Detailed explanation of the fiber architecture of React16.2
本文主要和大家分享React16.2的fiber架构详解,希望能帮助到大家。insertUpdateIntoFiber 会根据fiber的状态创建一个或两个列队对象,对象是长成这样的对象是长成这样的
//by 司徒正美, 加群:370262116 一起研究React与anujs
// https://github.com/RubyLouvre/anu 欢迎加star
function createUpdateQueue(baseState) {//我们现在是丢了一个null做传参
var queue = {
baseState: baseState,
expirationTime: NoWork,//NoWork会被立即执行
first: null,
last: null,
callbackList: null,
hasForceUpdate: false,
isInitialized: false
};
return queue;
}scheduleWork是一个奇怪的方法,只是添加一下参数
function scheduleWork(fiber, expirationTime) {
return scheduleWorkImpl(fiber, expirationTime, false);
}scheduleWorkImpl的最开头有一个recordScheduleUpdate方法,用来记录调度器的执行状态,如注释所示,它现在相当于什么都没有做
function recordScheduleUpdate() {
if (enableUserTimingAPI) {//全局变量,默认为true
if (isCommitting) {//全局变量,默认为false, 没有进入分支
hasScheduledUpdateInCurrentCommit = true;
}
//全局变量,默认为null,没有没有进入分支
if (currentPhase !== null && currentPhase !== 'componentWillMount' && currentPhase !== 'componentWillReceiveProps') {
hasScheduledUpdateInCurrentPhase = true;
}
}
}scheduleWorkImpl的一些分支非常复杂,我们打一些断点
function computeExpirationForFiber(fiber) {
var expirationTime = void 0;
if (expirationContext !== NoWork) {
// An explicit expiration context was set;
expirationTime = expirationContext;
} else if (isWorking) {
if (isCommitting) {
// Updates that occur during the commit phase should have sync priority
// by default.
expirationTime = Sync;
} else {
// Updates during the render phase should expire at the same time as
// the work that is being rendered.
expirationTime = nextRenderExpirationTime;
}
} else {
// No explicit expiration context was set, and we're not currently
// performing work. Calculate a new expiration time.
if (useSyncScheduling && !(fiber.internalContextTag & AsyncUpdates)) {
// This is a sync update
console.log("expirationTime", Sync)
expirationTime = Sync;//命中这里
} else {
// This is an async update
expirationTime = computeAsyncExpiration();
}
}
return expirationTime;
}
function checkRootNeedsClearing(root, fiber, expirationTime) {
if (!isWorking && root === nextRoot && expirationTime < nextRenderExpirationTime) {
console.log("checkRootNeedsClearing对nextRoot,nextUnitOfWork,nextRenderExpirationTime进行置空")
// Restart the root from the top.
if (nextUnitOfWork !== null) {
// This is an interruption. (Used for performance tracking.)
interruptedBy = fiber;
}
nextRoot = null;
nextUnitOfWork = null;
nextRenderExpirationTime = NoWork;
}else{
console.log("checkRootNeedsClearing就是想酱油")
}
}
function scheduleWorkImpl(fiber, expirationTime, isErrorRecovery) {
recordScheduleUpdate();//现在什么也没做
var node = fiber;
while (node !== null) {
// Walk the parent path to the root and update each node's
// expiration time.
