How to use jQuery's Promise correctly
How much do you know about how to use jQuery’s Promise? This article mainly shares with you how to use jQuery's Promise correctly, hoping to help you.
We previously learned about the Promise object of ES6, let’s take a look at Promise in jQuery, which is jQuery’s Deferred object.
Open the browser console first.
<script> var defer = $.Deferred(); console.log(defer); </script>
Running results:

looks a bit like the Promise object of ES6, and jQuery’s Deferred object also has resolve , reject, then methods, as well as done, fail, always... methods. jQuery uses this Deferred object to register callback functions for asynchronous operations, modify and transfer the status of asynchronous operations.
Play with Deferred:
<script>
function runAsync(){
var defer = $.Deferred();
//做一些异步操作
setTimeout(function(){
console.log('执行完成');
defer.resolve('异步请求成功之后返回的数据');
}, 1000);
return defer;
}
runAsync().then(function(data){
console.log(data)
});
</script>After running, the instance defer of the Deferred object returns the parameter "data returned after the asynchronous request is successful" through the resolve method. Go to the then method to receive and print.
is similar to ES6 Promise, but there is a little difference. Let’s look at Promise again:
##
<script>
function runAsync(){
var p = new Promise(function(resolve, reject){
setTimeout(function(){
console.log('执行完成');
resolve('异步请求成功之后返回的数据');
}, 1000);
});
return p;
}
runAsync().then(function(data){
console.log(data);
});
</script><script>
function runAsync(){
var defer = $.Deferred();
//做一些异步操作
setTimeout(function(){
console.log('执行完成');
defer.resolve('异步请求成功之后返回的数据');
}, 1000);
return defer;
}
var der = runAsync();
der.then(function(data){
console.log(data)
});
der.resolve('在外部结束');
</script><script>
function runAsync(){
var def = $.Deferred();
//做一些异步操作
setTimeout(function(){
console.log('执行完成');
def.resolve('请求成功之后返回的数据');
}, 2000);
return def.promise(); //就在这里调用
}
</script>The then method of the Deferred object and done and fail syntax sugar
We know that in the ES6 Promise specification, the then method accepts two parameters, namely execution completion and callback for execution failure, and jquery has been enhanced and can also accept the third parameter, which is the callback in the pending state, as follows:deferred.then( doneFilter [, failFilter ] [ , progressFilter ] )
<script>
function runAsync(){
var def = $.Deferred();
//做一些异步操作
setTimeout(function(){
var num = Math.ceil(Math.random()*10); //生成1-10的随机数
if(num<=5){
def.resolve(num);
}
else{
def.reject('数字太大了');
}
}, 2000);
return def.promise(); //就在这里调用
}
runAsync().then(function(d){
console.log("resolve");
console.log(d);
},function(d){
console.log("reject");
console.log(d);
})
</script>##
<script>
function runAsync(){
var def = $.Deferred();
//做一些异步操作
setTimeout(function(){
var num = Math.ceil(Math.random()*10); //生成1-10的随机数
if(num<=5){
def.resolve(num);
}
else{
def.reject('数字太大了');
}
}, 2000);
return def.promise(); //就在这里调用
}
runAsync().done(function(d){
console.log("resolve");
console.log(d);
}).fail(function(d){
console.log("reject");
console.log(d);
})
</script>Usage of always
There is also an always method on the Deferred object of jquery. Regardless of whether the execution is completed or failed, always will be executed, which is somewhat similar to complete in ajax.
#Usage of $.whenIn jquery, there is also a $.when method to implement Promise. It has the same function as the all method in ES6 and performs asynchronous operations in parallel. , the callback function is executed only after all asynchronous operations have been executed. However, $.when is not defined in $.Deferred. You can tell by looking at the name, $.when, it is a separate method. It is slightly different from the all parameter of ES6. It does not accept an array, but multiple Deferred objects, as follows:
<script>
function runAsync(){
var def = $.Deferred();
//做一些异步操作
setTimeout(function(){
var num = Math.ceil(Math.random()*10); //生成1-10的随机数
def.resolve(num);
}, 2000);
return def.promise(); //就在这里调用
}
$.when(runAsync(), runAsync(), runAsync()) .then(function(data1, data2, data3){
console.log('全部执行完成');
console.log(data1, data2, data3);
});
</script>There is no race in jquery like in ES6 Method? It's the method based on the fastest one. Right, it doesn't exist in jquery.
The above are the common methods of Deferred objects in jquery.
