Promise instance analysis in js
Everyone knows that nodejs is very fast. Why is it so fast? The reason is that node uses asynchronous callbacks to handle events that need to be waited for, so that the code will continue to execute without waiting somewhere. But there is also a disadvantage. When we have many callbacks, for example, after executing this callback, we need to execute the next callback, and then execute the next callback. This will cause layers of nesting and unclear code, which is very difficult. It is easy to enter the "callback jail", which can easily lead to the following example:
async(1, function(value){
async(value, function(value){
async(value, function(value){
async(value, function(value){
async(value, function(value){
async(value, final);
});
});
});
});
});This way of writing will make people collapse. So is there any way to solve this problem, or is there any other way of writing? The answer is yes. The new promise object of es6 and the async await of es7 can solve this problem. Of course, the promise object will be introduced here first, and the async await of es7 will be shared in the following articles. The Promise object will be introduced below.
2. Introduction
Promise is an object that is used to handle asynchronous operations. It allows us to write asynchronous calls more elegantly, more beautifully and easier to read. As the name suggests, it means promise, which means that after using Promise, he will definitely give us a reply, no matter whether it succeeds or fails, he will give us a reply, so we don't have to worry about him running away, haha. Therefore, Promise has three states: pending (in progress), resolved (completed), and rejected (failed). Only structures returned asynchronously can change their state. Therefore, there are generally only two promise processes: pending->resolved or pending->rejected.
The promise object also has a more commonly used then method, which is used to execute the callback function. The then method accepts two parameters. The first is a successful resolved callback, the other is a failed rejected callback, and the second Optional callback parameters for failure. And the then method can also return a promise object, so that it can be called in a chain. Next, the code:
var Pro = function (time) {
//返回一个Promise对象
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
console.log('123');
//模拟接口调用
setTimeout(function () {
//这里告诉Promise 成功了,然后去执行then方法的第一个函数
resolve('成功返回');
}, time);
})
};
(function(){
console.log('start');
Pro(3000)
.then(function(data){
console.log(data);
return Pro(5000);})
.then(function(data){
console.log(data);
console.log('end');
})
})();In the above code, a Pro variable is defined, and then an anonymous function is assigned to it. The function returns a Promise object, and then receives a function in the object, and uses the resolve and reject methods respectively. When the parameters are passed in, setTimeOut is used to simulate an asynchronous request. When the resolve method is executed, a function of the then method will be called. The results are as follows:

3. Promise API
1, Promise.resolve()
2, Promise.reject()
3 , Promise.prototype.then()
4, Promise.prototype.catch()
5, Promise.all() // All are completed, equivalent to
6, Promise.race( ) // Just complete one, which is equivalent to or
1. The function of Promise.resolve() is to convert the existing object into a Promise object resolvedl;Promise.resolve('test')==new Promise(resolve =>resolve('test'))
2. Promise.reject() also returns a Promise object with a status of rejected;
3. The then method has been introduced above, here it is No more introduction.
4. catch(): callback function when an error occurs.
5. Promise.all() is suitable for executing then() successfully after all results are completed. For example:
let p1 =new Promise(function(resolve,reject){
resolve(1);
});
let p2 = new Promise(function(resolve,reject){
resolve(2);
});
let p3 = new Promise(function(resolve,reject){
resolve(3);
});
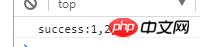
Promise.all([p1, p2, p3]).then(function (results) {
console.log('success:'+results);
}).catch(function(r){
console.log("error");
console.log(r);
});Final output:
6. The function of Promise.race() is to execute multiple instances at the same time, as long as one instance changes State, the Promise is changed to the state changed by that instance;
4. Example
var Pro = function () {
//返回一个Promise对象
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
//模拟接口调用
setTimeout(function () {
resolve(true);
}, 1000);
})
};
var Pro2 = function () {
//返回一个Promise对象
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
//模拟接口调用
setTimeout(function () {
resolve('Pro2成功执行');
}, 1000);
})
};
Pro().then(function(data){
var val = data;
console.log(val)
if (val) {
console.log(1111)
return Pro2()
}
}).then(function(data1){
console.log(data1)
})Output:
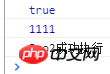
This way you can use The then method can now implement chain calls.
Related recommendations:
ES6 Promise extended always method instance detailed explanation
How to use jQuery’s Promise correctly
Detailed explanation of the sequential execution of promsie.all and promise
The above is the detailed content of Promise instance analysis in js. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system Introduction: With the continuous development of technology, speech recognition technology has become an important part of the field of artificial intelligence. The online speech recognition system based on WebSocket and JavaScript has the characteristics of low latency, real-time and cross-platform, and has become a widely used solution. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system.
 WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: Key technologies for realizing real-time monitoring systems Introduction: With the rapid development of Internet technology, real-time monitoring systems have been widely used in various fields. One of the key technologies to achieve real-time monitoring is the combination of WebSocket and JavaScript. This article will introduce the application of WebSocket and JavaScript in real-time monitoring systems, give code examples, and explain their implementation principles in detail. 1. WebSocket technology
 Keeping your word: The pros and cons of delivering on your promises
Feb 18, 2024 pm 08:06 PM
Keeping your word: The pros and cons of delivering on your promises
Feb 18, 2024 pm 08:06 PM
In daily life, we often encounter problems between promises and fulfillment. Whether in a personal relationship or a business transaction, delivering on promises is key to building trust. However, the pros and cons of commitment are often controversial. This article will explore the pros and cons of commitments and give some advice on how to keep your word. The promised benefits are obvious. First, commitment builds trust. When a person keeps his word, he makes others believe that he is a trustworthy person. Trust is the bond established between people, which can make people more
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecast system Introduction: Today, the accuracy of weather forecasts is of great significance to daily life and decision-making. As technology develops, we can provide more accurate and reliable weather forecasts by obtaining weather data in real time. In this article, we will learn how to use JavaScript and WebSocket technology to build an efficient real-time weather forecast system. This article will demonstrate the implementation process through specific code examples. We
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
 Learn more about Promise.resolve()
Feb 18, 2024 pm 07:13 PM
Learn more about Promise.resolve()
Feb 18, 2024 pm 07:13 PM
Detailed explanation of Promise.resolve() requires specific code examples. Promise is a mechanism in JavaScript for handling asynchronous operations. In actual development, it is often necessary to handle some asynchronous tasks that need to be executed in sequence, and the Promise.resolve() method is used to return a Promise object that has been fulfilled. Promise.resolve() is a static method of the Promise class, which accepts a
 Learn best practice examples of pointer conversion in Golang
Feb 24, 2024 pm 03:51 PM
Learn best practice examples of pointer conversion in Golang
Feb 24, 2024 pm 03:51 PM
Golang is a powerful and efficient programming language that can be used to develop various applications and services. In Golang, pointers are a very important concept, which can help us operate data more flexibly and efficiently. Pointer conversion refers to the process of pointer operations between different types. This article will use specific examples to learn the best practices of pointer conversion in Golang. 1. Basic concepts In Golang, each variable has an address, and the address is the location of the variable in memory.
 How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
Introduction to the method of obtaining HTTP status code in JavaScript: In front-end development, we often need to deal with the interaction with the back-end interface, and HTTP status code is a very important part of it. Understanding and obtaining HTTP status codes helps us better handle the data returned by the interface. This article will introduce how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide specific code examples. 1. What is HTTP status code? HTTP status code means that when the browser initiates a request to the server, the service




