Build a simple website with angular4 and nodejs-express
This article mainly shares with you how to build the front-end login and registration pages and implement angular routing.
In order to make it easier for everyone to understand, I simply drew a routing analysis diagram of my program:
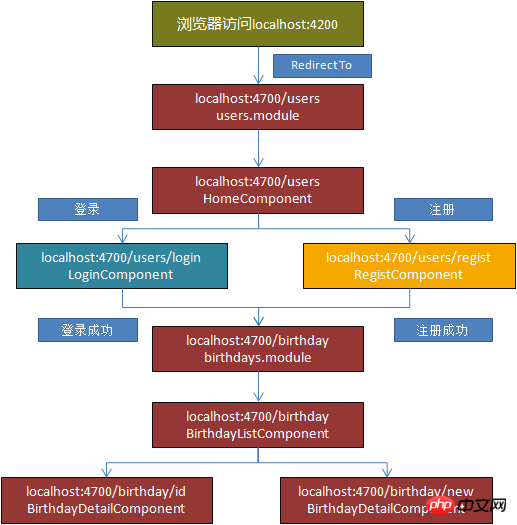
Create the initial page and Set the total route
The code of the initial page app.component.html is as follows:
<p class="bg">
<p class="jumbotron jumbotron-fluid text-center">
<p class="container">
<h1 class="display-3">{{title}}</h1>
<p class="lead">{{lead}}</p>
<hr class="my-4">
<p class="content">{{content}}
</p>
</p>
</p>
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
</p>It is composed of a bootstrap jumbotron component and a router-outlet. The title, lead and The content should change as you navigate to different pages, so I replaced the contents of these three tags with the interpolation expressions title, lead, and content respectively. In order to do this, I created a JumbotronServive service provider that implements message push through rxjs. The code of JumbotronServive is as follows:
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { Subject } from 'rxjs/Subject';
export class Jumbotron{
constructor(
public title:string,
public lead:string,
public content:string
){}
}
@Injectable()
export class JumbotronServive{
private jumbSource = new Subject<Jumbotron>();
jumb$ = this.jumbSource.asObservable();
setJumbotron(jumb: Jumbotron){
this.jumbSource.next(jumb);
}
}First create a Jumbotron class, which contains three attributes title, lead, and content corresponding to the title, lead, and content in jumbotron respectively, and then write a service provider class. In this class An rxjs Subject object is declared in (Subject is a special Observable that allows values to be multicast to multiple observers), and then the Subject's asObservable() is called to declare an Observable object jumb$ to subscribe to the messages sent by the Subject. Finally declare a setJumbotron to send the modified Jumbotron object. In the AppComponent class, we can subscribe to and change the title, lead and content in the jumbotron. The code is as follows:
jumServ.jumb$.subscribe(
jumb=>{
this.title = jumb.title;
this.lead = jumb.lead;
this.content = jumb.content;
});router-outlet: routing outlet, used to mark where the view should be displayed, that is to say, all routing views navigated to will be in <router-outlet></router -outlet> is displayed in the label.
angular-cli (hereinafter referred to as ng) has written the basic AppModule for us (the root module of the Angular program, Angular starts the application by guiding the root module), let’s take a look here:
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { NgbModule } from '@ng-bootstrap/ng-bootstrap';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent,
],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
NgbModule.forRoot(),
AppRoutingModule
],
providers: [
JumbotronServive,
],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }@NgModule decorator marks AppModule as an Angular module class (also called NgModule class). @NgModule accepts a metadata object that tells Angular how to compile and start the application.
@NgModule has the following attributes:
imports — The component template declared in this module requires classes in other modules, the most important of which is BrowserModule, which is used in each browser It is required to run applications on the server.
declarations —Declares the view classes owned in this module, and defines the only component of the application, AppComponent, in AppModule.
bootstrap — Root component, Angular creates it and inserts it into the index.html host page.
providers - the creator of the service and added to the global service list, which can be used in any part of the application. JumbotronServive is added here to provide title and lead in the jumbotron component of bootstrap. , content update.
AppRoutingModule is the routing module of the application. The specific code is:
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { RouterModule, Routes } from '@angular/router';
import { PageNotFoundComponent } from './page-not-found.component';
const appRoutes: Routes = [
{
path:'',
redirectTo:'/users',
pathMatch:'full'
},
{path: '**', component: PageNotFoundComponent}
];
@NgModule({
imports: [
RouterModule.forRoot(appRoutes)
],
exports:[
RouterModule
]
})
export class AppRoutingModule{}First define a routing array, in which the routing object includes the routing path (path) and the routing corresponding Component (component), because our website enters the user management interface as soon as it is opened. When navigating to the homepage, it needs to jump directly to the users route. The homepage route ('') does not have a corresponding component, but jumps directly to the users route. The purpose of the path:'**' route is to access the PageNotFoundComponent component when no route is found.
After defining the routing array, use the @NgModule decorator to import RouterModule, and pass the routing array to the forRoot array of RouterModule.
Finally export the RouterModule module.
Related recommendations:
Project preparation and environment building operations in Angular4
Detailed explanation of examples of routing Router class in Angular4
The above is the detailed content of Build a simple website with angular4 and nodejs-express. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1389
1389
 52
52
 How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system Introduction: With the continuous development of technology, speech recognition technology has become an important part of the field of artificial intelligence. The online speech recognition system based on WebSocket and JavaScript has the characteristics of low latency, real-time and cross-platform, and has become a widely used solution. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system.
 WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: Key technologies for realizing real-time monitoring systems Introduction: With the rapid development of Internet technology, real-time monitoring systems have been widely used in various fields. One of the key technologies to achieve real-time monitoring is the combination of WebSocket and JavaScript. This article will introduce the application of WebSocket and JavaScript in real-time monitoring systems, give code examples, and explain their implementation principles in detail. 1. WebSocket technology
 How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Introduction to how to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system: With the popularity of the Internet and the advancement of technology, more and more restaurants have begun to provide online ordering services. In order to implement a real-time online ordering system, we can use JavaScript and WebSocket technology. WebSocket is a full-duplex communication protocol based on the TCP protocol, which can realize real-time two-way communication between the client and the server. In the real-time online ordering system, when the user selects dishes and places an order
 How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system. In today's digital era, more and more businesses and services need to provide online reservation functions. It is crucial to implement an efficient and real-time online reservation system. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system, and provide specific code examples. 1. What is WebSocket? WebSocket is a full-duplex method on a single TCP connection.
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecast system Introduction: Today, the accuracy of weather forecasts is of great significance to daily life and decision-making. As technology develops, we can provide more accurate and reliable weather forecasts by obtaining weather data in real time. In this article, we will learn how to use JavaScript and WebSocket technology to build an efficient real-time weather forecast system. This article will demonstrate the implementation process through specific code examples. We
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
 How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
Usage: In JavaScript, the insertBefore() method is used to insert a new node in the DOM tree. This method requires two parameters: the new node to be inserted and the reference node (that is, the node where the new node will be inserted).
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time image processing system
Dec 17, 2023 am 08:41 AM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time image processing system
Dec 17, 2023 am 08:41 AM
JavaScript is a programming language widely used in web development, while WebSocket is a network protocol used for real-time communication. Combining the powerful functions of the two, we can create an efficient real-time image processing system. This article will introduce how to implement this system using JavaScript and WebSocket, and provide specific code examples. First, we need to clarify the requirements and goals of the real-time image processing system. Suppose we have a camera device that can collect real-time image data




