 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 Implementation code sharing of js stack, queue, and linked list data structures
Implementation code sharing of js stack, queue, and linked list data structures
Implementation code sharing of js stack, queue, and linked list data structures
Data structure has been mentioned before. The stack is an ordered collection that follows the last-in-first-out principle. The description of the stack in the book is very accurate. It is like a pile of plates. The first thing must be placed at the bottom. position, the top one is placed. When adding elements to the stack, the first element added is at the bottom of the stack, and the last element added is called the top element.
js implements stack and its methods
The specific content is
Creating a stack: In js we use an array analogy to a stack
Add elements to the stack push()
Remove elements delete()
Stack size size()
View the top element of the stack peek()
Check whether the stack is empty isEmpty()
Empty the stack empty()
Print stack print()
Use
Code
function Stack(){
var stack=[]; this.push=function(para){
stack.push(para);
}; this.delete=function(){
// 删除栈顶元素
stack.pop();//删除数组末尾元素,
} this.size=function(){
return stack.length;
} this.peek=function(){
return stack[stack.length-1];
} this.isEmpty=function(){
if(stack.length==0){ return true;
}else{ return false;
}
} this.emptyStack=function(){
stack=[];
} this.print=function(){
return stack.toString();
}
}Use
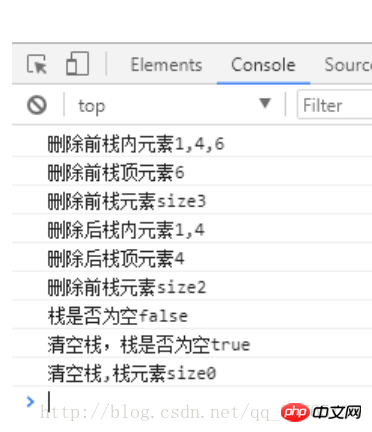
var myStack=new Stack(); myStack.push(1); myStack.push(4); myStack.push(6); console.log('删除前栈内元素'+myStack.print()); console.log('删除前栈顶元素'+myStack.peek()); console.log('删除前栈元素size'+myStack.size()); myStack.delete(); console.log('删除后栈内元素'+myStack.print()); console.log('删除后栈顶元素'+myStack.peek()); console.log('删除前栈元素size'+myStack.size()); console.log('栈是否为空'+myStack.isEmpty()); myStack.emptyStack(); console.log('清空栈,栈是否为空'+myStack.isEmpty()); console.log('清空栈,栈元素size'+myStack.size());
Queue
First in, first out, just like queuing up to drink Meng Po soup, those who come first will be in front. Those who come later will be at the end of the queue. If they want to be reincarnated, the person who finished drinking in front must go. The same is true for the operation queue. Elements are removed from the front of the queue and elements are added from the end of the queue. It is similar to the implementation of stack
function Queue(){
var queue=[]; this.push=function(para){
queue.push(para);
} this.delete=function(){
// 从队首移除,即删除的是数组第一位
queue.shift();
} this.queueFront=function(){
return queue[0];
} this.isEmpty=function(){
if(queue.length==0){ return true;
}else{ return false;
}
} this.size=function(){
return queue.length;
} this.emptyQueue=function(){
queue=[];
} this.print=function(){
return queue.toString();
}
}var myQueue=new Queue();
myQueue.push(1);
myQueue.push(4);
myQueue.push(6);
console.log('删除前队列内元素'+myQueue.print());
console.log('删除前队列顶元素'+myQueue.queueFront());
console.log('删除前队列元素size'+myQueue.size());
myQueue.delete();
console.log('删除后队列内元素'+myQueue.print());
console.log('删除后队列顶元素'+myQueue.queueFront());
console.log('删除前队列元素size'+myQueue.size());
console.log('队列是否为空'+myQueue.isEmpty());
myQueue.emptyQueue();
console.log('清空队列,队列是否为空'+myQueue.isEmpty());
console.log('清空队列,队列元素size'+myQueue.size());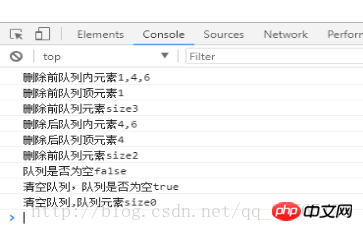
The difference in implementation
The method of deletion operation and accessing the head (top of stack) element is different. This is because This is caused by the different principles of last-in-first-out and first-in-first-out. The stack deletes the last bit of the array (pop()), while the queue deletes the first bit of the array (shift()). The top element of the stack is the last bit of the array, while The first element of the queue is the first element of the array.
