Vue generates token and saves it in the client. Detailed explanation
This article mainly introduces the method of Vue generating token and saving it in the client's localStorage. The editor thinks it is quite good. Now I will share it with you and give it as a reference. Let’s follow the editor to take a look, I hope it can help everyone.
We have already learned that data can be saved on the client (browser) through localStorage.
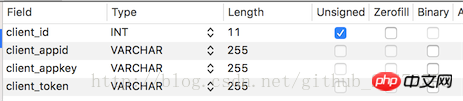
Our backend has such an interface:
http://localhost/yiiserver/web/index.php/token?client_appid=aaa&client_appkey=bbb
In fact, just Clients (understood as user table) generate a token
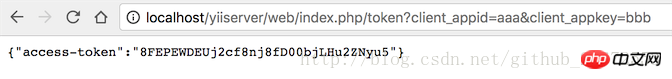
client_appid here is equivalent to the username, client_appkey is equivalent to the password.
In this way, a access-token will be generated after backend authentication. We need to save this access-token on the client.
Note: Our front-end is generally deployed on another server and will cross domains. The back-end needs to handle cross-domain issues. You can write the following code in PHP:
//指定允许其他域名访问
header("Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *");
header("Access-Control-Allow-Methods: GET,POST");
header('Access-Control-Allow-Headers: X-Requested-With,content-type,if-modified-since');Front-end routine
Note that since our project has already used VueX, then I will definitely use Store(Concept in vuex) to create a module.
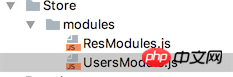
We have created a new UsersModule.js to handle the user login business. Be careful not to forget to add the entry file users-index Introduced in .js. If our "Member Backstage" also needs user-related data, it must also be introduced.
Modify in users-index.js:
//引入模块
import ResModule from './../Store/modules/ResModules';
import UsersModule from "./../Store/modules/UsersModule";
const vuex_config = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
res:ResModule,
users:UsersModule
}
});1, UsersModule.js
import Vue from "vue";
export default {
state:{
currentUser:{
get UserName(){
return localStorage.getItem("currentUser_name");
},
get UserToken(){
return localStorage.getItem("currentUser_token");
}
}
},
mutations:{
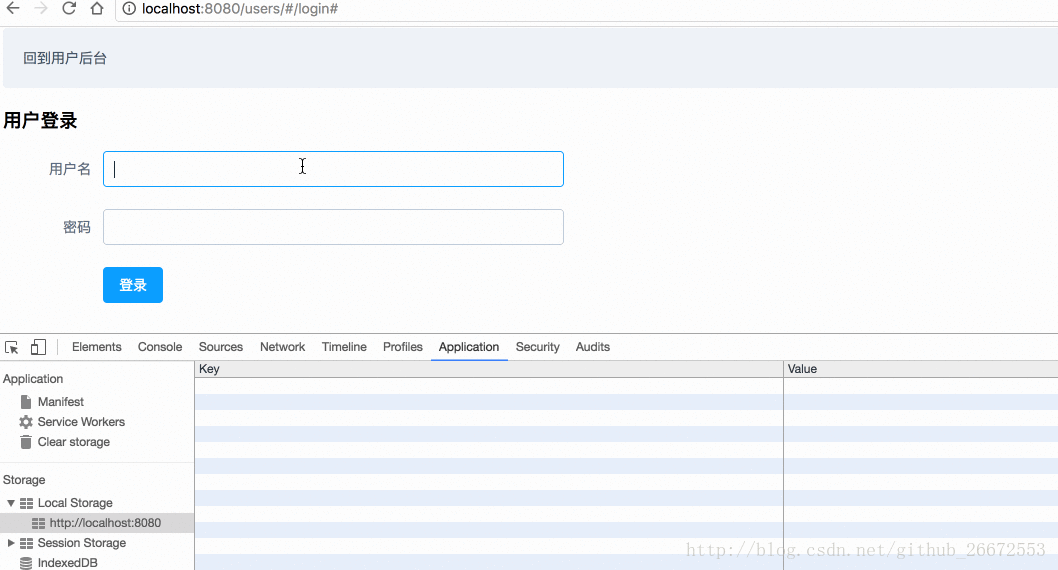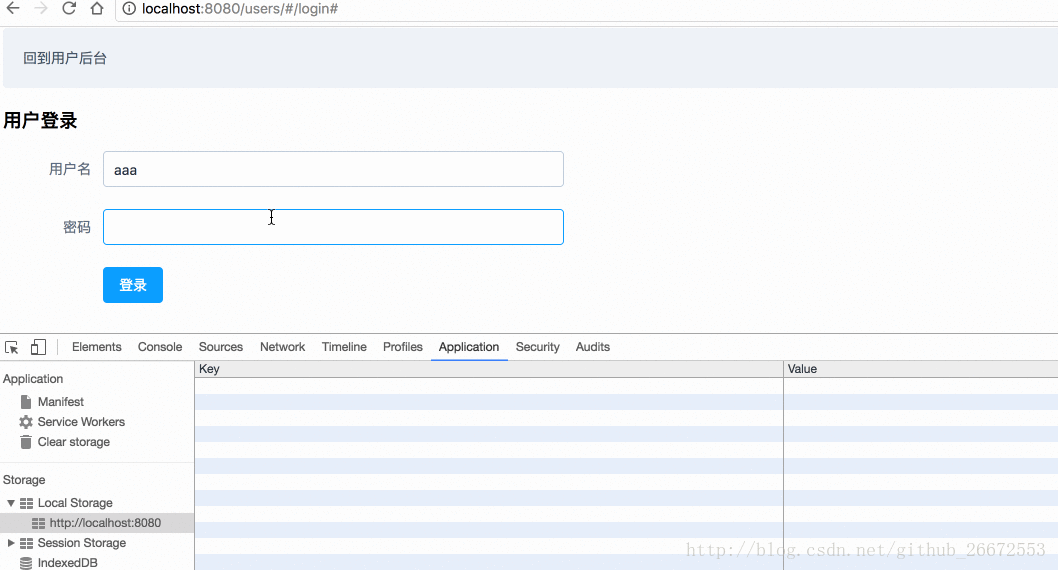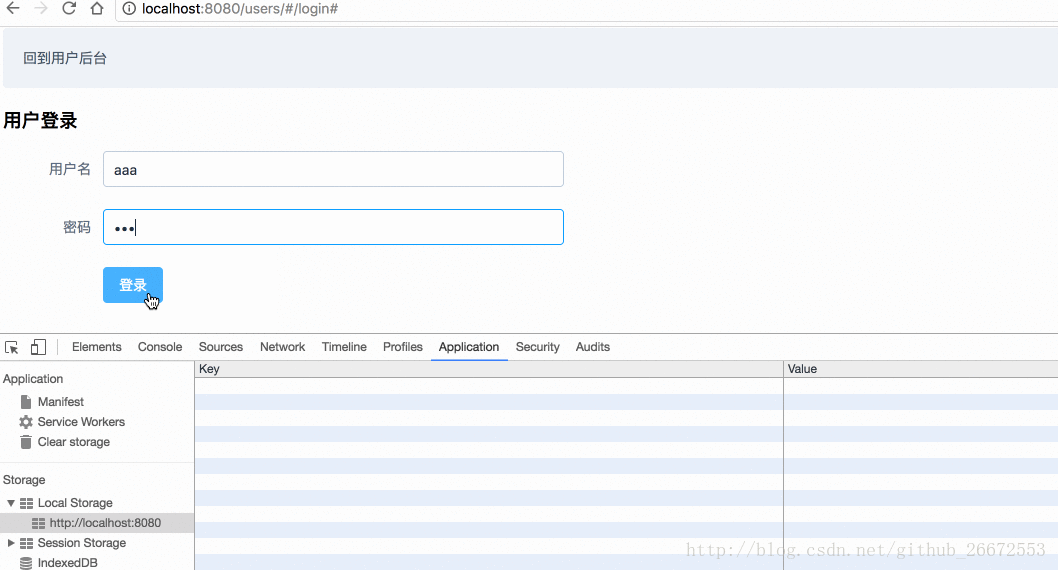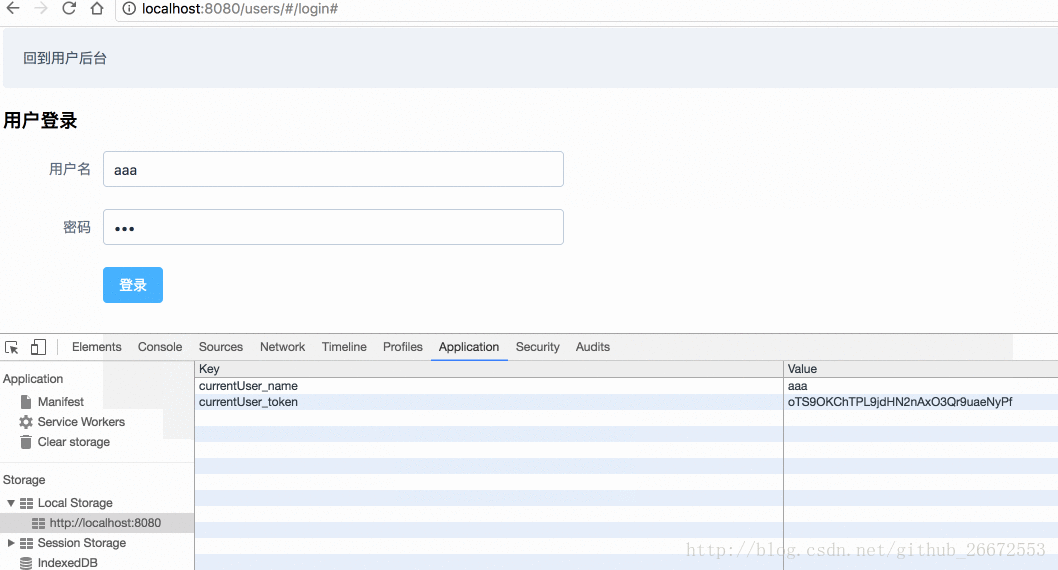
setUser(state,{user_name,user_token}){
// 在这里把用户名和token保存起来
localStorage.setItem("currentUser_name",user_name);
localStorage.setItem("currentUser_token",user_token);
}
},
actions:{
userLogin(context,{user_name,user_pass}){
// 发送get请求做权限认证(真实开发建议用post的方式)
let url = "http://localhost/yiiserver/web/index.php/token?client_appid="+user_name+"&client_appkey="+user_pass;
