How to implement image compression in JS
This article mainly introduces the image compression method in JS, including the method of compressing images in equal ratios. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it can help everyone.
First think about what needs we have? Most of the time we need to compress a File object and then turn it into a File object and pass it to the remote image server; sometimes we also need to compress a base64 string and then turn it into a base64 string and pass it to the remote database; sometimes it It may also be a canvas, or an Image object, or directly the URL address of a picture. We need to compress and upload them to the remote location; faced with so many demands, Wang Er simply drew a picture:
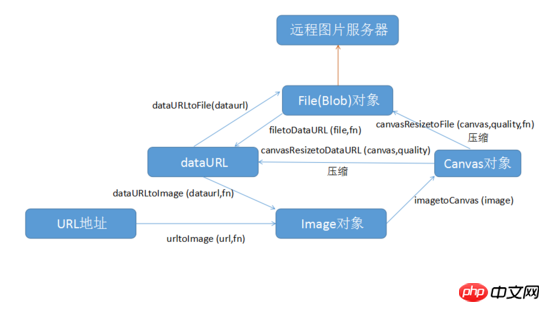
Alt text
2. Solution
As shown in the picture above, Wang Er wrote a total of seven methods, basically covering JS Conversion and compression of most file types, among which:
1. urltoImage(url,fn) will load the required image object through a url, where the url parameter is passed in the url of the image, and fn is the callback method , contains the parameters of an Image object, the code is as follows:
function urltoImage (url,fn){
var img = new Image();
img.src = url;
img.onload = function(){
fn(img);
}
};2. imagetoCanvas(image) will convert an Image object into a Canvas type object, in which the image parameter is passed into an Image object, the code is as follows:
function imagetoCanvas(image){
var cvs = document.createElement("canvas");
var ctx = cvs.getContext('2d');
cvs.width = image.width;
cvs.height = image.height;
ctx.drawImage(image, 0, 0, cvs.width, cvs.height);
return cvs ;
};3. canvasResizetoFile(canvas,quality,fn) will compress and convert a Canvas object into a Blob type object; the canvas parameter is passed in a Canvas object; the quality parameter is passed in a number type of 0-1, which means Image compression quality; fn is the callback method, containing the parameters of a Blob object; the code is as follows:
function canvasResizetoFile(canvas,quality,fn){
canvas.toBlob(function(blob) {
fn(blob);
},'image/jpeg',quality);
};The Blob object here represents immutable raw data similar to a file object. Blobs represent data that is not necessarily native to JavaScript. The File interface is based on Blob, inheriting the functionality of Blob and extending it to support files on the user's system. We can treat it as a File type. For more specific usage, please refer to MDN document
4. canvasResizetoDataURL(canvas,quality) will compress a Canvas object into a dataURL string, in which the canvas parameter is passed in A Canvas object; the quality parameter is passed in a number type of 0-1, indicating the image compression quality; the code is as follows:
methods.canvasResizetoDataURL = function(canvas,quality){
return canvas.toDataURL('image/jpeg',quality);
};The toDataURL API can refer to the MDN document
5, filetoDataURL(file ,fn) will convert the File (Blob) type file into a dataURL string, where the file parameter is passed in a File (Blob) type file; fn is the callback method, including a dataURL string parameter; the code is as follows:
function filetoDataURL(file,fn){
var reader = new FileReader();
reader.onloadend = function(e){
fn(e.target.result);
};
reader.readAsDataURL(file);
};6. dataURLtoImage(dataurl,fn) will convert a string of dataURL strings into an Image type file, in which the dataurl parameter is passed in a dataURL string, and fn is the callback method, including the parameters of an Image type file. The code is as follows:
function dataURLtoImage(dataurl,fn){
var img = new Image();
img.onload = function() {
fn(img);
};
img.src = dataurl;
};7. dataURLtoFile(dataurl) will convert a string of dataURL strings into a Blob type object, in which the dataurl parameter is passed in a dataURL string. The code is as follows:
function dataURLtoFile(dataurl) {
var arr = dataurl.split(','), mime = arr[0].match(/:(.*?);/)[1],
bstr = atob(arr[1]), n = bstr.length, u8arr = new Uint8Array(n);
while(n--){
u8arr[n] = bstr.charCodeAt(n);
}
return new Blob([u8arr], {type:mime});
};3. Further encapsulation
For the commonly used method of compressing a File object and then turning it into a File object, we can re-encapsulate the above method, refer to the following code:
function fileResizetoFile(file,quality,fn){
filetoDataURL (file,function(dataurl){
dataURLtoImage(dataurl,function(image){
canvasResizetoFile(imagetoCanvas(image),quality,fn);
})
})
}Among them, the file parameter is passed into a File (Blob) type file; the quality parameter is passed in a number type of 0-1, indicating the image compression quality; fn is the callback method, including a parameter of the Blob type file.
