Detailed explanation of scalability of Flex layout
Flexibility
The decisive feature of Flex scalable layout is to make flex items scalable, that is, to allow the width or height of flex items to automatically fill the remaining space. This can be done with the flex property. A scalable container will allocate remaining space proportionally according to the expansion ratio of each scalable item, and will shrink each item according to the shrinkage ratio to avoid overflow.
This article mainly introduces to you the relevant information about the scalability (Flexibility) of css Flex layout. The editor thinks it is quite good, so I will share it with you now and give it as a reference. Let’s follow the editor to take a look, I hope it can help everyone.
Flex attribute
The flex attribute can be used to specify the scalable length of the component: expansion ratio, contraction ratio, and expansion baseline. When an element is a stretch item, the flex property will replace the main-axis length property to determine the main-axis length of the element. If the element is not a flex item, the flex attribute will not take effect.
flex is the abbreviation of flex-grow, flex-shrink, and flex-basis
.item {
flex: none | [ <'flex-grow'> <'flex-shrink'>? || <'flex-basis'> ]
}<'flex-grow' > The value is
, which is used to specify the expansion ratio of the project; if this attribute value is omitted in the flex abbreviation, the specified value of flex-grow is 1; - ## <'flex-shrink'> takes the value of
, which is used to specify the shrink ratio of the item; if this attribute value is omitted in the flex abbreviation, the specified value of flex-shrink is 1; - <'flex-basis'>The value is
| auto, which is used to define the main axis space occupied by the item before allocating excess space, which is the base value of the child element, flex The specified range of -basis depends on box-sizing; if this attribute value is omitted in the flex abbreviation, the specified value of flex-basis is 0%.
Several situations of flex-basis value:
- Fixed length value, (such as 350px), Then the item will occupy a fixed length of space;
- auto will first retrieve the main size of the item (that is, the value of the width/height of the item, whether width or height depends on The direction of the main axis (the direction of the main axis is assumed to be the horizontal direction below), if the main size of the item is not auto, the flex-basis (basis value) of the item adopts the value of the main size; if the main size of the item is auto ( That is, when width:auto or the width attribute of the item is not set), the content size of the item is used as the baseline value; the
- percentage is based on its containing block (that is, the scaling parent container ) calculation of main dimensions. If the main size of the containing block is undefined (i.e. the main size of the parent container depends on the child element), the result is the same as if set to auto.
Common values of flex
Default value of flex: Since the three attribute values of flex-grow, flex-shrink, and flex-basis are in If not set, the default values are 0, 1, and auto respectively, so the default value of flex is: flex:0 1 auto;.item {
flex: 0 1 auto;
}
/*这种情况先根据width/height属性决定元素的尺寸。
(如果项目的主尺寸为auto,则会以其内容大小为基准)
