
<th>籍贯</th>
<th>员工状态</th>
<th>入职时间</th>
<th>离职时间</th>
<th>离职类别</th>
</tr>
<tr v-for="subContent in yemiandata">
<td>{{subContent.num}}</td>
<td>{{subContent.name}}</td>
<td>{{subContent.department}}</td>
<td>{{subContent.sex}}</td>
<td>{{subContent.addres}}</td>
<td>{{subContent.staic}}</td>
<td>{{subContent.jointime}}</td>
<td>{{subContent.leavetime}}</td>
<td>{{subContent.type}}</td>
</tr>
</table>
<p class="vuetab clearfix">
<ul class="fbtn clearfix" id="fbtn">
<li @click="prevlist()"><</li>
<!--<li @click="jemppage($event)">1</li>-->
<li v-for="list in listnum" @click="jemppage(list)">{{list}}</li>
<li @click="nextlist()">></li>
<p id="pages">共{{btnnum}}页</p>
<p id="gotoindex">到第 <input type="text" :value="jemp" v-model="jemp" id="inputnum"> 页</p>
<button id="gobtn" @click="goindex()">确定</button>
</ul>
</p>
</p>
</p>Let’s talk about the idea: First we need a local set of data and add it to the page through vue. In the second step we need to do paging, so we can write a function, right, so we have the following fenye (named irregularly, don’t blame prawns) function, so-called Pagination is nothing more than dividing a big data into each small page for display, so I wrote an array specifically for display, which is yemiandata (it is also not standardized. I said that because the website I made has too much content, the name has been changed. (Exhausted, do you believe it)? After that, we need to get as many pages as possible and turn it into a btn button. To save trouble, I added a watch: used to monitor startnum (starting page number) and change the display if it changes.
Step 3: If you want to paginate, you must have the previous page and the next page. This is much simpler. The next page will increase both startnum and endnum by one, and vice versa for the previous page.
Step 4: There must also be a button that clicks on the page number to jump. This is not difficult, just let the button be clicked to jump to the specified page, but do you need to write a function? It's unrealistic, right, so I used an array listnum to store how many buttons there are. Here's an explanation of why arrays are not used as variables. Because v-for in Vue does not support variable loops, I switched to arrays to facilitate the generation of nodes in the previous html.
The fifth step mentioned the need to filter. To filter, just change the element group that needs to be displayed into the one containing the specified keywords, filters function, use js filters and includes to filter, and see if you are done. Look, it failed and there were a lot of undefinds. Why? Take a closer look at the fact that the array is not reset, causing the second filtering to be based on the first filtering. Then reset it, check again, it’s done!
Related recommendations:
3.1.3 Multi-filter paging routing
In-depth understanding of jQuery layui paging control Use
LayUI to implement front-end paging function
The above is the detailed content of vuejs implements the filtering and paging function of local data. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1382
1382
 52
52
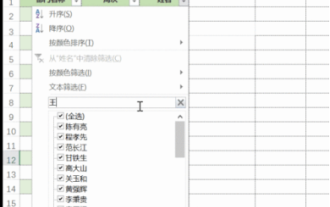 How to filter more than 3 keywords at the same time in excel
Mar 21, 2024 pm 03:16 PM
How to filter more than 3 keywords at the same time in excel
Mar 21, 2024 pm 03:16 PM
Excel is often used to process data in daily office work, and it is often necessary to use the "filter" function. When we choose to perform "filtering" in Excel, we can only filter up to two conditions for the same column. So, do you know how to filter more than 3 keywords at the same time in Excel? Next, let me demonstrate it to you. The first method is to gradually add the conditions to the filter. If you want to filter out three qualifying details at the same time, you first need to filter out one of them step by step. At the beginning, you can first filter out employees with the surname "Wang" based on the conditions. Then click [OK], and then check [Add current selection to filter] in the filter results. The steps are as follows. Similarly, perform filtering separately again
 What should I do if there is data in the Excel table but the blanks are filtered?
Mar 13, 2024 pm 06:38 PM
What should I do if there is data in the Excel table but the blanks are filtered?
Mar 13, 2024 pm 06:38 PM
Excel is a frequently used office software. Many users record various data in the table, but the table clearly contains data and is blank when filtering. Regarding this problem, many users don’t know how to solve it. It doesn’t matter. , the content of this software tutorial is to provide answers to the majority of users. Users in need are welcome to check out the solutions. What should I do if there is data in the Excel table but the blanks are filtered? The first reason is that the table contains blank rows. We want to filter all people with the surname "Li", but we can see that the correct results are not filtered out because the table contains blank rows. How to deal with this situation? Solution: Step 1: Select all content and then filter. Press c
 How to use Excel filter function with multiple conditions
Feb 26, 2024 am 10:19 AM
How to use Excel filter function with multiple conditions
Feb 26, 2024 am 10:19 AM
If you need to know how to use filtering with multiple criteria in Excel, the following tutorial will guide you through the steps to ensure you can filter and sort your data effectively. Excel's filtering function is very powerful and can help you extract the information you need from large amounts of data. This function can filter data according to the conditions you set and display only the parts that meet the conditions, making data management more efficient. By using the filter function, you can quickly find target data, saving time in finding and organizing data. This function can not only be applied to simple data lists, but can also be filtered based on multiple conditions to help you locate the information you need more accurately. Overall, Excel’s filtering function is a very practical
 How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system Introduction: With the continuous development of technology, speech recognition technology has become an important part of the field of artificial intelligence. The online speech recognition system based on WebSocket and JavaScript has the characteristics of low latency, real-time and cross-platform, and has become a widely used solution. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system.
 WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: Key technologies for realizing real-time monitoring systems Introduction: With the rapid development of Internet technology, real-time monitoring systems have been widely used in various fields. One of the key technologies to achieve real-time monitoring is the combination of WebSocket and JavaScript. This article will introduce the application of WebSocket and JavaScript in real-time monitoring systems, give code examples, and explain their implementation principles in detail. 1. WebSocket technology
 How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Introduction to how to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system: With the popularity of the Internet and the advancement of technology, more and more restaurants have begun to provide online ordering services. In order to implement a real-time online ordering system, we can use JavaScript and WebSocket technology. WebSocket is a full-duplex communication protocol based on the TCP protocol, which can realize real-time two-way communication between the client and the server. In the real-time online ordering system, when the user selects dishes and places an order
 How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system. In today's digital era, more and more businesses and services need to provide online reservation functions. It is crucial to implement an efficient and real-time online reservation system. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system, and provide specific code examples. 1. What is WebSocket? WebSocket is a full-duplex method on a single TCP connection.
 How to filter duplicate content in word
Mar 19, 2024 pm 07:01 PM
How to filter duplicate content in word
Mar 19, 2024 pm 07:01 PM
When it comes to filtering duplicate content, the first thing you may think of is filtering numerical values in Excel. In fact, in Word, we can also filter duplicate text in documents. When you are not sure whether you have typed a word incorrectly, you can use the filter to take a look. This step is very convenient. The editor below will lead you to learn how to filter duplicate content in Word. Friends who want to learn, come and study hard! 1. First, we open the word document we want to filter on the computer, as shown in the figure below. 2. Then, we select the text we want to find, as shown by the red arrow in the picture below. 3. Press [ctrl+H] on the keyboard to bring up the find and replace command. The red arrow in the figure below points to the