In the previous article and this article, one-time timers were used instead of asynchronous requests for data processing. Why don't you use ajax? It's not because of trouble. Here I want to talk about the connection between ajax and Deferred:
jquery's ajax returns a restricted Deferred object, that is, there is no resolve method and reject method, and it cannot be used from the outside. To change the state, since it is a Deferred object, all the features we mentioned above can also be used with ajax. For example, chain calls, sending multiple requests continuously:
<script>
req1 = function(){
return $.ajax(/* **** */);
}
req2 = function(){
return $.ajax(/* **** */);
}
req3 = function(){
return $.ajax(/* **** */);
}
req1().then(req2).then(req3).done(function(){ console.log('请求发送完毕'); });
</script>success, error and complete
These three methods are our Commonly used ajax syntactic sugar.
$.ajax(/*...*/)
.success(function(){/*...*/})
.error(function(){/*...*/})
.complete(function(){/*...*/})Sometimes I prefer to handle it internally as an attribute.
represents the callbacks of success, failure, and end of the ajax request respectively. What is the relationship between these three methods and Deferred? In fact, it is syntactic sugar, success corresponds to done, error corresponds to fail, and complete corresponds to always. That's it, just to keep the parameter names consistent with ajax.
Summary:
$.Deferred implements the Promise specification, then, done, fail, and always are the methods of the Deferred object. $.when is a global method used to run multiple asynchronous tasks in parallel, which is the same function as ES6's all. ajax returns a restricted Deferred object. Success, error, and complete are syntactic sugars provided by ajax. Their functions are consistent with done, fail, and always of the Deferred object.
Related recommendations:
Detailed explanation of promsie.all and promise sequence execution
Using Promise in JS to implement traffic light example code ( demo)
About the simple usage of promise objects
The above is the detailed content of How to use jQuery's Promise correctly. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
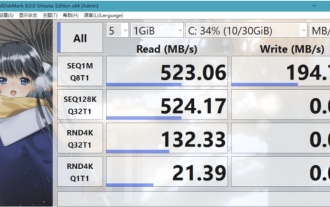 What software is crystaldiskmark? -How to use crystaldiskmark?
Mar 18, 2024 pm 02:58 PM
What software is crystaldiskmark? -How to use crystaldiskmark?
Mar 18, 2024 pm 02:58 PM
CrystalDiskMark is a small HDD benchmark tool for hard drives that quickly measures sequential and random read/write speeds. Next, let the editor introduce CrystalDiskMark to you and how to use crystaldiskmark~ 1. Introduction to CrystalDiskMark CrystalDiskMark is a widely used disk performance testing tool used to evaluate the read and write speed and performance of mechanical hard drives and solid-state drives (SSD). Random I/O performance. It is a free Windows application and provides a user-friendly interface and various test modes to evaluate different aspects of hard drive performance and is widely used in hardware reviews
 How to download foobar2000? -How to use foobar2000
Mar 18, 2024 am 10:58 AM
How to download foobar2000? -How to use foobar2000
Mar 18, 2024 am 10:58 AM
foobar2000 is a software that can listen to music resources at any time. It brings you all kinds of music with lossless sound quality. The enhanced version of the music player allows you to get a more comprehensive and comfortable music experience. Its design concept is to play the advanced audio on the computer The device is transplanted to mobile phones to provide a more convenient and efficient music playback experience. The interface design is simple, clear and easy to use. It adopts a minimalist design style without too many decorations and cumbersome operations to get started quickly. It also supports a variety of skins and Theme, personalize settings according to your own preferences, and create an exclusive music player that supports the playback of multiple audio formats. It also supports the audio gain function to adjust the volume according to your own hearing conditions to avoid hearing damage caused by excessive volume. Next, let me help you
 How to use NetEase Mailbox Master
Mar 27, 2024 pm 05:32 PM
How to use NetEase Mailbox Master
Mar 27, 2024 pm 05:32 PM
NetEase Mailbox, as an email address widely used by Chinese netizens, has always won the trust of users with its stable and efficient services. NetEase Mailbox Master is an email software specially created for mobile phone users. It greatly simplifies the process of sending and receiving emails and makes our email processing more convenient. So how to use NetEase Mailbox Master, and what specific functions it has. Below, the editor of this site will give you a detailed introduction, hoping to help you! First, you can search and download the NetEase Mailbox Master app in the mobile app store. Search for "NetEase Mailbox Master" in App Store or Baidu Mobile Assistant, and then follow the prompts to install it. After the download and installation is completed, we open the NetEase email account and log in. The login interface is as shown below
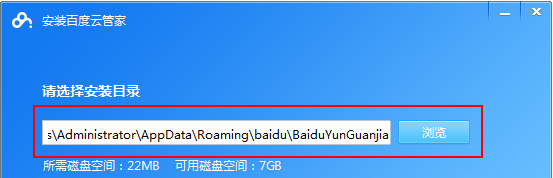 How to use Baidu Netdisk app
Mar 27, 2024 pm 06:46 PM
How to use Baidu Netdisk app
Mar 27, 2024 pm 06:46 PM
Cloud storage has become an indispensable part of our daily life and work nowadays. As one of the leading cloud storage services in China, Baidu Netdisk has won the favor of a large number of users with its powerful storage functions, efficient transmission speed and convenient operation experience. And whether you want to back up important files, share information, watch videos online, or listen to music, Baidu Cloud Disk can meet your needs. However, many users may not understand the specific use method of Baidu Netdisk app, so this tutorial will introduce in detail how to use Baidu Netdisk app. Users who are still confused can follow this article to learn more. ! How to use Baidu Cloud Network Disk: 1. Installation First, when downloading and installing Baidu Cloud software, please select the custom installation option.