console.log(url);
Vue.http.get(url)
.then((res)=>{
if (res!=null && res.body!=undefined && "access-token" in res.body){
var token = res.body["access-token"];
if (token != ""){
// 后端API验证通过
// 调用上面mutations里定义的方法
context.commit("setUser",{"user_name":user_name,"user_token":token});
}
}else{
alert("用户名密码错误");
}
},(res)=>{
alert("请求失败进入这里")
});
}
}
}actions part: We wrote a userLogin() method to send an http request to the back-end server. The data returned successfully by the request calls the ## defined in the mutations part. #setUser() method is saved to the client.
userLogin() method in actions is for calling on the user login page, that is, in userslogin.vue.
userlogin.vue and modify the following code:
localStorage中:
methods:{
login(){
// 这个验证是element-ui框架提供的方法
this.$refs["users"].validate(function (flag) {
if(flag){
/*localStorage.setItem("currentUser",this.UserModel.user_name);
alert("用户登录成功");*/
this.$store.dispatch("userLogin",{"user_name":this.UserModel.user_name,"user_pass":this.UserModel.user_pass})
}else{
alert("用户名密码必填");
}
}.bind(this));
}
}
member-index.js of the member backend module:
//引入Module
import ResModule from './../Store/modules/ResModules';
import UsersMoule from "./../Store/modules/UsersModule";
const vuex_config = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
res:ResModule,
users:UsersMoule
}
});<a href="##" rel="external nofollow" >{{this.$store.state.users.currentUser.UserName}}</a>
Vue-resource interceptor determines the token invalid jump detailed explanation
Vue uses token to jump to the login page after it expires
Detailed example of jQuery Ajax using token to verify identity
The above is the detailed content of Vue generates token and saves it in the client. Detailed explanation. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
![VMware Horizon Client cannot be opened [Fix]](https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/887/227/170835607042441.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_207,w_330) VMware Horizon Client cannot be opened [Fix]
Feb 19, 2024 pm 11:21 PM
VMware Horizon Client cannot be opened [Fix]
Feb 19, 2024 pm 11:21 PM
VMware Horizon Client helps you access virtual desktops conveniently. However, sometimes the virtual desktop infrastructure may experience startup issues. This article discusses the solutions you can take when the VMware Horizon client fails to start successfully. Why won't my VMware Horizon client open? When configuring VDI, if the VMWareHorizon client is not open, an error may occur. Please confirm that your IT administrator has provided the correct URL and credentials. If everything is fine, follow the solutions mentioned in this guide to resolve the issue. Fix VMWareHorizon Client Not Opening If VMW is not opening on your Windows computer