当剩余空间为正值时,伸缩项目无法伸缩,但当空间不足时,伸缩项目可收缩至其[最小]值。
默认状态下,伸缩项目不会收缩至比其最小内容尺寸更小。
可以通过设置「min-width」或「min-height」属性来改变这个默认状态。*/##
.item {
flex: auto; /*相当于flex:1 1 auto;*/
}
/*根据width/height属性决定元素的尺寸,但是完全可以伸缩,会吸收主轴上剩下的空间*/flex:none: equivalent to flex: 0 0 auto;
.item {
flex: none; /*相当于flex:0 0 auto;*/
}
/*根据width/height属性决定元素的尺寸,但是完全不可以伸缩*/When the value of flex is a positive number, the positive number is the value of flex-grow, because flex-shrink and flex-basis are omitted in the abbreviation of flex values, and their values when omitted are 1 and 0% respectively, so flex:1 is equivalent to flex:1 1 0%;
.item {
flex: 1; /*相当于flex:1 1 0%;*/
}
/*以父容器的宽度为基数计算,元素完全可伸缩*/When flex takes a length or percentage, it is regarded as a flex-basis value, flex-grow takes 1, and flex-shrink takes 1 (note that 0% is a percentage and not a non-negative number);
.item {
flex:120px; /*相当于flex:1 1 120px;*/
}
.item1 {
flex: 0%; /*相当于flex:1 1 0%;*/
}When flex takes two non-negative numbers, they are regarded as the values of flex-grow and flex-shrink respectively, and flex-basis takes 0%;
.item {
flex:2 1; /*相当于flex:2 1 0%;*/
}When flex takes a non-negative number and a length or percentage, it is regarded as the value of flex-grow and flex-basis respectively, and flex-shrink takes 1;
.item {
flex:2 120px; /*相当于flex:2 1 120px;*/
}For example
html is as follows:
<p class="box">
<p class="item-1"></p>
<p class="item-2"></p>
<p class="item-3"></p>
</p>css is as follows:
.box {
display: flex;
width: 800px;
}
.box > p {
height: 200px;
}
.item-1 {
width: 160px;
flex: 2 1 0%;
background: #2ecc71;
}
.item-2 {
width: 100px;
flex: 2 1 auto;
background: #3498db;
}
.item-3 {
flex: 1 1 200px;
background: #9b59b6;
}The results obtained are as follows:
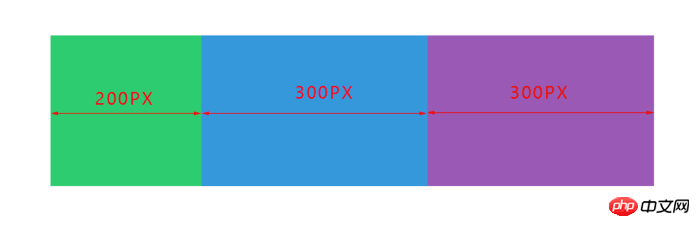 The total size of the parent container on the main axis is 800px
The total size of the parent container on the main axis is 800px
The total baseline value of the child elements It is: 0% + auto + 200px = 300px, where
- - 0% is 0 * 800px = 0 width
- - auto corresponding to The main size is 100px
- , so the remaining space is 800px - 300px = 500px
The sum of the scaling factors is: 2 + 2 + 1 = 5
The remaining space is allocated as follows:
- - item-1 and item-2 are allocated 2/5 each, each getting 200px
- item-3 allocate 1/5, get 100px
The final width of each item is:
- item-1 = 0% + 200px = 200px
- item-2 = auto + 200px = 300px
- item-3 = 200px + 100px = 300px
When the base value of item-1 is 0%, the item is regarded as zero size, so even if its size is declared to be 160px, there is no What's the use? It's useless
When item-2's base value is auto, according to the rules, the base value used is the main size value, which is 100px, so this 100px will not be included in the remaining space
Summary
The default value of flex is not the initial value of a single attribute. Among the abbreviations of flex attribute values, the default values of flex-grow, flex-shrink, and flex-basis are respectively 1, 1, 0%, instead of the default values 0, 1, and auto of these three attributes respectively;
When the project does not set a fixed width (for the horizontal case, that is, the width itself is auto), If flex-basis is also auto, then the usage value of flex-basis is the width supported by the content of the item itself (for horizontal situations).