The book uses the implementation method written with the new features of ES6. Emmmm, I don’t know much about ES6. I will wait for it in the future~~~
I will add it, priority queue
To put it bluntly There are privileges, and the book stipulates that those with lower priority are at the front. Then I implemented it myself. The code was different from the one in the book. I ran both.
First post the code in the book
function PriorityQueue(){
let items=[]; function QueueElement(element,priority){
this.element=element; this.priority=priority;
} this.enqueue=function(element,priority){
let queueElement=new QueueElement(element, priority); let added=false; for(let i=0;i<items.length;i++){ if(queueElement.priority<isFinite([i].priority)){
items.splice(i,0,queueElement);
added=true; break;
}
} if(!added){
items.push(queueElement);
}
}; this.print=function(){
return items;
}
}var pq=new PriorityQueue();
pq.enqueue('aa',2);
pq.enqueue('aba',4);
pq.enqueue('jjjj',8);
pq.enqueue('aaaaaaa',8);
pq.enqueue('aa',-1);
console.log(pq.print());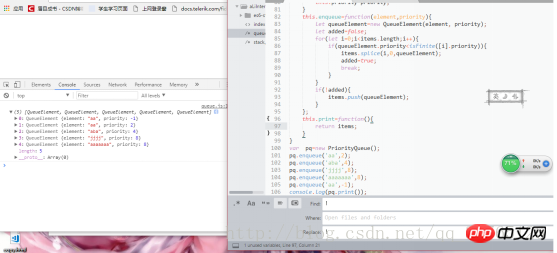
function PriorityQueue(){
// 按优先级从小到大排列,
var queue=[]; function QueueElement(ele,prior){
this.element=ele; this.prior=prior;
} this.enqueue=function(ele,prior){
//循环遍历队列内所有元素,如果当前优先级小,则放在该位之前
var curr=new QueueElement(ele, prior); if(queue.length==0){
queue.push(curr);
}else{ if(curr.prior<=queue[0].prior){
queue.splice(0,0,curr);
}else{
queue.push(curr);
}
}
} this.print=function(){
return queue;
}
}var pq=new PriorityQueue();
pq.enqueue('aa',2);
pq.enqueue('aba',4);
pq.enqueue('jjjj',8);
pq.enqueue('aaaaaaa',8);
pq.enqueue('aa',-1);
console.log(pq.print());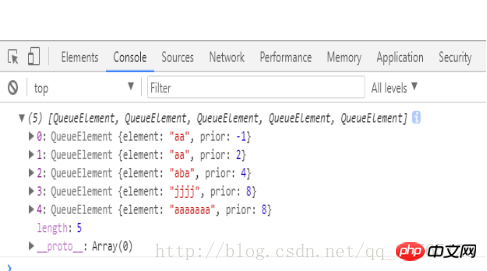
After taking the screenshot, I realized that element should be output at the end, without priority. Here are the print methods of the above two (note that I declared queue, in the book it is items ^_^)
this.print=function(){
var result=[]; for(let j = 0, length2 = items.length; j < length2; j++){
result[j]=items[j].element;
}
return result;
}Linked list
A linked list stores an ordered collection of elements, but unlike an array, the elements in a linked list are not placed continuously. Each element consists of a node that stores the element itself and a reference (pointer) pointing to the next element.
Singly linked list
The methods of the linked list class have:
append(para) 在链表尾部添加元素appendAt(element,index) 在指定位置添加元素deleteAt(index) 删除指定位置的链表元素getHead() 获得链表头元素size() 获得链表大小print() 打印出链表内容 toString() 输出链表元素的内容indexOf(para) 查找元素如果在链表中找到了就返回他的位置,没找到就返回-1isEmpty() 判断链表是否为空size() 获取链表长度
Specific code
Because we are writing one test section and one section, the functions are not written together. We separate them first and then summarize them later.