It works like this:
var file = document.getElementById('demo').files[0];
fileResizetoFile(file,0.6,function(res){
console.log(res);
//拿到res,做出你要上传的操作;
})In this case, image compression and uploading can be easily done. I have encapsulated the above 8 methods and put them on github. Like it If so, you can star hard.
Reference document:
MDN
ps: Let’s take a look at the method of JS equal-ratio compression of images
function proDownImage(path,imgObj) { // 等比压缩图片工具
//var proMaxHeight = 185;
var proMaxHeight=300;
var proMaxWidth = 175;
var size = new Object();
var image = new Image();
image.src = path;
image.attachEvent("onreadystatechange",
function() { // 当加载状态改变时执行此方法,因为img的加载有延迟
if (image.readyState == "complete") { // 当加载状态为完全结束时进入
if (image.width > 0 && image.height > 0) {
var ww = proMaxWidth / image.width;
var hh = proMaxHeight / image.height;
var rate = (ww < hh) ? ww: hh;
if (rate <= 1) {
alert("imgage width*rate is:" + image.width * rate);
size.width = image.width * rate;
size.height = image.height * rate;
} else {
alert("imgage width is:" + image.width);
size.width = image.width;
size.height = image.height;
}
}
}
imgObj.attr("width",size.width);
imgObj.attr("height",size.height);
});
}Related recommendations:
How to implement image compression method in JS
Sample code of Canvas and image compression
HTML5 implements image compression upload function In-depth analysis
The above is the detailed content of How to implement image compression in JS. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to write a novel in the Tomato Free Novel app. Share the tutorial on how to write a novel in Tomato Novel.
Mar 28, 2024 pm 12:50 PM
How to write a novel in the Tomato Free Novel app. Share the tutorial on how to write a novel in Tomato Novel.
Mar 28, 2024 pm 12:50 PM
Tomato Novel is a very popular novel reading software. We often have new novels and comics to read in Tomato Novel. Every novel and comic is very interesting. Many friends also want to write novels. Earn pocket money and edit the content of the novel you want to write into text. So how do we write the novel in it? My friends don’t know, so let’s go to this site together. Let’s take some time to look at an introduction to how to write a novel. Share the Tomato novel tutorial on how to write a novel. 1. First open the Tomato free novel app on your mobile phone and click on Personal Center - Writer Center. 2. Jump to the Tomato Writer Assistant page - click on Create a new book at the end of the novel.
 How to recover deleted contacts on WeChat (simple tutorial tells you how to recover deleted contacts)
May 01, 2024 pm 12:01 PM
How to recover deleted contacts on WeChat (simple tutorial tells you how to recover deleted contacts)
May 01, 2024 pm 12:01 PM
Unfortunately, people often delete certain contacts accidentally for some reasons. WeChat is a widely used social software. To help users solve this problem, this article will introduce how to retrieve deleted contacts in a simple way. 1. Understand the WeChat contact deletion mechanism. This provides us with the possibility to retrieve deleted contacts. The contact deletion mechanism in WeChat removes them from the address book, but does not delete them completely. 2. Use WeChat’s built-in “Contact Book Recovery” function. WeChat provides “Contact Book Recovery” to save time and energy. Users can quickly retrieve previously deleted contacts through this function. 3. Enter the WeChat settings page and click the lower right corner, open the WeChat application "Me" and click the settings icon in the upper right corner to enter the settings page.
 How to implement dual WeChat login on Huawei mobile phones?
Mar 24, 2024 am 11:27 AM
How to implement dual WeChat login on Huawei mobile phones?
