
1.BFC definition
BFC (Block formatting context) is literally translated as "block-level formatting context". It is an independent rendering area, with only Block-level boxes (block-level elements) participating. It stipulates how the internal Block-level Box is laid out and has nothing to do with the outside of this area.
In layman’s terms Said: The element that created the BFC is an independent box. The sub-elements inside will not affect the layout of the outside elements (no matter how the inside is laid out, it will not affect the outside). The BFC still belongs to the ordinary flow in the document.
If you know how to trigger BFC
You can trigger BFC and transform into BFC if you meet one of the following conditions
3. BFC layout rules:
What are the characteristics after transforming into BFC, as follows:
Use it come boby
1. Prevent margin overlapbfc causes the margins of child elements in the same bfc to overlap (the distance in the vertical direction of the Box Determined by margin. The margins of two adjacent boxes belonging to the same BFC will overlap)
Problem: As you can see from the picture, there is only a 20px margin between String1 and String2, which should logically be 40px. , but this is in bfc causing their margins to overlap
 Code:
Code:
<style>
.container1{
/* 通过overflow:hidden可以创建bfc */
overflow: hidden;
background-color: red;
width: 300px;
}
.sub1{
margin: 20px 0px;
background-color: #dea;
}
</style>
<p class="container1">
<p class="sub1">String1</p>
<p class="sub1">String2</p>
</p>Solution: We can wrap a container around p and trigger the container to generate a BFC. Then the two ps do not belong to the same BFC, and margin overlap will not occur.
 Code:
Code:
<style>
.newbfc{
overflow: hidden;
}
</style>
<p class="container1">
<p class="sub1">String1</p>
<p class="newbfc"><p class="sub1">String2</p></p>
</p>Problem: When all the child elements of an element are floated, there will be a phenomenon of height collapse, that is, the height of the parent container will not be stretched
 Code:
Code:
<style>
.pre2{
width: 200px;
border: 2px solid red;
}
.float1,.float2{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
float: left;
}
.float1{
background-color: #dee;
}
.float2{
background-color: #dcc;
}
</style>
<p class="pre2">
<p class="float1"></p>
<p class="float2"></p>
</p>bfc's rules: When calculating the height of BFC, floating elements also participate in the calculation, so as long as the parent container is set to bfc, the child elements can be included. :
This container will contain floated child elements, and its height will expand to contain its child elements, which, in this BFC, will flow back into the page's regular document flow.
.pre2{
width: 200px;
border: 2px solid red;
/* 设置overflow*/
overflow:hidden;
} Code:
Code:
<style>
.container2{
overflow: hidden;
width: 200px;
}
.box{
float: left;
width: 100px;
height: 30px;
background-color: #daa;
}
</style>
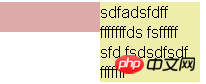
<p class="container2">
<p class="box"></p>
<p style="background-color: #eea">sdfadsfdff fffffffds fsfffff sfd fsdsdfsdf fffffff</p>
</p>BFC rules: The left side of the margin box of each element touches the left side of the containing block border box (for left-to-right formatting, otherwise the opposite). This is true even if there is float.
To solve this problem, just add overflow:hidden to the p element to make it a new bfc
 Related recommendations:
Related recommendations:
The above is the detailed content of CSS understands block-level formatting context BFC. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




