Detailed explanation of js combination design pattern
Composition mode combines objects into a tree structure to represent the "part-whole" hierarchy. The combination mode enables users to use single objects and combined objects consistently.
It blurs the concepts of simple elements and complex elements in our tree structure problems. The client program can process complex elements in the same way as simple elements, thus allowing the client program to resolve the internal structure of complex elements. coupling. It can help developers classify multiple objects with similar functions and improve standardized design
There are many examples of hierarchical data structures, making the combination pattern very useful. A common example of a hierarchical data structure is what you encounter every time you use a computer: the file system. A file system consists of directories and files. Each directory can contain content. The contents of a directory can be files or directories. In this way, the computer's file system is organized in a recursive structure. If you want to describe such a data structure, then you can use the composite pattern.
Involving roles
Features
There are two types of objects in the hierarchy of the composite pattern: leaf objects and composite objects. This is a recursive definition, but it is also useful. The reason is that a composite object can be composed of other composite objects and leaf objects, but the leaf object no longer contains sub-objects. The composite object is used for the classification of leaf nodes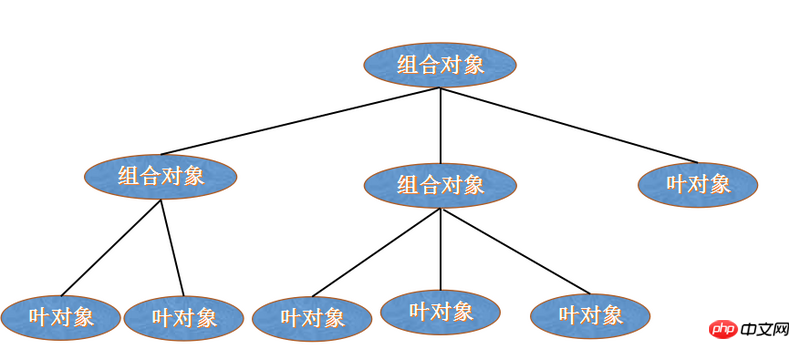
Design
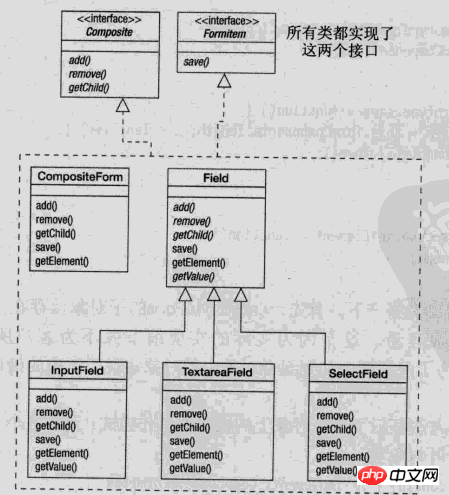
Here we borrow the diagram of javascript design pattern to illustrate the design of the combination pattern
Interface is the object declaration interface in the combination. Where appropriate, implement the default behavior of interfaces common to all classes. Declare an interface for accessing and managing Component subcomponents.
Field represents the leaf node object in the combination. The leaf node has no child nodes and can be designed as an abstract class. Different categories of leaf objects can be designed through inheritance.
Composite defines sub-node behaviors, which are used to store sub-components and implement operations related to sub-components in the Component interface, such as add (add) and delete (remove).