if (node.expirationTime === NoWork || node.expirationTime > expirationTime) {
node.expirationTime = expirationTime;//由于默认就是NoWork,因此会被重写 Sync
}
if (node.alternate !== null) {//这里进不去
if (node.alternate.expirationTime === NoWork || node.alternate.expirationTime > expirationTime) {
node.alternate.expirationTime = expirationTime;
}
}
if (node['return'] === null) {
if (node.tag === HostRoot) {//进入这里
var root = node.stateNode;
checkRootNeedsClearing(root, fiber, expirationTime);
console.log("requestWork",root, expirationTime)
requestWork(root, expirationTime);
checkRootNeedsClearing(root, fiber, expirationTime);
} else {
return;
}
}
node = node['return'];
}
}输出如下
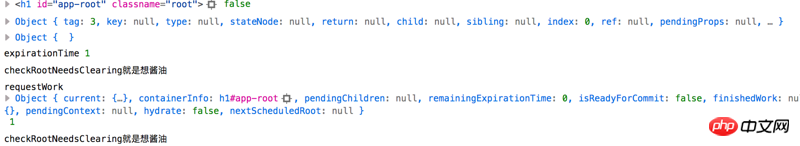
requestWork也很难理解,里面太多全局变量,觉得不是前端的人搞的。为了帮助理解,我们继续加日志
//by 司徒正美, 加群:370262116 一起研究React与anujs
// requestWork is called by the scheduler whenever a root receives an update.
// It's up to the renderer to call renderRoot at some point in the future.
/*
只要root收到更新(update对象),requestWork就会被调度程序调用。
渲染器在将来的某个时刻调用renderRoot。
*/
function requestWork(root, expirationTime) {
if (nestedUpdateCount > NESTED_UPDATE_LIMIT) {
invariant_1(false, 'Maximum update depth exceeded. This can happen when a component repeatedly calls setState inside componentWillUpdate or componentDidUpdate. React limits the number of nested updates to prevent infinite loops.');
}
// Add the root to the schedule.
// Check if this root is already part of the schedule.
if (root.nextScheduledRoot === null) {
// This root is not already scheduled. Add it.
console.log("设置remainingExpirationTime",expirationTime)
root.remainingExpirationTime = expirationTime;
if (lastScheduledRoot === null) {
console.log("设置firstScheduledRoot, lastScheduledRoot")
firstScheduledRoot = lastScheduledRoot = root;
root.nextScheduledRoot = root;
} else {
lastScheduledRoot.nextScheduledRoot = root;
lastScheduledRoot = root;
lastScheduledRoot.nextScheduledRoot = firstScheduledRoot;
}
} else {
// This root is already scheduled, but its priority may have increased.
var remainingExpirationTime = root.remainingExpirationTime;
if (remainingExpirationTime === NoWork || expirationTime < remainingExpirationTime) {
// Update the priority.
root.remainingExpirationTime = expirationTime;
}
}
if (isRendering) {
// Prevent reentrancy. Remaining work will be scheduled at the end of
// the currently rendering batch.
return;
}
if (isBatchingUpdates) {
// Flush work at the end of the batch.
if (isUnbatchingUpdates) {
// ...unless we're inside unbatchedUpdates, in which case we should
// flush it now.
nextFlushedRoot = root;
nextFlushedExpirationTime = Sync;
console.log("performWorkOnRoot")
performWorkOnRoot(nextFlushedRoot, nextFlushedExpirationTime);
}
return;
}
// TODO: Get rid of Sync and use current time?
if (expirationTime === Sync) {
console.log("进入performWork")
performWork(Sync, null);
} else {
scheduleCallbackWithExpiration(expirationTime);
}
}从日志输出来看,requestWork只是修改了两个全局变量,然后进入performWork。这三个内部方法起名很有意思。scheduleWork意为打算工作,requestWork意为申请工作,performWork意为努力工作(正式上班)
function performWork(minExpirationTime, dl) {
deadline = dl;
// Keep working on roots until there's no more work, or until the we reach
// the deadline.
//这里会将root设置为highestPriorityRoot
findHighestPriorityRoot();
if (enableUserTimingAPI && deadline !== null) {
var didExpire = nextFlushedExpirationTime < recalculateCurrentTime();
console.log(didExpire)
stopRequestCallbackTimer(didExpire);
}
while (nextFlushedRoot !== null
&& nextFlushedExpirationTime !== NoWork
&& (minExpirationTime === NoWork || nextFlushedExpirationTime <= minExpirationTime)
&& !deadlineDidExpire) {
console.log("performWorkOnRoot")
performWorkOnRoot(highestPriorityRoot, nextFlushedExpirationTime);
// Find the next highest priority work.
findHighestPriorityRoot();
}
// We're done flushing work. Either we ran out of time in this callback,
// or there's no more work left with sufficient priority.