Related recommendations:
java concurrent programming (4) Performance and scalability
DB2 physics for OLTP environment Database design: reliability, availability and scalability
Detailed examples of specific usage of CSS Flexbox
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of scalability of Flex layout. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Detailed explanation of the mode function in C++
Nov 18, 2023 pm 03:08 PM
Detailed explanation of the mode function in C++
Nov 18, 2023 pm 03:08 PM
Detailed explanation of the mode function in C++ In statistics, the mode refers to the value that appears most frequently in a set of data. In C++ language, we can find the mode in any set of data by writing a mode function. The mode function can be implemented in many different ways, two of the commonly used methods will be introduced in detail below. The first method is to use a hash table to count the number of occurrences of each number. First, we need to define a hash table with each number as the key and the number of occurrences as the value. Then, for a given data set, we run
 Detailed explanation of obtaining administrator rights in Win11
Mar 08, 2024 pm 03:06 PM
Detailed explanation of obtaining administrator rights in Win11
Mar 08, 2024 pm 03:06 PM
Windows operating system is one of the most popular operating systems in the world, and its new version Win11 has attracted much attention. In the Win11 system, obtaining administrator rights is an important operation. Administrator rights allow users to perform more operations and settings on the system. This article will introduce in detail how to obtain administrator permissions in Win11 system and how to effectively manage permissions. In the Win11 system, administrator rights are divided into two types: local administrator and domain administrator. A local administrator has full administrative rights to the local computer
 Detailed explanation of division operation in Oracle SQL
Mar 10, 2024 am 09:51 AM
Detailed explanation of division operation in Oracle SQL
Mar 10, 2024 am 09:51 AM
Detailed explanation of division operation in OracleSQL In OracleSQL, division operation is a common and important mathematical operation, used to calculate the result of dividing two numbers. Division is often used in database queries, so understanding the division operation and its usage in OracleSQL is one of the essential skills for database developers. This article will discuss the relevant knowledge of division operations in OracleSQL in detail and provide specific code examples for readers' reference. 1. Division operation in OracleSQL
 Detailed explanation of remainder function in C++
Nov 18, 2023 pm 02:41 PM
Detailed explanation of remainder function in C++
Nov 18, 2023 pm 02:41 PM
Detailed explanation of the remainder function in C++ In C++, the remainder operator (%) is used to calculate the remainder of the division of two numbers. It is a binary operator whose operands can be any integer type (including char, short, int, long, etc.) or a floating-point number type (such as float, double). The remainder operator returns a result with the same sign as the dividend. For example, for the remainder operation of integers, we can use the following code to implement: inta=10;intb=3;
 20 Best Practices for Java ActiveMQ
Feb 20, 2024 pm 09:48 PM
20 Best Practices for Java ActiveMQ
Feb 20, 2024 pm 09:48 PM
1. Choose the appropriate client transport protocol ActiveMQ supports a variety of client transport protocols, including STOMP, AMQP and OpenWire. Choose the right protocol based on your application needs to optimize performance and reliability. 2. Configure message persistence. Persistent messages are persisted even after server restarts, while non-persistent messages are not. For critical messages, choose persistence to ensure reliable delivery. Demo code: //Set message persistence MessageProducerproducer=session.createProducer(destination);producer.setDeliveryMode(Deliv
 Detailed explanation of the role and usage of PHP modulo operator
Mar 19, 2024 pm 04:33 PM
Detailed explanation of the role and usage of PHP modulo operator
Mar 19, 2024 pm 04:33 PM
The modulo operator (%) in PHP is used to obtain the remainder of the division of two numbers. In this article, we will discuss the role and usage of the modulo operator in detail, and provide specific code examples to help readers better understand. 1. The role of the modulo operator In mathematics, when we divide an integer by another integer, we get a quotient and a remainder. For example, when we divide 10 by 3, the quotient is 3 and the remainder is 1. The modulo operator is used to obtain this remainder. 2. Usage of the modulo operator In PHP, use the % symbol to represent the modulus
 Detailed explanation of the linux system call system() function
Feb 22, 2024 pm 08:21 PM
Detailed explanation of the linux system call system() function
Feb 22, 2024 pm 08:21 PM
Detailed explanation of Linux system call system() function System call is a very important part of the Linux operating system. It provides a way to interact with the system kernel. Among them, the system() function is one of the commonly used system call functions. This article will introduce the use of the system() function in detail and provide corresponding code examples. Basic Concepts of System Calls System calls are a way for user programs to interact with the operating system kernel. User programs request the operating system by calling system call functions
 Detailed analysis of C language learning route
Feb 18, 2024 am 10:38 AM
Detailed analysis of C language learning route
Feb 18, 2024 am 10:38 AM
As a programming language widely used in the field of software development, C language is the first choice for many beginner programmers. Learning C language can not only help us establish the basic knowledge of programming, but also improve our problem-solving and thinking abilities. This article will introduce in detail a C language learning roadmap to help beginners better plan their learning process. 1. Learn basic grammar Before starting to learn C language, we first need to understand the basic grammar rules of C language. This includes variables and data types, operators, control statements (such as if statements,