![VMware Horizon client freezes or stalls while connecting [Fix]](https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/887/227/170942987315391.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_207,w_330) VMware Horizon client freezes or stalls while connecting [Fix]
Mar 03, 2024 am 09:37 AM
VMware Horizon client freezes or stalls while connecting [Fix]
Mar 03, 2024 am 09:37 AM
When connecting to a VDI using the VMWareHorizon client, we may encounter situations where the application freezes during authentication or the connection blocks. This article will explore this issue and provide ways to resolve this situation. When the VMWareHorizon client experiences freezing or connection issues, there are a few things you can do to resolve the issue. Fix VMWareHorizon client freezes or gets stuck while connecting If VMWareHorizon client freezes or fails to connect on Windows 11/10, do the below mentioned solutions: Check network connection Restart Horizon client Check Horizon server status Clear client cache Fix Ho
 Detailed explanation of the mode function in C++
Nov 18, 2023 pm 03:08 PM
Detailed explanation of the mode function in C++
Nov 18, 2023 pm 03:08 PM
Detailed explanation of the mode function in C++ In statistics, the mode refers to the value that appears most frequently in a set of data. In C++ language, we can find the mode in any set of data by writing a mode function. The mode function can be implemented in many different ways, two of the commonly used methods will be introduced in detail below. The first method is to use a hash table to count the number of occurrences of each number. First, we need to define a hash table with each number as the key and the number of occurrences as the value. Then, for a given data set, we run
 Detailed explanation of obtaining administrator rights in Win11
Mar 08, 2024 pm 03:06 PM
Detailed explanation of obtaining administrator rights in Win11
Mar 08, 2024 pm 03:06 PM
Windows operating system is one of the most popular operating systems in the world, and its new version Win11 has attracted much attention. In the Win11 system, obtaining administrator rights is an important operation. Administrator rights allow users to perform more operations and settings on the system. This article will introduce in detail how to obtain administrator permissions in Win11 system and how to effectively manage permissions. In the Win11 system, administrator rights are divided into two types: local administrator and domain administrator. A local administrator has full administrative rights to the local computer
 How to solve the problem of invalid login token
Sep 14, 2023 am 10:57 AM