// If we're inside a callback, set this to false since we just completed it.
if (deadline !== null) {
callbackExpirationTime = NoWork;
callbackID = -1;
}
// If there's work left over, schedule a new callback.
if (nextFlushedExpirationTime !== NoWork) {
console.log("scheduleCallbackWithExpiration")
scheduleCallbackWithExpiration(nextFlushedExpirationTime);
}
// Clean-up.
deadline = null;
deadlineDidExpire = false;
nestedUpdateCount = 0;
if (hasUnhandledError) { //如果有没处理的错误则throw
var _error4 = unhandledError;
unhandledError = null;
hasUnhandledError = false;
throw _error4;
}
}
我们终于进入performWorkOnRoot,performWorkOnRoot的作用是区分同步渲染还是异步渲染,expirationTime等于1,因此进入同步。导步肯定为false
// https://github.com/RubyLouvre/anu 欢迎加star
function performWorkOnRoot(root, expirationTime) {
isRendering = true;
// Check if this is async work or sync/expired work.
// TODO: Pass current time as argument to renderRoot, commitRoot
if (expirationTime <= recalculateCurrentTime()) {
// Flush sync work.
var finishedWork = root.finishedWork;
console.log("Flush sync work.", finishedWork)
if (finishedWork !== null) {
// This root is already complete. We can commit it.
root.finishedWork = null;
console.log("commitRoot")
root.remainingExpirationTime = commitRoot(finishedWork);
} else {
root.finishedWork = null;
console.log("renderRoot")
finishedWork = renderRoot(root, expirationTime);
if (finishedWork !== null) {
console.log("继续commitRoot")
// We've completed the root. Commit it.
root.remainingExpirationTime = commitRoot(finishedWork);
}
}
} else {
console.log("Flush async work.")
// Flush async work.
// ...略
}
isRendering = false;
}
renderRoot也是怒长,React16代码的特点是许多巨型类,巨型方法,有JAVA之遗风。renderRoot只有前面几行是可能处理虚拟DOM(或叫fiber),后面都是错误边界的
function renderRoot(root, expirationTime) {
isWorking = true;
// We're about to mutate the work-in-progress tree. If the root was pending
// commit, it no longer is: we'll need to complete it again.
root.isReadyForCommit = false;
// Check if we're starting from a fresh stack, or if we're resuming from
// previously yielded work.
if (root !== nextRoot || expirationTime !== nextRenderExpirationTime || nextUnitOfWork === null) {
// Reset the stack and start working from the root.
resetContextStack();
nextRoot = root;
nextRenderExpirationTime = expirationTime;
//可能是用来工作的代码
console.log("createWorkInProgress")
nextUnitOfWork = createWorkInProgress(nextRoot.current, null, expirationTime);
}
//可能是用来工作的代码
console.log("startWorkLoopTimer")
startWorkLoopTimer(nextUnitOfWork);
// 处理错误边界
var didError = false;
var error = null;
invokeGuardedCallback$1(null, workLoop, null, expirationTime);
// An error was thrown during the render phase.
while (didError) {
console.log("componentDidCatch的相关实现")
if (didFatal) {
// This was a fatal error. Don't attempt to recover from it.
firstUncaughtError = error;
break;
}
var failedWork = nextUnitOfWork;
if (failedWork === null) {
// An error was thrown but there's no current unit of work. This can
// happen during the commit phase if there's a bug in the renderer.