function LinkList(){
let Node=function(element){
this.element=element; this.next=null;
}; var list=[];
let length=0;
let head=null;
let currNode=null; this.append=function(para){
//链表尾部追加元素
var node=new Node(para); var current;//一直指向上一个添加的节点
if(head==null){ //插入第一个元素
head=node;
currNode=head; // console.log(head);
}else{ //不是第一个元素
//上一个的next指针指向当前node;
currNode.next=node; // console.log(currNode);
currNode=node;
}
length++; // list.push(node);
} this.getHead=function(){
return head;
} this.appendAt=function(element,index){
if(index>=0 && index<=length){ var node=new Node(element); var current=head; var previous; var position=0; if(index==0){
node.next=current;
head=node;
}else{ while(position++<index){
previous=current;
current=current.next
}
node.next=current;
previous.next=node;
}
length++; // return
}else{
alert("参数错误");
}
} this.deleteAt=function(index){
//从特定位置移除一个元素,index索引
if(index>=0 && index<length){ var previousNode=null; var node=head; var position=0; if(index==0){
head=node.next; return node.element;
}else{ // console.log(node);
while(position++<index){ // console.log(node);
previousNode=node;
node=node.next;
}
previousNode.next=node.next; return node.element;
}
}else{
alert("参数不正确!"); return null;
}
length--;
} this.size=function(){
return list.length;
} this.print=function(){
var result=[]; for(let i = 0, length1 = list.length; i < length1; i++){
result[i]=list[i];
} return result;
}
}var linkList=new LinkList(); linkList.append('lorry1'); linkList.append('lorry2'); linkList.append('lorry3'); linkList.appendAt('lorry4',0); linkList.appendAt('lorry5',0);// 那么当前链表的元素顺序是 lorry5,lorry4,lorry1,lorry2,lorry3console.log(linkList.deleteAt(2)); console.log(linkList.getHead().next);//获取头元素的下一个元素
控制台打印出来的内容:lorry1 linkList.js:112 Node {element: "lorry4", next: Node} linkList.js:115
element:"lorry4"
next:Node {element: "lorry2", next: Node}
__proto__:Object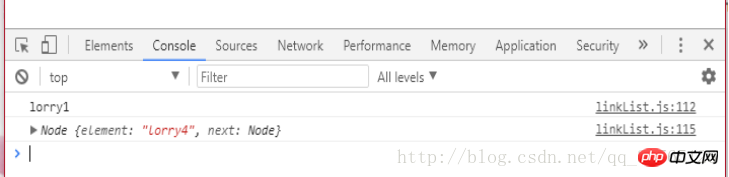
toString, size, indexOf method
this.toString=function(){
var current=head; var str=''; var i=0; while(current){
str+=current.element+' ';
current=current.next;
} return str;
} this.indexOf=function(para){
//返回首个出现该参数的位置
var current=head; var index=-1; // var i=0;
while(current){
index+=1; if(current.element==para){ return index;
}
current=current.next;
} return -1;
} this.isEmpty=function(){
return length==0;
} this.size=function(){
return length;
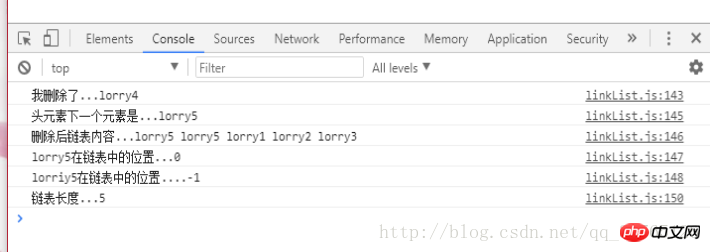
}var linkList=new LinkList(); linkList.append('lorry1'); linkList.append('lorry2'); linkList.append('lorry3'); linkList.appendAt('lorry4',0); linkList.appendAt('lorry5',1); linkList.appendAt('lorry5',0);console.log('我删除了...'+linkList.deleteAt(1));console.log('头元素下一个元素是...'+linkList.getHead().next.element);console.log('删除后链表内容...'+linkList.toString());console.log('lorry5在链表中的位置...'+linkList.indexOf('lorry5'));console.log('lorriy5在链表中的位置....'+linkList.indexOf('lorriy5'));console.log('链表长度...'+linkList.size());
linkList.js:143 我删除了...lorry4linkList.js:145 头元素下一个元素是...lorry5linkList.js:146 删除后链表内容...lorry5 lorry5 lorry1 lorry2 lorry3 linkList.js:147 lorry5在链表中的位置...0linkList.js:148 lorriy5在链表中的位置....-1linkList.js:150 链表长度...5
PHP implements stack data structure and bracket matching
PHP uses two stacks to implement the queue function
php Detailed explanation of the push and pop of linear tables
The above is the detailed content of Implementation code sharing of js stack, queue, and linked list data structures. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1371
1371
 52
52
 How to share Quark Netdisk to Baidu Netdisk?
Mar 14, 2024 pm 04:40 PM
How to share Quark Netdisk to Baidu Netdisk?
Mar 14, 2024 pm 04:40 PM
Quark Netdisk and Baidu Netdisk are very convenient storage tools. Many users are asking whether these two softwares are interoperable? How to share Quark Netdisk to Baidu Netdisk? Let this site introduce to users in detail how to save Quark network disk files to Baidu network disk. How to save files from Quark Network Disk to Baidu Network Disk Method 1. If you want to know how to transfer files from Quark Network Disk to Baidu Network Disk, first download the files that need to be saved on Quark Network Disk, and then open the Baidu Network Disk client. , select the folder where the compressed file is to be saved, and double-click to open the folder. 2. After opening the folder, click "Upload" in the upper left corner of the window. 3. Find the compressed file that needs to be uploaded on your computer and click to select it.