- ##Interface
/* Interfaces. */ var Composite = new Interface('Composite', ['add', 'remove', 'getChild']); var FormItem = new Interface('FormItem', ['save']);Copy after login - Combined Object Class
/* CompositeForm class. */ var CompositeForm = function(id, method, action) { // implements Composite, FormItem this.formComponents = []; this.element = document.createElement('form'); this.element.id = id; this.element.method = method || 'POST'; this.element.action = action || '#'; }; CompositeForm.prototype.add = function(child) { Interface.ensureImplements(child, Composite, FormItem); this.formComponents.push(child); this.element.appendChild(child.getElement()); }; CompositeForm.prototype.remove = function(child) { for(var i = 0, len = this.formComponents.length; i < len; i++) { if(this.formComponents[i] === child) { this.formComponents.splice(i, 1); // Remove one element from the array at // position i. break; } } }; CompositeForm.prototype.getChild = function(i) { return this.formComponents[i]; }; CompositeForm.prototype.save = function() { for(var i = 0, len = this.formComponents.length; i < len; i++) { this.formComponents[i].save(); } }; CompositeForm.prototype.getElement = function() { return this.element; };Copy after login - Leaf Object Class
The leaf object can be a simple class, or it can be designed as an abstract class to construct different types of leaves. Here, abstract classes are used to design different types of leaves
/* Field class, abstract. */ var Field = function(id) { // implements Composite, FormItem this.id = id; this.element; }; Field.prototype.add = function() {}; Field.prototype.remove = function() {}; Field.prototype.getChild = function() {}; Field.prototype.save = function() { setCookie(this.id, this.getValue); }; Field.prototype.getElement = function() { return this.element; }; Field.prototype.getValue = function() { throw new Error('Unsupported operation on the class Field.'); };Copy after login - InputField class
/* InputField class. */ var InputField = function(id, label) { // implements Composite, FormItem Field.call(this, id); this.input = document.createElement('input'); this.input.id = id; this.label = document.createElement('label'); var labelTextNode = document.createTextNode(label); this.label.appendChild(labelTextNode); this.element = document.createElement('p'); this.element.className = 'input-field'; this.element.appendChild(this.label); this.element.appendChild(this.input); }; extend(InputField, Field); // Inherit from Field. InputField.prototype.getValue = function() { return this.input.value; };Copy after login - TextareaField class
/* TextareaField class. */ var TextareaField = function(id, label) { // implements Composite, FormItem Field.call(this, id); this.textarea = document.createElement('textarea'); this.textarea.id = id; this.label = document.createElement('label'); var labelTextNode = document.createTextNode(label); this.label.appendChild(labelTextNode); this.element = document.createElement('p'); this.element.className = 'input-field'; this.element.appendChild(this.label); this.element.appendChild(this.textarea); }; extend(TextareaField, Field); // Inherit from Field. TextareaField.prototype.getValue = function() { return this.textarea.value; };Copy after login - SelectField class
/* SelectField class. */ var SelectField = function(id, label) { // implements Composite, FormItem Field.call(this, id); this.select = document.createElement('select'); this.select.id = id; this.label = document.createElement('label'); var labelTextNode = document.createTextNode(label); this.label.appendChild(labelTextNode); this.element = document.createElement('p'); this.element.className = 'input-field'; this.element.appendChild(this.label); this.element.appendChild(this.select); }; extend(SelectField, Field); // Inherit from Field. SelectField.prototype.getValue = function() { return this.select.options[this.select.selectedIndex].value; };Copy after login
/* Usage. */
var contactForm = new CompositeForm('contact-form', 'POST', 'contact.php');
contactForm.add(new InputField('first-name', 'First Name'));
contactForm.add(new InputField('last-name', 'Last Name'));
contactForm.add(new InputField('address', 'Address'));
contactForm.add(new InputField('city', 'City'));
contactForm.add(new SelectField('state', 'State', stateArray));
// var stateArray =[{'al', 'Alabama'}, ...]
contactForm.add(new InputField('zip', 'Zip'));
contactForm.add(new TextareaField('comments', 'Comments'));
addEvent(window, 'unload', contactForm.save);Copy after login
The combination mode is suitable for operating a large number of objects, and the operating objects have hierarchical relationships. By classifying objects, the coupling between objects is weakened. This mode makes the code more modular and hierarchical. More distinct and better maintainabilityRelated recommendations:
/* Usage. */
var contactForm = new CompositeForm('contact-form', 'POST', 'contact.php');
contactForm.add(new InputField('first-name', 'First Name'));
contactForm.add(new InputField('last-name', 'Last Name'));
contactForm.add(new InputField('address', 'Address'));
contactForm.add(new InputField('city', 'City'));
contactForm.add(new SelectField('state', 'State', stateArray));
// var stateArray =[{'al', 'Alabama'}, ...]