didFatal = true;
continue;
}
// 处理错误边界
var boundary = captureError(failedWork, error);
!(boundary !== null) ? invariant_1(false, 'Should have found an error boundary. This error is likely caused by a bug in React. Please file an issue.') : void 0;
if (didFatal) {
// The error we just captured was a fatal error. This happens
// when the error propagates to the root more than once.
continue;
}
// 处理错误边界
didError = false;
error = null;
// We're finished working. Exit the error loop.
break;
}
// 处理错误边界
var uncaughtError = firstUncaughtError;
// We're done performing work. Time to clean up.
stopWorkLoopTimer(interruptedBy);
interruptedBy = null;
isWorking = false;
didFatal = false;
firstUncaughtError = null;
// 处理错误边界
if (uncaughtError !== null) {
onUncaughtError(uncaughtError);
}
return root.isReadyForCommit ? root.current.alternate : null;
}
function resetContextStack() {
// Reset the stack
reset$1();
// Reset the cursors
resetContext();
resetHostContainer();
}
function reset$1() {
console.log("reset",index)
while (index > -1) {
valueStack[index] = null;
{
fiberStack[index] = null;
}
index--;
}
}
function resetContext() {
consoel.log("resetContext")
previousContext = emptyObject_1;
contextStackCursor.current = emptyObject_1;
didPerformWorkStackCursor.current = false;
}
function resetHostContainer() {
console.log("resetHostContainer",contextStackCursor, rootInstanceStackCursor, NO_CONTEXT )
contextStackCursor.current = NO_CONTEXT;
rootInstanceStackCursor.current = NO_CONTEXT;
}
createWorkInProgress就是将根组件的fiber对象再复制一份,变成其alternate属性。因此 将虚拟DOM转换为真实DOM的重任就交给invokeGuardedCallback
var invokeGuardedCallback = function (name, func, context, a, b, c, d, e, f) {
ReactErrorUtils._hasCaughtError = false;
ReactErrorUtils._caughtError = null;
var funcArgs = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments, 3);
try {
func.apply(context, funcArgs);
} catch (error) {
ReactErrorUtils._caughtError = error;
ReactErrorUtils._hasCaughtError = true;
}
//这下面还有怒长(100-150L )的关于错误边界的处理,略过
};func为workLoop
//by 司徒正美, 加群:370262116 一起研究React与anujs
function workLoop(expirationTime) {
if (capturedErrors !== null) {
// If there are unhandled errors, switch to the slow work loop.
// TODO: How to avoid this check in the fast path? Maybe the renderer
// could keep track of which roots have unhandled errors and call a
// forked version of renderRoot.
slowWorkLoopThatChecksForFailedWork(expirationTime);
return;
}
if (nextRenderExpirationTime === NoWork || nextRenderExpirationTime > expirationTime) {
return;
}
if (nextRenderExpirationTime <= mostRecentCurrentTime) {
// Flush all expired work.
while (nextUnitOfWork !== null) {
console.log("performUnitOfWork",nextUnitOfWork)
nextUnitOfWork = performUnitOfWork(nextUnitOfWork);
}
} else {
// Flush asynchronous work until the deadline runs out of time.
while (nextUnitOfWork !== null && !shouldYield()) {
nextUnitOfWork = performUnitOfWork(nextUnitOfWork);
}
}
}
我们终于看到工作的代码了。 这个nextUnitOfWork 是renderRoot生成的
performUnitOfWork与beginWork的代码,里面会根据fiber的tag进入各种操作
//by 司徒正美, 加群:370262116 一起研究React与anujs
// https://github.com/RubyLouvre/anu 欢迎加star
function performUnitOfWork(workInProgress) {
// The current, flushed, state of this fiber is the alternate.