 How to share NetEase Cloud Music to WeChat Moments_Tutorial on sharing NetEase Cloud Music to WeChat Moments
Mar 25, 2024 am 11:41 AM
How to share NetEase Cloud Music to WeChat Moments_Tutorial on sharing NetEase Cloud Music to WeChat Moments
Mar 25, 2024 am 11:41 AM
1. First, we enter NetEase Cloud Music, and then click on the software homepage interface to enter the song playback interface. 2. Then in the song playback interface, find the sharing function button in the upper right corner, as shown in the red box in the figure below, click to select the sharing channel; in the sharing channel, click the "Share to" option at the bottom, and then select the first "WeChat Moments" allows you to share content to WeChat Moments.
 How to share files with friends on Baidu Netdisk
Mar 25, 2024 pm 06:52 PM
How to share files with friends on Baidu Netdisk
Mar 25, 2024 pm 06:52 PM
Recently, Baidu Netdisk Android client has ushered in a new version 8.0.0. This version not only brings many changes, but also adds many practical functions. Among them, the most eye-catching is the enhancement of the folder sharing function. Now, users can easily invite friends to join and share important files in work and life, achieving more convenient collaboration and sharing. So how do you share the files you need to share with your friends? Below, the editor of this site will give you a detailed introduction. I hope it can help you! 1) Open Baidu Cloud APP, first click to select the relevant folder on the homepage, and then click the [...] icon in the upper right corner of the interface; (as shown below) 2) Then click [+] in the "Shared Members" column 】, and finally check all
 Compare complex data structures using Java function comparison
Apr 19, 2024 pm 10:24 PM
Compare complex data structures using Java function comparison
Apr 19, 2024 pm 10:24 PM
When using complex data structures in Java, Comparator is used to provide a flexible comparison mechanism. Specific steps include: defining the comparator class, rewriting the compare method to define the comparison logic. Create a comparator instance. Use the Collections.sort method, passing in the collection and comparator instances.
 Share two installation methods for HP printer drivers
Mar 13, 2024 pm 05:16 PM
Share two installation methods for HP printer drivers
Mar 13, 2024 pm 05:16 PM
HP printers are essential printing equipment in many offices. Installing the printer driver on the computer can perfectly solve problems such as the printer being unable to connect. So how to install HP printer driver? The editor below will introduce you to two HP printer driver installation methods. The first method: download the driver from the official website 1. Search the HP China official website in the search engine, and in the support column, select [Software and Drivers]. 2. Select the [Printer] category, enter your printer model in the search box, and click [Submit] to find your printer driver. 3. Select the corresponding printer according to your computer system. For win10, select the driver for win10 system. 4. After downloading successfully, find it in the folder
 Java data structures and algorithms: in-depth explanation
May 08, 2024 pm 10:12 PM
Java data structures and algorithms: in-depth explanation
May 08, 2024 pm 10:12 PM
Data structures and algorithms are the basis of Java development. This article deeply explores the key data structures (such as arrays, linked lists, trees, etc.) and algorithms (such as sorting, search, graph algorithms, etc.) in Java. These structures are illustrated through practical examples, including using arrays to store scores, linked lists to manage shopping lists, stacks to implement recursion, queues to synchronize threads, and trees and hash tables for fast search and authentication. Understanding these concepts allows you to write efficient and maintainable Java code.
 Solve the problem that Discuz WeChat sharing cannot be displayed
Mar 09, 2024 pm 03:39 PM
Solve the problem that Discuz WeChat sharing cannot be displayed
Mar 09, 2024 pm 03:39 PM
Title: To solve the problem that Discuz WeChat shares cannot be displayed, specific code examples are needed. With the development of the mobile Internet, WeChat has become an indispensable part of people's daily lives. In website development, in order to improve user experience and expand website exposure, many websites will integrate WeChat sharing functions, allowing users to easily share website content to Moments or WeChat groups. However, sometimes when using open source forum systems such as Discuz, you will encounter the problem that WeChat shares cannot be displayed, which brings certain difficulties to the user experience.
 PHP data structure: The balance of AVL trees, maintaining an efficient and orderly data structure
Jun 03, 2024 am 09:58 AM
PHP data structure: The balance of AVL trees, maintaining an efficient and orderly data structure
Jun 03, 2024 am 09:58 AM
AVL tree is a balanced binary search tree that ensures fast and efficient data operations. To achieve balance, it performs left- and right-turn operations, adjusting subtrees that violate balance. AVL trees utilize height balancing to ensure that the height of the tree is always small relative to the number of nodes, thereby achieving logarithmic time complexity (O(logn)) search operations and maintaining the efficiency of the data structure even on large data sets.