 BTCC tutorial: How to bind and use MetaMask wallet on BTCC exchange?
Apr 26, 2024 am 09:40 AM
BTCC tutorial: How to bind and use MetaMask wallet on BTCC exchange?
Apr 26, 2024 am 09:40 AM
MetaMask (also called Little Fox Wallet in Chinese) is a free and well-received encryption wallet software. Currently, BTCC supports binding to the MetaMask wallet. After binding, you can use the MetaMask wallet to quickly log in, store value, buy coins, etc., and you can also get 20 USDT trial bonus for the first time binding. In the BTCCMetaMask wallet tutorial, we will introduce in detail how to register and use MetaMask, and how to bind and use the Little Fox wallet in BTCC. What is MetaMask wallet? With over 30 million users, MetaMask Little Fox Wallet is one of the most popular cryptocurrency wallets today. It is free to use and can be installed on the network as an extension
 Teach you how to use the new advanced features of iOS 17.4 'Stolen Device Protection'
Mar 10, 2024 pm 04:34 PM
Teach you how to use the new advanced features of iOS 17.4 'Stolen Device Protection'
Mar 10, 2024 pm 04:34 PM
Apple rolled out the iOS 17.4 update on Tuesday, bringing a slew of new features and fixes to iPhones. The update includes new emojis, and EU users will also be able to download them from other app stores. In addition, the update also strengthens the control of iPhone security and introduces more "Stolen Device Protection" setting options to provide users with more choices and protection. "iOS17.3 introduces the "Stolen Device Protection" function for the first time, adding extra security to users' sensitive information. When the user is away from home and other familiar places, this function requires the user to enter biometric information for the first time, and after one hour You must enter information again to access and change certain data, such as changing your Apple ID password or turning off stolen device protection.
 How to use Xiaomi Auto app
Apr 01, 2024 pm 09:19 PM
How to use Xiaomi Auto app
Apr 01, 2024 pm 09:19 PM
Xiaomi car software provides remote car control functions, allowing users to remotely control the vehicle through mobile phones or computers, such as opening and closing the vehicle's doors and windows, starting the engine, controlling the vehicle's air conditioner and audio, etc. The following is the use and content of this software, let's learn about it together . Comprehensive list of Xiaomi Auto app functions and usage methods 1. The Xiaomi Auto app was launched on the Apple AppStore on March 25, and can now be downloaded from the app store on Android phones; Car purchase: Learn about the core highlights and technical parameters of Xiaomi Auto, and make an appointment for a test drive. Configure and order your Xiaomi car, and support online processing of car pickup to-do items. 3. Community: Understand Xiaomi Auto brand information, exchange car experience, and share wonderful car life; 4. Car control: The mobile phone is the remote control, remote control, real-time security, easy
 How to use the little black box cdkey
Mar 12, 2024 pm 07:34 PM
How to use the little black box cdkey
Mar 12, 2024 pm 07:34 PM
How to use the Little Black Box cdkey? To put it simply, you can directly purchase games on the Steam platform from the Little Black Box, and you will receive a CDK redemption code after successful purchase. Next, use this redemption code in the Steam Mall to purchase the corresponding game. Many friends may not know how to use the small black box cdkey. Below I will explain the redemption steps in detail. I hope it will be helpful to you. How to use the Little Black Box cdkey 1. First copy the CDK redemption code obtained after purchasing the Little Black Box game. 2. Then start the Steam platform. 3. Click on the "Game" option in the menu in the upper left corner. 4. Find and click "Activate Product on Steam" in the new menu. 5. Click Next directly on the pop-up interface. 6. Purchase the small black box