// Ideally nothing should rely on this, but relying on it here
// means that we don't need an additional field on the work in
// progress.
var current = workInProgress.alternate;
// See if beginning this work spawns more work.
startWorkTimer(workInProgress);
{
ReactDebugCurrentFiber.setCurrentFiber(workInProgress);
}
console.log("beginWork")
var next = beginWork(current, workInProgress, nextRenderExpirationTime);
{
ReactDebugCurrentFiber.resetCurrentFiber();
}
if (true && ReactFiberInstrumentation_1.debugTool) {
ReactFiberInstrumentation_1.debugTool.onBeginWork(workInProgress);
}
if (next === null) {
console.log("next")
// If this doesn't spawn new work, complete the current work.
next = completeUnitOfWork(workInProgress);
}
ReactCurrentOwner.current = null;
return next;
}
function beginWork(current, workInProgress, renderExpirationTime) {
if (workInProgress.expirationTime === NoWork || workInProgress.expirationTime > renderExpirationTime) {
return bailoutOnLowPriority(current, workInProgress);
}
switch (workInProgress.tag) {
case IndeterminateComponent:
return mountIndeterminateComponent(current, workInProgress, renderExpirationTime);
case FunctionalComponent:
return updateFunctionalComponent(current, workInProgress);
case ClassComponent:
return updateClassComponent(current, workInProgress, renderExpirationTime);
case HostRoot:
return updateHostRoot(current, workInProgress, renderExpirationTime);
case HostComponent:
return updateHostComponent(current, workInProgress, renderExpirationTime);
case HostText:
return updateHostText(current, workInProgress);
case CallHandlerPhase:
// This is a restart. Reset the tag to the initial phase.
workInProgress.tag = CallComponent;
// Intentionally fall through since this is now the same.
case CallComponent:
return updateCallComponent(current, workInProgress, renderExpirationTime);
case ReturnComponent:
// A return component is just a placeholder, we can just run through the
// next one immediately.
return null;
case HostPortal:
return updatePortalComponent(current, workInProgress, renderExpirationTime);
case Fragment:
return updateFragment(current, workInProgress);
default:
invariant_1(false, 'Unknown unit of work tag. This error is likely caused by a bug in React. Please file an issue.');
}
}我们再调查一下workInProgress.tag是什么
https://github.com/facebook/r...
这里有全部fiber节点的类型描述,我们创建一个对象
// https://github.com/RubyLouvre/anu 欢迎加star
var mapBeginWork = {
3: "HostRoot 根组件",
0: "IndeterminateComponent 只知道type为函数",
2: "ClassComponent 普通类组件" ,
5: "HostComponent 元素节点",
6: "HostText 文本节点"
}
function beginWork(current, workInProgress, renderExpirationTime) {
if (workInProgress.expirationTime === NoWork || workInProgress.expirationTime > renderExpirationTime) {
return bailoutOnLowPriority(current, workInProgress);
}
console.log(workInProgress.tag, mapBeginWork[workInProgress.tag])
switch (workInProgress.tag) {
//略
}
}
相关推荐:
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of the fiber architecture of React16.2. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Detailed explanation of obtaining administrator rights in Win11
Mar 08, 2024 pm 03:06 PM
Detailed explanation of obtaining administrator rights in Win11
Mar 08, 2024 pm 03:06 PM
Windows operating system is one of the most popular operating systems in the world, and its new version Win11 has attracted much attention. In the Win11 system, obtaining administrator rights is an important operation. Administrator rights allow users to perform more operations and settings on the system. This article will introduce in detail how to obtain administrator permissions in Win11 system and how to effectively manage permissions. In the Win11 system, administrator rights are divided into two types: local administrator and domain administrator. A local administrator has full administrative rights to the local computer
 Detailed explanation of the mode function in C++
Nov 18, 2023 pm 03:08 PM
Detailed explanation of the mode function in C++
Nov 18, 2023 pm 03:08 PM
Detailed explanation of the mode function in C++ In statistics, the mode refers to the value that appears most frequently in a set of data. In C++ language, we can find the mode in any set of data by writing a mode function. The mode function can be implemented in many different ways, two of the commonly used methods will be introduced in detail below. The first method is to use a hash table to count the number of occurrences of each number. First, we need to define a hash table with each number as the key and the number of occurrences as the value. Then, for a given data set, we run