Mar 24, 2024 am 11:27 AM
How to implement dual WeChat login on Huawei mobile phones? With the rise of social media, WeChat has become one of the indispensable communication tools in people's daily lives. However, many people may encounter a problem: logging into multiple WeChat accounts at the same time on the same mobile phone. For Huawei mobile phone users, it is not difficult to achieve dual WeChat login. This article will introduce how to achieve dual WeChat login on Huawei mobile phones. First of all, the EMUI system that comes with Huawei mobile phones provides a very convenient function - dual application opening. Through the application dual opening function, users can simultaneously
 The secret of hatching mobile dragon eggs is revealed (step by step to teach you how to successfully hatch mobile dragon eggs)
May 04, 2024 pm 06:01 PM
The secret of hatching mobile dragon eggs is revealed (step by step to teach you how to successfully hatch mobile dragon eggs)
May 04, 2024 pm 06:01 PM
Mobile games have become an integral part of people's lives with the development of technology. It has attracted the attention of many players with its cute dragon egg image and interesting hatching process, and one of the games that has attracted much attention is the mobile version of Dragon Egg. To help players better cultivate and grow their own dragons in the game, this article will introduce to you how to hatch dragon eggs in the mobile version. 1. Choose the appropriate type of dragon egg. Players need to carefully choose the type of dragon egg that they like and suit themselves, based on the different types of dragon egg attributes and abilities provided in the game. 2. Upgrade the level of the incubation machine. Players need to improve the level of the incubation machine by completing tasks and collecting props. The level of the incubation machine determines the hatching speed and hatching success rate. 3. Collect the resources required for hatching. Players need to be in the game
 How to set font size on mobile phone (easily adjust font size on mobile phone)
May 07, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
How to set font size on mobile phone (easily adjust font size on mobile phone)
May 07, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
Setting font size has become an important personalization requirement as mobile phones become an important tool in people's daily lives. In order to meet the needs of different users, this article will introduce how to improve the mobile phone use experience and adjust the font size of the mobile phone through simple operations. Why do you need to adjust the font size of your mobile phone - Adjusting the font size can make the text clearer and easier to read - Suitable for the reading needs of users of different ages - Convenient for users with poor vision to use the font size setting function of the mobile phone system - How to enter the system settings interface - In Find and enter the "Display" option in the settings interface - find the "Font Size" option and adjust it. Adjust the font size with a third-party application - download and install an application that supports font size adjustment - open the application and enter the relevant settings interface - according to the individual
 Quickly master: How to open two WeChat accounts on Huawei mobile phones revealed!
Mar 23, 2024 am 10:42 AM
Quickly master: How to open two WeChat accounts on Huawei mobile phones revealed!
Mar 23, 2024 am 10:42 AM
In today's society, mobile phones have become an indispensable part of our lives. As an important tool for our daily communication, work, and life, WeChat is often used. However, it may be necessary to separate two WeChat accounts when handling different transactions, which requires the mobile phone to support logging in to two WeChat accounts at the same time. As a well-known domestic brand, Huawei mobile phones are used by many people. So what is the method to open two WeChat accounts on Huawei mobile phones? Let’s reveal the secret of this method. First of all, you need to use two WeChat accounts at the same time on your Huawei mobile phone. The easiest way is to
 PHP Programming Guide: Methods to Implement Fibonacci Sequence
Mar 20, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
PHP Programming Guide: Methods to Implement Fibonacci Sequence
Mar 20, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
The programming language PHP is a powerful tool for web development, capable of supporting a variety of different programming logics and algorithms. Among them, implementing the Fibonacci sequence is a common and classic programming problem. In this article, we will introduce how to use the PHP programming language to implement the Fibonacci sequence, and attach specific code examples. The Fibonacci sequence is a mathematical sequence defined as follows: the first and second elements of the sequence are 1, and starting from the third element, the value of each element is equal to the sum of the previous two elements. The first few elements of the sequence
 How to implement the WeChat clone function on Huawei mobile phones
Mar 24, 2024 pm 06:03 PM
How to implement the WeChat clone function on Huawei mobile phones
Mar 24, 2024 pm 06:03 PM
How to implement the WeChat clone function on Huawei mobile phones With the popularity of social software and people's increasing emphasis on privacy and security, the WeChat clone function has gradually become the focus of people's attention. The WeChat clone function can help users log in to multiple WeChat accounts on the same mobile phone at the same time, making it easier to manage and use. It is not difficult to implement the WeChat clone function on Huawei mobile phones. You only need to follow the following steps. Step 1: Make sure that the mobile phone system version and WeChat version meet the requirements. First, make sure that your Huawei mobile phone system version has been updated to the latest version, as well as the WeChat App.