contactForm.add(new InputField('zip', 'Zip'));
contactForm.add(new TextareaField('comments', 'Comments'));
addEvent(window, 'unload', contactForm.save);Detailed explanation of js bridge design pattern
General basic design pattern in Node.js Example analysis
Detailed explanation of js proxy design pattern
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of js combination design pattern. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 The difference between design patterns and architectural patterns in Java framework
Jun 02, 2024 pm 12:59 PM
The difference between design patterns and architectural patterns in Java framework
Jun 02, 2024 pm 12:59 PM
In the Java framework, the difference between design patterns and architectural patterns is that design patterns define abstract solutions to common problems in software design, focusing on the interaction between classes and objects, such as factory patterns. Architectural patterns define the relationship between system structures and modules, focusing on the organization and interaction of system components, such as layered architecture.
 Analysis of the Decorator Pattern in Java Design Patterns
May 09, 2024 pm 03:12 PM
Analysis of the Decorator Pattern in Java Design Patterns
May 09, 2024 pm 03:12 PM
The decorator pattern is a structural design pattern that allows dynamic addition of object functionality without modifying the original class. It is implemented through the collaboration of abstract components, concrete components, abstract decorators and concrete decorators, and can flexibly expand class functions to meet changing needs. In this example, milk and mocha decorators are added to Espresso for a total price of $2.29, demonstrating the power of the decorator pattern in dynamically modifying the behavior of objects.
 PHP design pattern practical case analysis
May 08, 2024 am 08:09 AM
PHP design pattern practical case analysis
May 08, 2024 am 08:09 AM
1. Factory pattern: Separate object creation and business logic, and create objects of specified types through factory classes. 2. Observer pattern: allows subject objects to notify observer objects of their state changes, achieving loose coupling and observer pattern.
 How design patterns deal with code maintenance challenges
May 09, 2024 pm 12:45 PM
How design patterns deal with code maintenance challenges
May 09, 2024 pm 12:45 PM
Design patterns solve code maintenance challenges by providing reusable and extensible solutions: Observer Pattern: Allows objects to subscribe to events and receive notifications when they occur. Factory Pattern: Provides a centralized way to create objects without relying on concrete classes. Singleton pattern: ensures that a class has only one instance, which is used to create globally accessible objects.
 The wonderful use of the adapter pattern in Java design patterns
May 09, 2024 pm 12:54 PM
The wonderful use of the adapter pattern in Java design patterns
May 09, 2024 pm 12:54 PM
The Adapter pattern is a structural design pattern that allows incompatible objects to work together. It converts one interface into another so that the objects can interact smoothly. The object adapter implements the adapter pattern by creating an adapter object containing the adapted object and implementing the target interface. In a practical case, through the adapter mode, the client (such as MediaPlayer) can play advanced format media (such as VLC), although it itself only supports ordinary media formats (such as MP3).
 PHP Design Patterns: Test Driven Development in Practice
Jun 03, 2024 pm 02:14 PM
PHP Design Patterns: Test Driven Development in Practice
Jun 03, 2024 pm 02:14 PM
TDD is used to write high-quality PHP code. The steps include: writing test cases, describing the expected functionality and making them fail. Write code so that only the test cases pass without excessive optimization or detailed design. After the test cases pass, optimize and refactor the code to improve readability, maintainability, and scalability.
 Application of design patterns in Guice framework
Jun 02, 2024 pm 10:49 PM
Application of design patterns in Guice framework
Jun 02, 2024 pm 10:49 PM
The Guice framework applies a number of design patterns, including: Singleton pattern: ensuring that a class has only one instance through the @Singleton annotation. Factory method pattern: Create a factory method through the @Provides annotation and obtain the object instance during dependency injection. Strategy mode: Encapsulate the algorithm into different strategy classes and specify the specific strategy through the @Named annotation.
 What are the advantages and disadvantages of using design patterns in java framework?
Jun 01, 2024 pm 02:13 PM
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using design patterns in java framework?
Jun 01, 2024 pm 02:13 PM
The advantages of using design patterns in Java frameworks include: enhanced code readability, maintainability, and scalability. Disadvantages include complexity, performance overhead, and steep learning curve due to overuse. Practical case: Proxy mode is used to lazy load objects. Use design patterns wisely to take advantage of their advantages and minimize their disadvantages.