 Detailed explanation of division operation in Oracle SQL
Mar 10, 2024 am 09:51 AM
Detailed explanation of division operation in Oracle SQL
Mar 10, 2024 am 09:51 AM
Detailed explanation of division operation in OracleSQL In OracleSQL, division operation is a common and important mathematical operation, used to calculate the result of dividing two numbers. Division is often used in database queries, so understanding the division operation and its usage in OracleSQL is one of the essential skills for database developers. This article will discuss the relevant knowledge of division operations in OracleSQL in detail and provide specific code examples for readers' reference. 1. Division operation in OracleSQL
 Detailed explanation of remainder function in C++
Nov 18, 2023 pm 02:41 PM
Detailed explanation of remainder function in C++
Nov 18, 2023 pm 02:41 PM
Detailed explanation of the remainder function in C++ In C++, the remainder operator (%) is used to calculate the remainder of the division of two numbers. It is a binary operator whose operands can be any integer type (including char, short, int, long, etc.) or a floating-point number type (such as float, double). The remainder operator returns a result with the same sign as the dividend. For example, for the remainder operation of integers, we can use the following code to implement: inta=10;intb=3;
 Detailed explanation of the usage of Vue.nextTick function and its application in asynchronous updates
Jul 26, 2023 am 08:57 AM
Detailed explanation of the usage of Vue.nextTick function and its application in asynchronous updates
Jul 26, 2023 am 08:57 AM
Detailed explanation of the usage of Vue.nextTick function and its application in asynchronous updates. In Vue development, we often encounter situations where data needs to be updated asynchronously. For example, data needs to be updated immediately after modifying the DOM or related operations need to be performed immediately after the data is updated. The .nextTick function provided by Vue emerged to solve this type of problem. This article will introduce the usage of the Vue.nextTick function in detail, and combine it with code examples to illustrate its application in asynchronous updates. 1. Vue.nex
 Detailed explanation of php-fpm tuning method
Jul 08, 2023 pm 04:31 PM
Detailed explanation of php-fpm tuning method
Jul 08, 2023 pm 04:31 PM
PHP-FPM is a commonly used PHP process manager used to provide better PHP performance and stability. However, in a high-load environment, the default configuration of PHP-FPM may not meet the needs, so we need to tune it. This article will introduce the tuning method of PHP-FPM in detail and give some code examples. 1. Increase the number of processes. By default, PHP-FPM only starts a small number of processes to handle requests. In a high-load environment, we can improve the concurrency of PHP-FPM by increasing the number of processes
 Detailed explanation of the role and usage of PHP modulo operator
Mar 19, 2024 pm 04:33 PM
Detailed explanation of the role and usage of PHP modulo operator
Mar 19, 2024 pm 04:33 PM
The modulo operator (%) in PHP is used to obtain the remainder of the division of two numbers. In this article, we will discuss the role and usage of the modulo operator in detail, and provide specific code examples to help readers better understand. 1. The role of the modulo operator In mathematics, when we divide an integer by another integer, we get a quotient and a remainder. For example, when we divide 10 by 3, the quotient is 3 and the remainder is 1. The modulo operator is used to obtain this remainder. 2. Usage of the modulo operator In PHP, use the % symbol to represent the modulus
 Detailed explanation of the linux system call system() function
Feb 22, 2024 pm 08:21 PM
Detailed explanation of the linux system call system() function
Feb 22, 2024 pm 08:21 PM
Detailed explanation of Linux system call system() function System call is a very important part of the Linux operating system. It provides a way to interact with the system kernel. Among them, the system() function is one of the commonly used system call functions. This article will introduce the use of the system() function in detail and provide corresponding code examples. Basic Concepts of System Calls System calls are a way for user programs to interact with the operating system kernel. User programs request the operating system by calling system call functions