How to solve the problem of invalid login token
Sep 14, 2023 am 10:57 AM
The problem of invalid login token can be solved by checking the network connection, checking the token validity period, clearing cache and cookies, checking login status, contacting the application developer and strengthening account security. Detailed introduction: 1. Check the network connection, reconnect to the network or change the network environment; 2. Check the token validity period, obtain a new token, or contact the developer of the application; 3. Clear cache and cookies, clear browser cache and Cookie, and then log in to the application again; 4. Check the login status.
 Detailed explanation of remainder function in C++
Nov 18, 2023 pm 02:41 PM
Detailed explanation of remainder function in C++
Nov 18, 2023 pm 02:41 PM
Detailed explanation of the remainder function in C++ In C++, the remainder operator (%) is used to calculate the remainder of the division of two numbers. It is a binary operator whose operands can be any integer type (including char, short, int, long, etc.) or a floating-point number type (such as float, double). The remainder operator returns a result with the same sign as the dividend. For example, for the remainder operation of integers, we can use the following code to implement: inta=10;intb=3;
 Detailed explanation of division operation in Oracle SQL
Mar 10, 2024 am 09:51 AM
Detailed explanation of division operation in Oracle SQL
Mar 10, 2024 am 09:51 AM
Detailed explanation of division operation in OracleSQL In OracleSQL, division operation is a common and important mathematical operation, used to calculate the result of dividing two numbers. Division is often used in database queries, so understanding the division operation and its usage in OracleSQL is one of the essential skills for database developers. This article will discuss the relevant knowledge of division operations in OracleSQL in detail and provide specific code examples for readers' reference. 1. Division operation in OracleSQL
 What to do if the login token is invalid
Sep 14, 2023 am 11:33 AM
What to do if the login token is invalid
Sep 14, 2023 am 11:33 AM
Solutions to invalid login token include checking whether the Token has expired, checking whether the Token is correct, checking whether the Token has been tampered with, checking whether the Token matches the user, clearing the cache or cookies, checking the network connection and server status, logging in again or requesting a new Token. Contact technical support or developers, etc. Detailed introduction: 1. Check whether the Token has expired. The login Token usually has a validity period set. Once the validity period exceeds, it will be considered invalid, etc.






